歡迎來到JDBC面試問題和答案。JDBC API用於連接到關聯式數據庫並從Java程序運行SQL查詢。在過去的幾篇文章中,我們了解了JDBC API及其重要特性。本文旨在提供一些重要的JDBC面試問題及答案,以幫助您應對Java面試。
JDBC面試問題

- JDBC API是什麼?何時使用它?
- JDBC驅動程序有哪些不同類型?
- JDBC API如何幫助我們實現Java程序和JDBC驅動程序API之間的鬆耦合?
- JDBC連接是什麼?解釋在簡單的Java程序中獲取數據庫連接的步驟。
- JDBC DriverManager類的用途是什麼?
- 如何在Java程序中獲取數據庫服務器詳細信息?
- 什麼是JDBC Statement?
- execute、executeQuery、executeUpdate之間的區別是什麼?
- 什麼是JDBC PreparedStatement?
- 如何在JDBC PreparedStatement中設置NULL值?
- 在 Statement 中,getGeneratedKeys() 方法的用途是什麼?
- PreparedStatement 相比 Statement 有什麼好處?
- PreparedStatement 的限制是什麼,如何克服?
- JDBC ResultSet 是什麼?
- ResultSet 有哪些不同類型?
- 在 Statement 中,setFetchSize() 和 setMaxRows() 方法的用途是什麼?
- 如何使用 JDBC API 調用存儲過程?
- JDBC 批量處理是什麼,有什麼好處?
- JDBC 事務管理是什麼,為什麼我們需要它?
- 如何回滾 JDBC 事務?
- JDBC Savepoint 是什麼?如何使用?
- JDBC DataSource 是什麼,有哪些好處?
- 如何在 Apache Tomcat 伺服器中使用 JDBC DataSource 和 JNDI 實現 JDBC 連接池?
- Apache DBCP API 是什麼?
- JDBC 連接隔離級別是什麼?
- JDBC RowSet 是什麼?有哪些不同類型的 RowSet?
- ResultSet和RowSet之間有何不同?
- 什麼是常見的JDBC異常?
- JDBC中的CLOB和BLOB數據類型是什麼?
- JDBC中的“dirty read”是什麼?哪個隔離級別可以防止dirty read?
- 什麼是2階段提交?
- JDBC中有哪些不同類型的鎖定?
- DDL和DML語句的含義是什麼?
- java.util.Date和java.sql.Date之間有什麼區別?
- 如何將圖像或原始數據插入到數據庫中?
- 什麼是幻讀,哪個隔離級別可以防止它?
- 什麼是SQL Warning?如何在JDBC程序中檢索SQL警告?
- 如何調用具有數據庫對象的Oracle存儲過程,作為IN/OUT參數?
- 什麼時候會出現java.sql.SQLException:找不到合適的驅動程序?
- JDBC最佳實踐有哪些?
JDBC 面試問題與答案
-
JDBC API 是什麼?何時使用它?
Java DataBase Connectivity API 允許我們與關聯式數據庫進行交互。JDBC API 的接口和類位於
java.sql和javax.sql包中。我們可以使用 JDBC API 獲取數據庫連接,在數據庫服務器上運行 SQL 查詢和存儲過程並處理結果。JDBC API 的設計使我們的 Java 程序與實際的 JDBC 驅動程序之間鬆散耦合,這樣在從一個數據庫切換到另一個數據庫服務器時更加輕鬆。 -
什麼是不同類型的JDBC驅動程序?
有四種類型的JDBC驅動程序。任何與數據庫一起工作的Java程序都有兩個部分,第一部分是JDBC API,第二部分是執行實際工作的驅動程序。
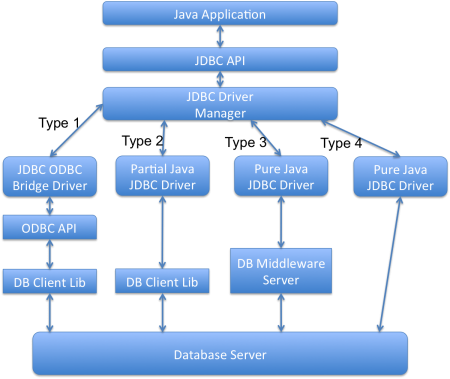
- JDBC-ODBC橋接器加ODBC驅動程序(類型1):它使用ODBC驅動程序連接到數據庫。我們應該安裝ODBC驅動程序才能連接到數據庫,這就是為什麼這個驅動程序幾乎已經過時的原因。
- 本機API部分使用Java技術啟用的驅動程序(類型2):此驅動程序將JDBC類轉換為數據庫服務器的客戶端API。我們應該安裝數據庫客戶端API。由於對數據庫客戶端API驅動程序的額外依賴,這也不是首選的驅動程序。
- 用於數據庫中間件的純Java驅動程序(類型3):此驅動程序將JDBC調用發送到可以連接到不同類型數據庫的中間件服務器。我們應該安裝中間件服務器來使用此驅動程序。這會增加額外的網絡調用並降低性能,這就是為什麼這個JDBC驅動程序沒有被廣泛使用的原因。
- 直接對數據庫的純Java驅動程序(類型4):此驅動程序將JDBC調用轉換為數據庫服務器理解的網絡協議。此解決方案簡單且適用於通過網絡連接的數據庫。然而,對於此解決方案,我們應該使用特定於數據庫的驅動程序,例如Oracle的OJDBC jars用於Oracle數據庫和MySQL Connector/J用於MySQL數據庫。
-
JDBC API 如何幫助我們實現 Java 程式和 JDBC 驅動程式 API 之間的鬆耦合?
JDBC API 使用 Java 反射 API 實現了 Java 程式和 JDBC 驅動程式之間的鬆耦合。如果您看一個簡單的 JDBC 範例,您會注意到所有的編程都是以 JDBC API 的術語進行的,並且只有當通過反射使用
Class.forName()方法加載驅動程式時,驅動程式才會出現。我認為這是在核心 Java 類中使用反射的最佳示例之一,以確保我們的應用程序不直接與驅動程式 API 交互,這使得從一個數據庫轉移到另一個數據庫非常容易。請閱讀更多關於 反射 在 JDBC 範例 中的信息。 -
什麼是 JDBC 連線?解釋在一個簡單的 Java 程式中如何獲取數據庫連線的步驟。
JDBC 連線就像是與數據庫伺服器建立的一個會話。您也可以將連線視為來自數據庫伺服器的套接字連線。創建 JDBC 連線非常簡單,只需兩個步驟:
- 註冊並加載驅動程序:使用
Class.forName(),將驅動程序類註冊到 DriverManager 中並加載到內存中。 - 使用 DriverManager 獲取連線對象:通過將數據庫 URL 字符串、用戶名和密碼作為參數傳遞給
DriverManager.getConnection()來獲取連線對象。
Connection con = null; try{ // 加載驅動程序類 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // 現在創建連線 con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/UserDB", "pankaj", "pankaj123"); }catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println("檢查數據庫是否運行並檢查配置是否正確"); e.printStackTrace(); }catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("請在類路徑中包含 JDBC MySQL jar 檔案"); e.printStackTrace(); } - 註冊並加載驅動程序:使用
-
JDBC DriverManager類的用途是什麼?
JDBC `DriverManager` is the factory class through which we get the Database Connection object. When we load the JDBC Driver class, it registers itself to the DriverManager, you can look up the JDBC Driver classes source code to check this. Then when we call `DriverManager.getConnection()` method by passing the database configuration details, DriverManager uses the registered drivers to get the Connection and return it to the caller program.
We can use `DatabaseMetaData` object to get the database server details. When the database connection is created successfully, we can get the meta data object by calling `getMetaData()` method. There are so many methods in DatabaseMetaData that we can use to get the database product name, it's version and configuration details.
```
DatabaseMetaData metaData = con.getMetaData();
String dbProduct = metaData.getDatabaseProductName();
```
JDBC API `Statement` is used to execute SQL queries in the database. We can create the Statement object by calling Connection `createStatement()` method. We can use Statement to execute static SQL queries by passing query through different execute methods such as execute(), executeQuery(), executeUpdate() etc. Since the query is generated in the java program, if the user input is not properly validated it can lead to SQL injection issue, more details can be found at [SQL Injection Example](/community/tutorials/jdbc-statement-vs-preparedstatement-sql-injection-example). By default, only one ResultSet object per Statement object can be open at the same time. Therefore, if we want to work with multiple ResultSet objects, then each must have been generated by different Statement objects. All execute() methods in the Statement interface implicitly close a statment's current ResultSet object if an open one exists.
Statement `execute(String query)` is used to execute any SQL query and it returns TRUE if the result is an ResultSet such as running Select queries. The output is FALSE when there is no ResultSet object such as running Insert or Update queries. We can use `getResultSet()` to get the ResultSet and `getUpdateCount()` method to retrieve the update count. Statement `executeQuery(String query)` is used to execute Select queries and returns the ResultSet. ResultSet returned is never null even if there are no records matching the query. When executing select queries we should use the executeQuery method so that if someone tries to execute insert/update statement it will throw java.sql.SQLException with message "executeQuery method cannot be used for update". Statement executeUpdate(String query) is used to execute Insert/Update/Delete (DML) statements or DDL statements that returns nothing. The output is int and equals the row count for SQL Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements. For DDL statements, the output is 0. You should use execute() method only when you are not sure about the type of statement else use executeQuery or executeUpdate method.
JDBC `PreparedStatement` object represents a precompiled SQL statement. We can use it's setter method to set the variables for the query. Since PreparedStatement is precompiled, it can then be used to efficiently execute this statement multiple times. PreparedStatement is better choice that Statement because it automatically escapes the special characters and avoid SQL injection attacks.
We can use PreparedStatement setNull() method to bind the null variable to a parameter. The setNull method takes index and SQL Types as argument, for example `ps.setNull(10, java.sql.Types.INTEGER);`.
Sometimes a table can have auto generated keys used to insert the unique column value for primary key. We can use Statement `getGeneratedKeys()` method to get the value of this auto generated key.
Some of the benefits of PreparedStatement over Statement are:
- PreparedStatement helps us in preventing SQL injection attacks because it automatically escapes the special characters.
- PreparedStatement allows us to execute dynamic queries with parameter inputs.
- PreparedStatement is faster than Statement. It becomes more visible when we reuse the PreparedStatement or use it’s batch processing methods for executing multiple queries.
- PreparedStatement helps us in writing object Oriented code with setter methods whereas with Statement we have to use String Concatenation to create the query. If there are multiple parameters to set, writing Query using String concatenation looks very ugly and error prone.
One of the limitation of PreparedStatement is that we can't use it directly with IN clause statements. Some of the alternative approaches to use PreparedStatement with IN clause are;
1. **Execute Single Queries** - very slow performance and not recommended
2. **Using Stored Procedure** - Database specific and hence not suitable for multiple database applications.
3. **Creating PreparedStatement Query dynamically** - Good approach but looses the benefit of cached PreparedStatement.
4. **Using NULL in PreparedStatement Query** - A good approach when you know the maximum number of variables inputs, can be extended to allow unlimited parameters by executing in parts.
A more detailed analysis can be found at [JDBC PreparedStatement IN clause alternatives](/community/tutorials/java-preparedstatement-in-clause-alternatives).
JDBC `ResultSet` is like a table of data representing a database result set, which is usually generated by executing a statement that queries the database. ResultSet object maintains a cursor pointing to its current row of data. Initially, the cursor is positioned before the first row. The next() method moves the cursor to the next row. If there are no more rows, next() method returns false and it can be used in a while loop to iterate through the result set. A default ResultSet object is not updatable and has a cursor that moves forward only. Thus, you can iterate through it only once and only from the first row to the last row. It is possible to produce ResultSet objects that are scrollable and/or updatable using below syntax.
```
Statement stmt = con.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,
ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);
```
A ResultSet object is automatically closed when the Statement object that generated it is closed, re-executed, or used to retrieve the next result from a sequence of multiple results. We can use ResultSet getter method with column name or index number starting from 1 to retrieve the column data.
There are different types of ResultSet objects that we can get based on the user input while creating the Statement. If you will look into the Connection methods, you will see that createStatement() and prepareStatement() method are overloaded to provide ResultSet type and concurrency as input argument. There are three types of ResultSet object.
1. **ResultSet.TYPE\_FORWARD\_ONLY**: This is the default type and cursor can only move forward in the result set.
2. **ResultSet.TYPE\_SCROLL\_INSENSITIVE**: The cursor can move forward and backward, and the result set is not sensitive to changes made by others to the database after the result set was created.
3. **ResultSet.TYPE\_SCROLL\_SENSITIVE**: The cursor can move forward and backward, and the result set is sensitive to changes made by others to the database after the result set was created.
Based on the concurrency there are two types of ResultSet object.
1. **ResultSet.CONCUR\_READ\_ONLY**: The result set is read only, this is the default concurrency type.
2. **ResultSet.CONCUR\_UPDATABLE**: We can use ResultSet update method to update the rows data.
We can use `setMaxRows(int i)` method to limit the number of rows that the database returns from the query. You can achieve the same thing using the SQL query itself. For example, in MySQL, we can use the [LIMIT](/community/tutorials/sql-limit-mysql-limit) clause to set the max rows that will be returned by the query. Understanding **fetchSize** can be tricky, for that you should know how Statement and ResultSet works. When we execute a query in the database, the result is obtained and maintained in the database cache and ResultSet is returned. ResultSet is the cursor that has the reference to the result in the database. Let's say we have a query that returns 100 rows and we have set fetchSize to 10, so in every database trip JDBC driver will fetch only 10 rows and hence there will be 10 trips to fetch all the rows. Setting optimal fetchSize is helpful when you need a lot of processing time for each row and number of rows in the result is huge. We can set fetchSize through Statement object but it can be overridden through ResultSet object setFetchSize() method.
Stored Procedures are group of SQL queries that are compiled in the database and can be executed from JDBC API. JDBC `CallableStatement` can be used to execute stored procedures in the database. The syntax to initialize CallableStatement is;
```
CallableStatement stmt = con.prepareCall("{call insertEmployee(?,?,?,?,?,?)}");
stmt.setInt(1, id);
stmt.setString(2, name);
stmt.setString(3, role);
stmt.setString(4, city);
stmt.setString(5, country);
// 在調用存儲過程之前註冊 OUT 參數
stmt.registerOutParameter(6, java.sql.Types.VARCHAR);
stmt.executeUpdate();
```
We need to register the OUT parameters before executing the CallableStatement. More details about this can be found at [JDBC CallableStatement Example](/community/tutorials/callablestatement-in-java-example).
Sometimes we need to run bulk queries of a similar kind for a database. For example, loading data from CSV files to relational database tables. As we know that we have the option to use Statement or PreparedStatement to execute queries. Apart from that JDBC API provides Batch Processing feature through which we can execute the bulk of queries in one go for a database. JDBC API supports batch processing through Statement and PreparedStatement `addBatch()` and `executeBatch()` methods. Batch Processing is faster than executing one statement at a time because the number of database calls is less. Read more at [JDBC Batch Processing Example](/community/tutorials/jdbc-batch-insert-update-mysql-oracle).
By default when we create a database connection, it runs in auto-commit mode. It means that whenever we execute a query and it’s completed, the commit is fired automatically. So every SQL query we fire is a transaction and if we are running some DML or DDL queries, the changes are getting saved into the database after every SQL statement finishes. Sometimes we want a group of SQL queries to be part of a transaction so that we can commit them when all the queries run fine and if we get an exception, we have a choice of rollback all the queries executed as part of the transaction. JDBC API provide method `setAutoCommit(boolean flag)` through which we can disable the auto commit feature of the connection. We should disable auto commit only when it’s required because the transaction will not be committed unless we call the commit() method on connection. Database servers uses table locks to achieve transaction management and it’s resource intensive process. So we should commit the transaction as soon as we are done with it. Read more with example program at [JDBC Transaction Management Example](/community/tutorials/java-jdbc-transaction-management-savepoint).
We can use Connection object `rollback()` method to rollback the transaction. It will rollback all the changes made by the transaction and release any database locks currently held by this Connection object.
Sometimes a transaction can be group of multiple statements and we would like to rollback to a particular point in the transaction. JDBC Savepoint helps us in creating checkpoints in a transaction and we can rollback to that particular checkpoint. Any savepoint created for a transaction is automatically released and become invalid when the transaction is committed, or when the entire transaction is rolled back. Rolling a transaction back to a savepoint automatically releases and makes invalid any other savepoints that were created after the savepoint in question. Read more at [JDBC Savepoint Example](/community/tutorials/java-jdbc-transaction-management-savepoint).
JDBC DataSource is the interface defined in `javax.sql` package and it is more powerful that DriverManager for database connections. We can use DataSource to create the database connection and Driver implementation classes does the actual work for getting connection. Apart from getting Database connection, DataSource provides some additional features such as:
- Caching of PreparedStatement for faster processing
- Connection timeout settings
- Logging features
- ResultSet maximum size threshold
- Connection Pooling in servlet container using JNDI support
Read more about DataSource at [JDBC DataSource Example](/community/tutorials/java-datasource-jdbc-datasource-example).
For web applications deployed in a servlet container, creating JDBC connection pool is very easy and involve only few steps.
1. Creating JDBC JNDI resource in the container configuration files, usually server.xml or context.xml. For example `server.xml`
```
<Resource name="jdbc/MyDB"
global="jdbc/MyDB"
auth="Container"
type="javax.sql.DataSource"
driverClassName="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/UserDB"
username="pankaj"
password="pankaj123"
maxActive="100"
maxIdle="20"
minIdle="5"
maxWait="10000"/>
```
`context.xml`
```
<ResourceLink name="jdbc/MyLocalDB"
global="jdbc/MyDB"
auth="Container"
type="javax.sql.DataSource" />
```
2. In web application, using InitialContext to look up the JNDI resource configured in the first step and then get the connection.
```
Context ctx = new InitialContext();
DataSource ds = (DataSource) ctx.lookup("java:/comp/env/jdbc/MyLocalDB");
```
For a complete example, read [Tomcat DataSource JNDI Example](/community/tutorials/tomcat-datasource-jndi-example-java).
If you use `DataSource` to get the Database connection, usually the code to get the connection is tightly coupled with the Driver specific DataSource implementation. Also most of the code is boiler-plate code except the choice of the DataSource implementation class. Apache DBCP helps us in getting rid of these issues by providing DataSource implementation that works as an abstraction layer between our program and different JDBC drivers. Apache DBCP library depends on Commons Pool library, so make sure they both are in the build path. For a complete example, read [Apache DBCP Example](/community/tutorials/java-datasource-jdbc-datasource-example).
When we use JDBC Transactions for data integrity, DBMS uses locks to block access by others to the data being accessed by the transaction. DBMS uses locks to prevent Dirty Read, Non-Repeatable Reads and Phantom-Read issue. JDBC transaction isolation level is used by DBMS to use the locking mechanism, we can get the isolation level information through Connection getTransactionIsolation() method and set it with the setTransactionIsolation() method.
| Isolation Level | Transaction | Dirty Read | Non-Repeatable Read | Phantom Read |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| TRANSACTION\_NONE | Not Supported | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | Not Applicable |
| TRANSACTION\_READ\_COMMITTED | Supported | Prevented | Allowed | Allowed |
| TRANSACTION\_READ\_UNCOMMITTED | Supported | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| TRANSACTION\_REPEATABLE\_READ | Supported | Prevented | Prevented | Allowed |
| TRANSACTION\_SERIALIZABLE | Supported | Prevented | Prevented | Prevented |
JDBC `RowSet` holds tabular data in more flexible ways that ResultSet. All RowSet objects are derived from ResultSet, so they have all the capabilities of ResultSet with some additional features. RowSet interface is defined in `javax.sql` package. Some additional features provided by RowSet are:
- Functions as Java Beans with properties and their getter-setter methods. RowSet uses JavaBeans event model and they can send notifications to any registered component for events such as cursor movement, update/insert/delete of a row and change to RowSet contents.
- RowSet objects are scrollable and updatable by default, so if DBMS doesn't support scrollable or updatable ResultSet, we can use RowSet to get these features.
RowSet are broadly divided into two types:
1. **Connected RowSet Objects** - These objects are connected to database and are most similar to ResultSet object. JDBC API provides only one connected RowSet object `javax.sql.rowset.JdbcRowSet` and it's standard implementation class is `com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl`
2. **Disconnected RowSet Objects** - These RowSet objects are not required to connected to a database, so they are more lightweight and serializable. They are suitable for sending data over a network. There are four types of disconnected RowSet implementations.
- CachedRowSet - They can get the connection and execute a query and read the ResultSet data to populate the RowSet data. We can manipulate and update data while it is disconnected and reconnect to database and write the changes.
- WebRowSet derived from CachedRowSet - They can read and write XML document.
- JoinRowSet derived from WebRowSet - They can form SQL JOIN without having to connect to a data source.
- FilteredRowSet derived from WebRowSet - We can apply filtering criteria so that only selected data is visible.
RowSet objects are derived from ResultSet, so they have all the features of ResultSet with some additional features. One of the huge benefit of RowSet is that they can be disconnected and that makes it lightweight and easy to transfer over a network. Whether to use ResultSet or RowSet depends on your requirements but if you are planning to use ResultSet for longer duration, then a disconnected RowSet is better choice to free database resources.
Some of the common JDBC Exceptions are:
1. java.sql.SQLException - This is the base exception class for JDBC exceptions.
2. java.sql.BatchUpdateException - This exception is thrown when Batch operation fails, but it depends on the JDBC driver whether they throw this exception or the base SQLException.
3. java.sql.SQLWarning - For warning messages in SQL operations.
4. java.sql.DataTruncation - when a data values is unexpectedly truncated for reasons other than its having exceeded MaxFieldSize.
Character Large OBjects (CLOBs) are character string made up of single-byte characters with an associated code page. This data type is appropriate for storing text-oriented information where the amount of information can grow beyond the limits of a regular VARCHAR data type (upper limit of 32K bytes). Binary Large Objects (BLOBs) are a binary string made up of bytes with no associated code page. This data type can store binary data larger than VARBINARY (32K limit). This data type is good for storing image, voice, graphical, and other types of business or application-specific data.
When we work with transactions, there is a chance that a row is updated and at the same time, another query can read the updated value. This results in a dirty read because the updated value is not permanent yet, the transaction that has updated the row can rollback to a previous value resulting in invalid data. Dirty Read is prevented by isolation levels TRANSACTION\_READ\_COMMITTED, TRANSACTION\_REPEATABLE\_READ, and TRANSACTION\_SERIALIZABLE.
When we work in distributed systems where multiple databases are involved, we are required to use 2 phase commit protocol. 2 phase commit protocol is an atomic commitment protocol for distributed systems. In the first phase, the transaction manager sends commit-request to all the transaction resources. If all the transaction resources are OK, the transaction manager commits the transaction changes for all the resources. If any of the transaction resources responds as Abort, then the transaction manager can rollback all the transaction changes.
On a broad level, there are two types of locking mechanism to prevent data corruption because of more than one user working with the same data.
1. Optimistic Locking - This locking is achieved with code. An extra column is introduced in the table to keep a count of updates. When you select the row, you read this column too, say 'version'. Now when you are trying to update/delete the row, you pass this 'version' in the where clause. So if there are updates from other threads performed in between, the update will fail. It's a good way to avoid data corruption but it can be error prone if someone missed updating the 'version' in their update statement. The update query looks something like below in this way of locking.
```
mysql> update emp SET name = 'David', version = 5 WHERE id = 10 and version = 4;
```
2. Pessimistic Locking - Locking the record from the select to read, update and commit phase. This is usually done by database vendor software and triggered by the use of `SELECT FOR UPDATE` query. This way of locking the row can lead to slow performance and deadlock if threads are handling the lock for longer time.Apart from that some DBMS systems provide locking mechanism to lock single row, table or database.
Data Definition Language (DDL) statements are used to define the database schema. Create, Alter, Drop, Truncate, Rename statements comes under DDL statements and usually they don't return any result. Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements are used to manipulate data in the database schema. Select, Insert, Update, Delete, Call etc are example of DML statements.
java.util.Date contains information about the date and time whereas java.sql.Date contains information only about the date, it doesn't have time information. So if you have to keep time information in the database, it is advisable to use Timestamp or DateTime fields.
We can use BLOB to insert image or raw binary data into database.
A phantom read is the situation where a transaction executes a query multiple times and get different data. Suppose a transaction is executing a query to get data based on a condition and then another transaction inserts a row that matches the condition. Now when same transaction will execute the query again, a new row will be part of the result set. This new row is referred as Phantom Row and this situation is termed as Phantom Read. Phantom read can be prevented only with TRANSACTION\_SERIALIZABLE isolation level.
SQLWarning is the subclass of SQLException and we can retrieve it by calling getWarnings() method on Connection, Statement, and ResultSet objects. SQL Warnings doesn't stop the execution of the script but alerts the user about the warning.
If Oracle Stored Procedure has IN/OUT parameters as DB Objects then we need to create an Object array of the same size in the program and then use it to create Oracle STRUCT object. Then we can set this STRUCT object for the database object by calling setSTRUCT() method and work with it.
You get No suitable driver found exception when the SQL URL String is not properly formatted. You can get this exception in both simple java application using DriverManager or with JNDI resource using DataSource. The exception stack trace looks like below.
```
org.apache.tomcat.dbcp.dbcp.SQLNestedException: Cannot create JDBC driver of class 'com.mysql.jdbc.Driver' for connect URL ''jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/UserDB'
at org.apache.tomcat.dbcp.dbcp.BasicDataSource.createConnectionFactory(BasicDataSource.java:1452)
at org.apache.tomcat.dbcp.dbcp.BasicDataSource.createDataSource(BasicDataSource.java:1371)
at org.apache.tomcat.dbcp.dbcp.BasicDataSource.getConnection(BasicDataSource.java:1044)
java.sql.SQLException: No suitable driver found for 'jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/UserDB
at java.sql.DriverManager.getConnection(DriverManager.java:604)
at java.sql.DriverManager.getConnection(DriverManager.java:221)
at com.journaldev.jdbc.DBConnection.getConnection(DBConnection.java:24)
at com.journaldev.jdbc.DBConnectionTest.main(DBConnectionTest.java:15)
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
at com.journaldev.jdbc.DBConnectionTest.main(DBConnectionTest.java:16)
```
While debugging this exception, just check the URL getting printed in the logs, as in above logs the URL String is 'jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/UserDB whereas it should be jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/UserDB.
Some of the JDBC Best Practices are:
- Database resources are heavy, so make sure you close it as soon as you are done with it. Connection, Statement, ResultSet and all other JDBC objects have close() method defined to close them.
- Always close the result set, statement and connection explicitly in the code, because if you are working in connection pooling environment, the connection might be returned to the pool leaving open result sets and statement objects resulting in resource leak.
- Close the resources in the finally block to make sure they are closed even in case of exception scenarios.
- Use batch processing for bulk operations of similar kind.
- Always use PreparedStatement over Statement to avoid SQL Injection and get pre-compilation and caching benefits of PreparedStatement.
- If you are retrieving bulk data into result set, setting an optimal value for fetchSize helps in getting good performance.
- The database server might not support all isolation levels, so check it before assuming.
- More strict isolation levels result in slow performance, so make sure you have optimal isolation level set for your database connections.
- If you are creating database connections in a web application, try to use JDBC DataSource resources using JNDI context for re-using the connections.
- Try to use disconnected RowSet when you need to work with ResultSet for a long time.
這就是有關JDBC面試問題和答案的全部內容,我希望它能幫助到你在JDBC面試中。如果我漏掉了任何重要問題,請讓我知道,我會將其添加到列表中。
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/jdbc-interview-questions-and-answers













