在這個教程中,我們將提供Android佈局的概述。我們還將探索一些特定的佈局控件,用於組織屏幕內容,即Android LinearLayout和Android RelativeLayout。
Android佈局
用戶界面的基本組件是從View類創建的View對象,它佔據屏幕上的矩形區域。View是UI組件(如TextView、Button、EditText等)的基類。ViewGroup是View的子類。一個或多個View可以被分組到一個ViewGroup中。ViewGroup提供了Android佈局,我們可以通過它來設置視圖的外觀和順序。ViewGroup的示例有LinearLayout、FrameLayout、RelativeLayout等。
Android佈局類型
Android提供了以下ViewGroup或佈局:
LinearLayout:是一個ViewGroup,將所有子視圖在單一方向上對齊,可以是垂直或水平的RelativeLayout:是一個ViewGroup,以相對位置顯示子視圖AbsoluteLayout:允許我們指定子視圖和小部件的確切位置TableLayout:將其子視圖分組為行和列的視圖FrameLayout:在屏幕上充當單個視圖的佔位符ScrollView:是FrameLayout的一種特殊類型,允許用戶滾動佔用比物理顯示屏更多空間的視圖列表。ScrollView只能包含一個子視圖或ViewGroup,通常是LinearLayoutListView:顯示可滾動項目列表的視圖組GridView:在二維滾動網格中顯示項目的ViewGroup。網格中的項目來自與此視圖關聯的ListAdapter
在本教程中,我們將重點介紹兩個最常用的Android佈局:
- LinearLayout
- RelativeLayout
Android佈局屬性
- android:id:這是唯一識別視圖的ID
- android:layout_width:這是佈局的寬度
- android:layout_height:這是佈局的高度
- android:layout_margin:這是視圖之外的額外空間。例如,如果您給出
android:marginLeft=20dp,則視圖將從左側排列20dp後 - android:layout_padding:這與android:layout_margin類似,只是它指定了視圖內部的額外空間
- android:layout_gravity:這指定子視圖的位置
- android:layout_weight:這指定佈局中額外空間應分配給視圖的比例
- android:layout_x:這指定佈局的x坐標
- android:layout_y:這指定佈局的y坐標
android:layout_width=wrap_content告訴視圖根據其內容需要的尺寸調整自身。android:layout_width=match_parent告訴視圖變得和其父視圖一樣大。
視圖識別
在XML標籤中,ID的語法為:
- 開始的at符號(@)表示XML解析器應該解析並展開ID字符串的其餘部分,並將其識別為ID資源
- 加號(+)表示這是一個新的資源名稱,必須創建並添加到我們的資源中
Android LinearLayout
Android LinearLayout將元素沿著一條線排列。我們可以使用android:orientation來指定該行是垂直還是水平。默認情況下,方向是水平的。垂直LinearLayout每行只有一個子元素(因此它是單個元素的列),而水平LinearLayout在屏幕上只有一行單個元素android:layout_weight屬性表示元素的重要性。具有較大權重的元素佔用更多的屏幕空間。以下是使用LinearLayout的示例Layout XML:layout_linear.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_margin="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin">
<Button
android:id="@+id/backbutton"
android:text="Back"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:text="Row 2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:text="Row 3"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:text="Row 4"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:text="Row 5"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button
android:id="@+id/next_button"
android:text="next"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:text="Row 6b"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:text="Row 6c"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:text="Row 6d"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
在此佈局中,我們有一個父LinearLayout,它具有垂直方向,包含按鈕,文本視圖和一個嵌套的線性佈局(具有水平方向)作為子視圖。 注意:嵌套佈局不一定是一種類型。例如,我們可以在RelativeLayout的子元素中有一個LinearLayout,反之亦然。
Android RelativeLayout
Android RelativeLayout 是一種基於元素之間和父容器相互關係進行佈局的方式。這是一種最複雜的佈局,我們需要多個屬性來實現我們所需的佈局。也就是說,使用 RelativeLayout,我們可以將一個視圖定位為其兄弟視圖的左邊、右邊、下方或上方。我們還可以將一個視圖相對於其父視圖定位,例如水平居中、垂直居中或兩者兼有,或者與父 RelativeLayout 的任何邊緣對齊。如果在子視圖上未指定這些屬性中的任何一個,則該視圖將默認呈現在左上角位置。
Android RelativeLayout 屬性
以下是在 RelativeLayout 中使用的主要屬性。它們分為三個不同的類別:
相對於容器
- android:layout_alignParentBottom:將元素的底部放在容器的底部
- android:layout_alignParentLeft:將元素的左側放在容器的左側
- android:layout_alignParentRight :將元素的右側放置在容器的右側
- android:layout_alignParentTop :將元素放置在容器的頂部
- android:layout_centerHorizontal :將元素水平居中在其父容器內
- android:layout_centerInParent :將元素在其容器內水平和垂直居中
- android:layout_centerVertical :將元素在其父容器內垂直居中
相對於兄弟元素
- android:layout_above :將元素放置在指定元素的上方
- android:layout_below :將元素放置在指定元素的下方
- android:layout_toLeftOf :將元素放置在指定元素的左側
- android:layout_toRightOf :將元素放置在指定元素的右側
“@id/XXXXX”用於通過其id引用元素。要記住的一件事是,在聲明之前引用一個元素將產生錯誤,因此在這種情況下應使用@+id/。
與其他元素對齊
- android:layout_alignBaseline :將新元素的基線與指定元素的基線對齊
- android:layout_alignBottom :將新元素的底部與指定元素的底部對齊
- android:layout_alignLeft :將新元素的左邊緣與指定元素的左邊緣對齊
- android:layout_alignRight:將新元素的右邊緣與指定元素的右邊緣對齊
- android:layout_alignTop:將新元素的頂部與指定元素的頂部對齊
以下的 XML 佈局使用 RelativeLayout:layout_relative.xml
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<Button
android:id="@+id/backbutton"
android:text="Back"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/firstName"
android:text="First Name"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/backbutton" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/editFirstName"
android:text="JournalDev"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/firstName"
android:layout_below="@id/backbutton"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/editLastName"
android:text="Layout Tutorial Example"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignTop="@+id/lastName"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/lastName"
android:layout_toEndOf="@+id/lastName" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/lastName"
android:text="Last Name"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="48dp"
android:layout_below="@+id/firstName"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentStart="true"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="40dp"
android:layout_marginStart="40dp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/next"
android:text="Next"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/editLastName"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/editLastName"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/editLastName"
android:layout_marginTop="37dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
如您所見,我們可以根據元素的相對位置重新排列它們。以下的 XML 佈局代表了一個包含嵌套線性佈局和相對佈局的自定義佈局:layout_mixed.xml
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/parent_rl"
android:text="Parent RelativeLayout"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/linearLayout"
android:layout_below="@id/parent_rl"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_alignParentEnd="true">
<TextView
android:text="Nested Horizontal"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:text="LL"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:text="Double Nested"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:text="Vertical"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:text="LL"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_below="@id/linearLayout">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Nested Relative Layout"
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/back_button_pressed"
android:text="back"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="66dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
Android 佈局專案結構
Android 佈局代碼
該應用啟動到 MainActivity,通過以下代碼加載layout_linear.xml 的內容:
package com.journaldev.layouts;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Button back,next;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.layout_linear);
back=(Button)findViewById(R.id.back_button);
next=(Button)findViewById(R.id.next_button);
next.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent=new Intent(MainActivity.this,SecondActivity.class);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
back.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
finish();
}
});
}
}
{
“error”: “Upstream error…”
}
package com.journaldev.layouts;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class SecondActivity extends Activity {
Button back,next;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.layout_relative);
back=(Button)findViewById(R.id.backbutton);
next=(Button)findViewById(R.id.next);
next.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent=new Intent(SecondActivity.this,ThirdActivity.class);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
back.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent=new Intent(SecondActivity.this,MainActivity.class);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}
package com.journaldev.layouts;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class ThirdActivity extends Activity {
Button back;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.layout_mixed);
back=(Button)findViewById(R.id.back_button_pressed);
back.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent=new Intent(ThirdActivity.this,SecondActivity.class);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}
以下是三个布局文件的图像输出:layout_linear.xml 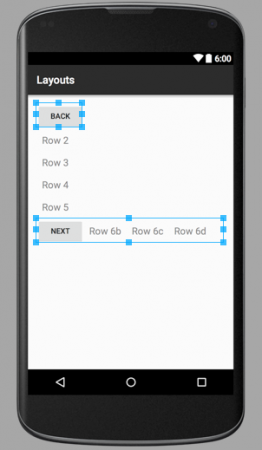 如您所见,父LinearLayout包含6个子元素,位于单个垂直列中,其中一个是包含4个组件的嵌套LinearLayout子视图,其方向为水平。 layout_relative.xml
如您所见,父LinearLayout包含6个子元素,位于单个垂直列中,其中一个是包含4个组件的嵌套LinearLayout子视图,其方向为水平。 layout_relative.xml 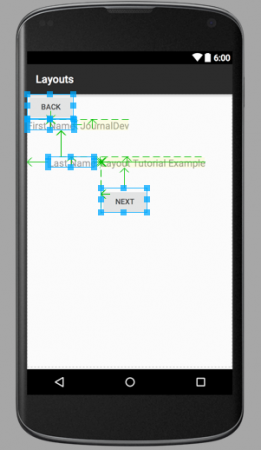 图像中的箭头显示了兄弟元素相对于彼此和容器的位置关系。 layout_mixed.xml
图像中的箭头显示了兄弟元素相对于彼此和容器的位置关系。 layout_mixed.xml 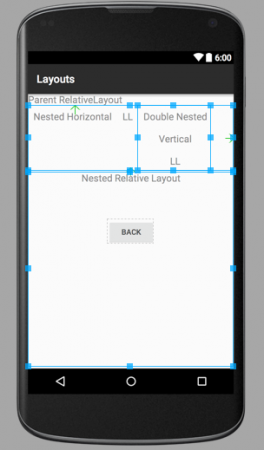 此相对布局包含一个嵌套的垂直LinearLayout以及一个子RelativeLayout的水平LinearLayout。注意:属于不同布局的组件不是兄弟元素,因此无法相对于彼此定位。它们的容器布局是兄弟元素,可以相对于彼此定位。如果您对蓝色矩形和箭头感到好奇,那是因为这些图像来自XML布局的图形视图。当您运行应用程序时,这些蓝色线和矩形将不会显示。这标志着Android布局教程的结束。我们将在下一个教程中介绍其他Android布局。您可以从以下链接下载最终的Android布局项目。
此相对布局包含一个嵌套的垂直LinearLayout以及一个子RelativeLayout的水平LinearLayout。注意:属于不同布局的组件不是兄弟元素,因此无法相对于彼此定位。它们的容器布局是兄弟元素,可以相对于彼此定位。如果您对蓝色矩形和箭头感到好奇,那是因为这些图像来自XML布局的图形视图。当您运行应用程序时,这些蓝色线和矩形将不会显示。这标志着Android布局教程的结束。我们将在下一个教程中介绍其他Android布局。您可以从以下链接下载最终的Android布局项目。
下載 Android LinearLayout RelativeLayout 範例專案
參考資料:API 文件
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/android-layout-linearlayout-relativelayout