Spring @Async註釋允許我們在spring中創建異步方法。讓我們在這個spring框架教程中探索@Async。簡單來說,當我們對一個bean的方法進行標註@Async時,Spring將在一個獨立的線程中執行它,方法的調用者將不會等待該方法完成執行。我們將定義自己的Service並在這個示例中使用Spring Boot 2。讓我們開始吧!
Spring @Async示例
我們將使用Maven來為演示創建一個示例項目。要創建項目,請在您將用作工作空間的目錄中執行以下命令:
mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.journaldev.asynchmethods -DartifactId=JD-SpringBoot-AsyncMethods -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart -DinteractiveMode=false
如果您首次运行Maven,执行生成命令可能需要几秒钟,因为Maven必须下载所有所需的插件和构件,以完成生成任务。以下是项目创建的样子: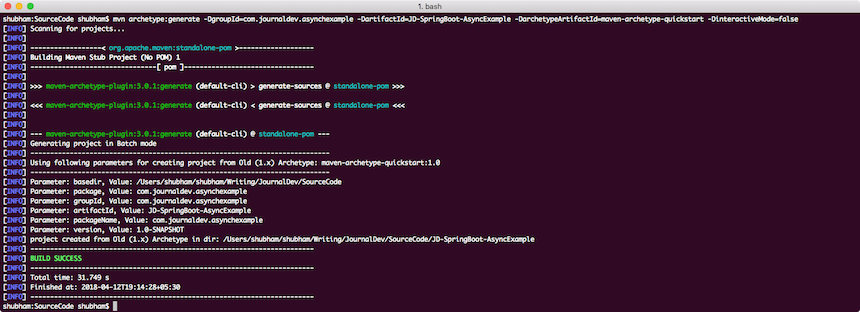 创建项目后,随时在您喜欢的IDE中打开它。下一步是向项目添加适当的Maven依赖项。这是包含适当依赖项的
创建项目后,随时在您喜欢的IDE中打开它。下一步是向项目添加适当的Maven依赖项。这是包含适当依赖项的pom.xml文件:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
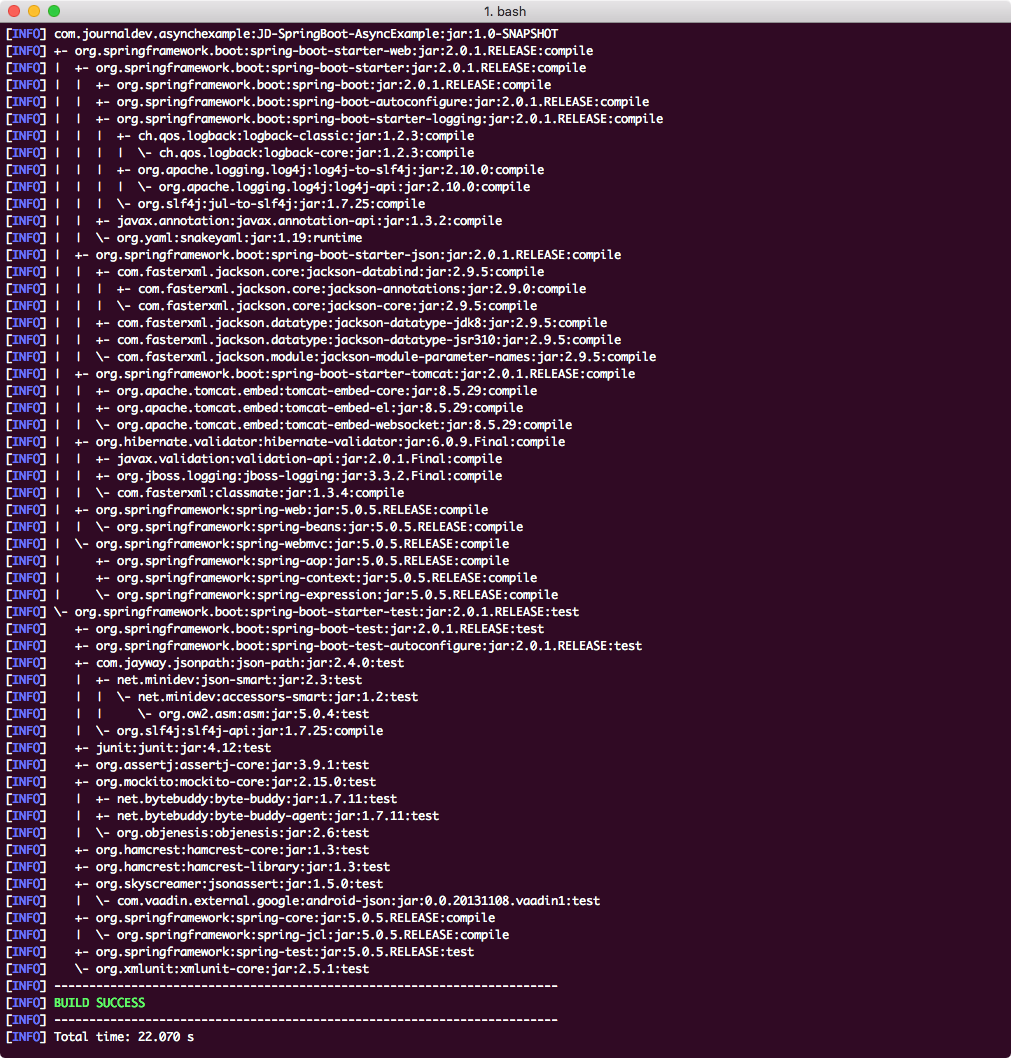
最后,为了了解添加此依赖项时添加到项目的所有JAR文件,我们可以运行一个简单的Maven命令,允许我们查看项目的完整依赖关系树。以下是我们可以使用的命令:
mvn dependency:tree
启用异步支持
啟用異步支援也只是單一標註的問題。除了啟用異步執行外,我們還將使用 Executor,這使我們能夠定義線程限制。更多相關資訊將在編寫代碼時提供:
package com.journaldev.asynchexample;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncApp {
...
}
在這裡,我們使用了 @EnableAsync 標註,這使得 Spring 能夠在後台線程池中運行異步方法。接下來,我們還添加了提到的 Executor:
@Bean
public Executor asyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(2);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(2);
executor.setQueueCapacity(500);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("JDAsync-");
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
這裡,我們設置了最多兩個線程可以並發運行,佇列大小設置為 500。這是包含導入語句的類的完整代碼:
package com.journaldev.asynchexample;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AsyncApp.class, args).close();
}
@Bean
public Executor asyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(2);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(2);
executor.setQueueCapacity(500);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("JDAsync-");
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
接下來我們將創建一個服務,實際上執行線程。
創建模型
我們將使用一個公共 電影 API,該 API 返回電影數據。我們將為其定義我們的模型:
package com.journaldev.asynchexample;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
@JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true)
public class MovieModel {
private String title;
private String producer;
// 標準的 getter 和 setter
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("MovieModel{title='%s', producer='%s'}", title, producer);
}
}
我們使用了 @JsonIgnoreProperties,這樣如果響應中有更多屬性,Spring 就可以安全地忽略它們。
創建服務
該是我們定義服務的時候了,該服務將調用所提到的電影 API。我們將使用一個簡單的 RestTemplate 來發送 GET API 請求並異步獲取結果。讓我們來看一下我們使用的示例代碼:
package com.journaldev.asynchexample;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.web.client.RestTemplateBuilder;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
@Service
public class MovieService {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MovieService.class);
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
public MovieService(RestTemplateBuilder restTemplateBuilder) {
this.restTemplate = restTemplateBuilder.build();
}
@Async
public CompletableFuture lookForMovie(String movieId) throws InterruptedException {
LOG.info("Looking up Movie ID: {}", movieId);
String url = String.format("https://ghibliapi.herokuapp.com/films/%s", movieId);
MovieModel results = restTemplate.getForObject(url, MovieModel.class);
// 人為延遲 1 秒,僅用於演示目的
Thread.sleep(1000L);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(results);
}
}
這個類是一個 @Service,這使它有資格進行 Spring 組件掃描。lookForMovie 方法的返回類型是 CompletableFuture,這是任何異步服務的要求。由於 API 的時間可能有所不同,我們添加了 2 秒的延遲以進行演示。
創建一個命令行運行器
我們將使用 CommandLineRunner 運行我們的應用程序,這是測試我們應用程序的最簡單的方法。CommandLineRunner 會在應用程序的所有 bean 都被初始化之後立即運行。讓我們看一下 CommandLineRunner 的代碼:
package com.journaldev.asynchexample;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
@Component
public class ApplicationRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ApplicationRunner.class);
private final MovieService movieService;
public ApplicationRunner(MovieService movieService) {
this.movieService = movieService;
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
// 開始計時
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 啟動多個異步查找
CompletableFuture page1 = movieService.lookForMovie("58611129-2dbc-4a81-a72f-77ddfc1b1b49");
CompletableFuture page2 = movieService.lookForMovie("2baf70d1-42bb-4437-b551-e5fed5a87abe");
CompletableFuture page3 = movieService.lookForMovie("4e236f34-b981-41c3-8c65-f8c9000b94e7");
// 加入所有線程,以便我們等待直到所有操作完成
CompletableFuture.allOf(page1, page2, page3).join();
// 打印結果,包括經過的時間
LOG.info("Elapsed time: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
LOG.info("--> " + page1.get());
LOG.info("--> " + page2.get());
LOG.info("--> " + page3.get());
}
}
我們只是使用 RestTemplate 來發送我們使用的示例 API,並隨機選擇了一些電影 ID。我們將運行我們的應用程序,查看它顯示了什麼輸出。
執行應用程式
當我們執行應用程式時,我們會看到以下輸出:
2018-04-13 INFO 17868 --- [JDAsync-1] c.j.a.MovieService : Looking up Movie ID: 58611129-2dbc-4a81-a72f-77ddfc1b1b49
2018-04-13 08:00:09.518 INFO 17868 --- [JDAsync-2] c.j.a.MovieService : Looking up Movie ID: 2baf70d1-42bb-4437-b551-e5fed5a87abe
2018-04-13 08:00:12.254 INFO 17868 --- [JDAsync-1] c.j.a.MovieService : Looking up Movie ID: 4e236f34-b981-41c3-8c65-f8c9000b94e7
2018-04-13 08:00:13.565 INFO 17868 --- [main] c.j.a.ApplicationRunner : Elapsed time: 4056
2018-04-13 08:00:13.565 INFO 17868 --- [main] c.j.a.ApplicationRunner : --> MovieModel{title='My Neighbor Totoro', producer='Hayao Miyazaki'}
2018-04-13 08:00:13.565 INFO 17868 --- [main] c.j.a.ApplicationRunner : --> MovieModel{title='Castle in the Sky', producer='Isao Takahata'}
2018-04-13 08:00:13.566 INFO 17868 --- [main] c.j.a.ApplicationRunner : --> MovieModel{title='Only Yesterday', producer='Toshio Suzuki'}
如果你仔細觀察,你會發現只有兩個線程被執行在應用程式中,分別是 JDAsync-1 和 JDAsync-2。
結論
在這堂課中,我們學習了如何使用Spring Boot 2的Spring異步能力。閱讀更多Spring相關文章請點擊這裡。
下載原始碼
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/spring-async-annotation