Spring是最广泛使用的Java EE框架之一。我们之前已经看过如何使用Spring MVC来创建基于Java的Web应用程序。今天我们将学习如何使用Spring MVC创建Spring Restful Web Services,然后使用Rest客户端进行测试。最后,我们还将了解如何使用Spring RestTemplate API调用Spring Restful Web服务。
Spring REST
我们将使用Spring的最新版本4.0.0.RELEASE,并利用Spring的Jackson JSON集成在REST调用响应中发送JSON响应。该教程是在Spring STS IDE中开发的,可以轻松创建Spring MVC骨架代码,然后扩展以实现RESTful架构。在STS中创建一个新的Spring MVC项目,我们的最终项目将如下图所示。我们将逐个查看每个组件。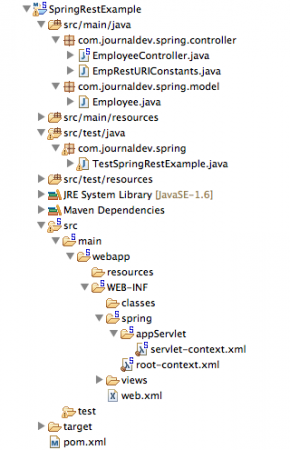
Spring REST配置XML文件
我们的pom.xml文件如下所示。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.journaldev</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringRestExample</artifactId>
<name>SpringRestExample</name>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>1.0.0-BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<java-version>1.6</java-version>
<org.springframework-version>4.0.0.RELEASE</org.springframework-version>
<org.aspectj-version>1.7.4</org.aspectj-version>
<org.slf4j-version>1.7.5</org.slf4j-version>
<jackson.databind-version>2.2.3</jackson.databind-version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Jackson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.databind-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
<exclusions>
<!-- Exclude Commons Logging in favor of SLF4j -->
<exclusion>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- AspectJ -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>${org.aspectj-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Logging -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.mail</groupId>
<artifactId>mail</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.jms</groupId>
<artifactId>jms</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.sun.jdmk</groupId>
<artifactId>jmxtools</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.sun.jmx</groupId>
<artifactId>jmxri</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- @Inject -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.inject</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.inject</artifactId>
<version>1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Servlet -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.7</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-eclipse-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.9</version>
<configuration>
<additionalProjectnatures>
<projectnature>org.springframework.ide.eclipse.core.springnature</projectnature>
</additionalProjectnatures>
<additionalBuildcommands>
<buildcommand>org.springframework.ide.eclipse.core.springbuilder</buildcommand>
</additionalBuildcommands>
<downloadSources>true</downloadSources>
<downloadJavadocs>true</downloadJavadocs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.6</source>
<target>1.6</target>
<compilerArgument>-Xlint:all</compilerArgument>
<showWarnings>true</showWarnings>
<showDeprecation>true</showDeprecation>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>exec-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.2.1</version>
<configuration>
<mainClass>org.test.int1.Main</mainClass>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
STS工具为我们生成了pom.xml文件。但是,我已将Spring框架、AspectJ、SLF4J和Jackson版本更新为今天最新的版本。大部分部分是通用的并自动生成的,需要注意的重点是我已将Jackson JSON库添加到依赖项中,因为我们将使用它来将对象转换为JSON,反之亦然。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="2.5" xmlns="https://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee https://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
<!-- The definition of the Root Spring Container shared by all Servlets and Filters -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/root-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- Creates the Spring Container shared by all Servlets and Filters -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- Processes application requests -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/appServlet/servlet-context.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
这个文件是自动生成的,我并没有改变其中的任何内容。但是,如果你想改变上下文配置文件及其位置,你可以在 web.xml 文件中进行。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- Root Context: defines shared resources visible to all other web components -->
</beans>
这个文件包含了共享资源,这些资源对所有的 Web 组件都是可见的,我们将开发一个简单的 REST 服务,这就是为什么我在这里没有改变任何东西。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:beans="https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="https://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- DispatcherServlet Context: defines this servlet's request-processing infrastructure -->
<!-- Enables the Spring MVC @Controller programming model -->
<annotation-driven />
<!-- Handles HTTP GET requests for /resources/** by efficiently serving up static resources in the ${webappRoot}/resources directory -->
<resources mapping="/resources/**" location="/resources/" />
<!-- Resolves views selected for rendering by @Controllers to .jsp resources in the /WEB-INF/views directory -->
<beans:bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<beans:property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/" />
<beans:property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</beans:bean>
<!-- Configure to plugin JSON as request and response in method handler -->
<beans:bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter">
<beans:property name="messageConverters">
<beans:list>
<beans:ref bean="jsonMessageConverter"/>
</beans:list>
</beans:property>
</beans:bean>
<!-- Configure bean to convert JSON to POJO and vice versa -->
<beans:bean id="jsonMessageConverter" class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter">
</beans:bean>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.journaldev.spring.controller" />
</beans:beans>
大部分都是自动生成的,并包含样板配置。然而,需要注意的重要点是使用 annotation-driven 元素来支持基于注解的配置,并将 MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 插入到 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 的 messageConverters 中,以便使用 Jackson API 进行 JSON 到 Java Beans 的转换,反之亦然。通过这个配置,我们将在请求体中使用 JSON,并在响应中接收 JSON 数据。
Spring REST 模型类
让我们编写一个简单的 POJO 类,作为我们的 Restful Web 服务方法的输入和输出。
package com.journaldev.spring.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonSerialize;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser.std.DateSerializer;
public class Employee implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -7788619177798333712L;
private int id;
private String name;
private Date createdDate;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@JsonSerialize(using=DateSerializer.class)
public Date getCreatedDate() {
return createdDate;
}
public void setCreatedDate(Date createdDate) {
this.createdDate = createdDate;
}
}
唯一需要注意的重要点是使用 @JsonSerialize 注解来使用 DateSerializer 类进行从 Java 类型到 JSON 格式的日期转换,反之亦然。
Spring Restful Web服务端点
我们将拥有以下REST Web服务端点。
| Sl. No | URI | HTTP Method | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | /rest/emp/dummy | GET | Health Check service, to insert a dummy data in the Employees data storage |
| 2 | /rest/emp/{id} | GET | To get the Employee object based on the id |
| 3 | /rest/emps | GET | To get the list of all the Employees in the data store |
| 4 | /rest/emp/create | POST | To create the Employee object and store it |
| 5 | /rest/emp/delete/{id} | PUT | To delete the Employee object from the data storage based on the id |
我们有一个类,将所有这些URI定义为字符串常量。
package com.journaldev.spring.controller;
public class EmpRestURIConstants {
public static final String DUMMY_EMP = "/rest/emp/dummy";
public static final String GET_EMP = "/rest/emp/{id}";
public static final String GET_ALL_EMP = "/rest/emps";
public static final String CREATE_EMP = "/rest/emp/create";
public static final String DELETE_EMP = "/rest/emp/delete/{id}";
}
Spring Restful Web服务控制器类
我们的EmployeeController类将发布上述所有Web服务端点。让我们先看看类的代码,然后我们将详细了解每个方法。
package com.journaldev.spring.controller;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.journaldev.spring.model.Employee;
/**
* Handles requests for the Employee service.
*/
@Controller
public class EmployeeController {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EmployeeController.class);
//Map用于存储员工,理想情况下我们应该使用数据库
Map empData = new HashMap();
@RequestMapping(value = EmpRestURIConstants.DUMMY_EMP, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody Employee getDummyEmployee() {
logger.info("Start getDummyEmployee");
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.setId(9999);
emp.setName("Dummy");
emp.setCreatedDate(new Date());
empData.put(9999, emp);
return emp;
}
@RequestMapping(value = EmpRestURIConstants.GET_EMP, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody Employee getEmployee(@PathVariable("id") int empId) {
logger.info("Start getEmployee. ID="+empId);
return empData.get(empId);
}
@RequestMapping(value = EmpRestURIConstants.GET_ALL_EMP, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody List getAllEmployees() {
logger.info("Start getAllEmployees.");
List emps = new ArrayList();
Set empIdKeys = empData.keySet();
for(Integer i : empIdKeys){
emps.add(empData.get(i));
}
return emps;
}
@RequestMapping(value = EmpRestURIConstants.CREATE_EMP, method = RequestMethod.POST)
public @ResponseBody Employee createEmployee(@RequestBody Employee emp) {
logger.info("Start createEmployee.");
emp.setCreatedDate(new Date());
empData.put(emp.getId(), emp);
return emp;
}
@RequestMapping(value = EmpRestURIConstants.DELETE_EMP, method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public @ResponseBody Employee deleteEmployee(@PathVariable("id") int empId) {
logger.info("Start deleteEmployee.");
Employee emp = empData.get(empId);
empData.remove(empId);
return emp;
}
}
为简便起见,我将所有员工数据存储在HashMap empData中。使用@RequestMapping注解将请求URI映射到处理方法。我们还可以指定客户端应使用的HTTP方法来调用REST方法。@ResponseBody注解用于将响应对象映射到响应体中。一旦处理程序方法返回响应对象,MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter就会启动并将其转换为JSON响应。@PathVariable注解是从REST URI中提取数据并将其映射到方法参数的简便方法。@RequestBody注解用于将请求体JSON数据映射到Employee对象,同样由MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter完成映射。其余的代码简单而容易理解,我们的应用程序已准备好部署和测试。只需导出为WAR文件并将其复制到Servlet容器Web应用程序目录中。如果在STS中配置了服务器,您只需在服务器上运行它即可完成部署。我使用WizTools RestClient调用REST调用,但您也可以使用Chrome扩展Postman。以下屏幕截图显示了我们的应用程序公开的REST API的不同调用及其输出。健康检查 – 获取虚拟员工REST调用 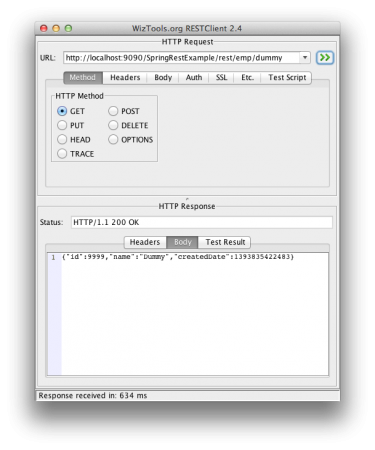 创建员工POST REST调用:确保请求Content-Type设置为“application/json”,否则将收到HTTP错误代码415。
创建员工POST REST调用:确保请求Content-Type设置为“application/json”,否则将收到HTTP错误代码415。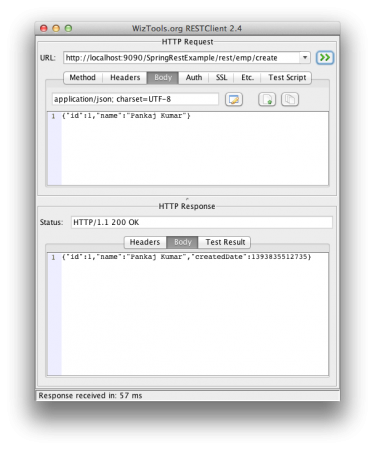 获取员工REST调用
获取员工REST调用  删除员工REST调用
删除员工REST调用 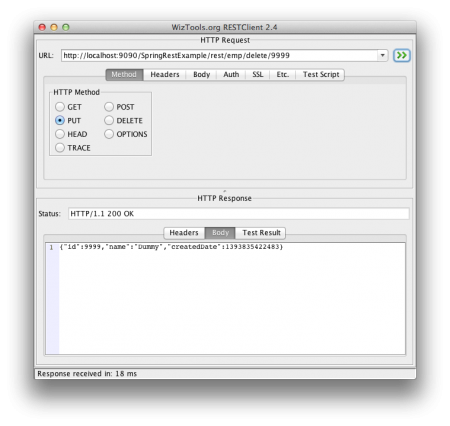 获取所有员工REST调用
获取所有员工REST调用 
Spring Rest客户端程序
Rest客户端对于测试我们的rest网络服务非常有用,但大多数情况下,我们需要通过我们的程序调用rest服务。我们可以使用Spring RestTemplate轻松调用这些方法。下面是一个简单的程序,使用RestTemplate API调用我们应用的rest方法。
package com.journaldev.spring;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import com.journaldev.spring.controller.EmpRestURIConstants;
import com.journaldev.spring.model.Employee;
public class TestSpringRestExample {
public static final String SERVER_URI = "https://localhost:9090/SpringRestExample";
public static void main(String args[]){
testGetDummyEmployee();
System.out.println("*****");
testCreateEmployee();
System.out.println("*****");
testGetEmployee();
System.out.println("*****");
testGetAllEmployee();
}
private static void testGetAllEmployee() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
//我们无法得到List因为JSON转换器不知道
//列表中对象的类型,因此将其转换为默认JSON对象类型LinkedHashMap
List emps = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVER_URI+EmpRestURIConstants.GET_ALL_EMP, List.class);
System.out.println(emps.size());
for(LinkedHashMap map : emps){
System.out.println("ID="+map.get("id")+",Name="+map.get("name")+",CreatedDate="+map.get("createdDate"));;
}
}
private static void testCreateEmployee() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.setId(1);emp.setName("Pankaj Kumar");
Employee response = restTemplate.postForObject(SERVER_URI+EmpRestURIConstants.CREATE_EMP, emp, Employee.class);
printEmpData(response);
}
private static void testGetEmployee() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
Employee emp = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVER_URI+"/rest/emp/1", Employee.class);
printEmpData(emp);
}
private static void testGetDummyEmployee() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
Employee emp = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVER_URI+EmpRestURIConstants.DUMMY_EMP, Employee.class);
printEmpData(emp);
}
public static void printEmpData(Employee emp){
System.out.println("ID="+emp.getId()+",Name="+emp.getName()+",CreatedDate="+emp.getCreatedDate());
}
}
大多数程序都很容易理解,但是当调用返回集合的rest方法时,我们需要使用LinkedHashMap,因为JSON转换为对象时不知道Employee对象,会将其转换为LinkedHashMap的集合。我们可以编写一个实用方法将LinkedHashMap转换为我们的Java Bean对象。当我们运行上面的程序时,我们在控制台上获得以下输出。
ID=9999,Name=Dummy,CreatedDate=Tue Mar 04 21:02:41 PST 2014
*****
ID=1,Name=Pankaj Kumar,CreatedDate=Tue Mar 04 21:02:41 PST 2014
*****
ID=1,Name=Pankaj Kumar,CreatedDate=Tue Mar 04 21:02:41 PST 2014
*****
2
ID=1,Name=Pankaj Kumar,CreatedDate=1393995761654
ID=9999,Name=Dummy,CreatedDate=1393995761381
另一个要注意的地方是RestTemplate的put方法没有选项来设置响应对象,因为PUT方法应该用于将某些内容存储在服务器上,简单的HTTP 200状态代码就足够了。
这就是关于Spring Restful Web应用程序教程的全部内容。从上面的链接下载示例项目并尽情玩耍,以获取更多知识。更新:由于有很多请求希望提供类似的带有XML支持以及同时支持XML和JSON的示例,我已经扩展了这个应用程序,在Spring REST XML JSON示例中支持XML和JSON的请求和响应。我强烈建议您查看一下,以了解Spring框架的美丽以及实现这一点的简易性。
您可以从我们的GitHub代码库下载完整的项目。













