欢迎来到春季国际化(i18n)教程。任何面向全球用户的Web应用程序,国际化(i18n)或本地化(L10n)对于更好的用户交互都非常重要。大多数Web应用程序框架都提供了根据用户区域设置本地化应用程序的简便方法。Spring也遵循这一模式,通过使用Spring拦截器、区域设置解析器和不同区域的资源包,为国际化(i18n)提供了广泛的支持。关于Java中i18n的一些早期文章。
Spring国际化i18n
让我们创建一个简单的Spring MVC项目,在这个项目中,我们将使用请求参数来获取用户的区域设置,并根据此设置来设置来自特定区域设置资源包的响应页面标签值。在Spring工具套件中创建一个Spring MVC项目,以获得我们应用程序的基本代码。如果您对Spring工具套件或Spring MVC项目不熟悉,请阅读Spring MVC示例。我们最终带有本地化更改的项目如下图所示。我们将逐个查看应用程序的所有部分。
Spring i18n Maven配置
我们的Spring MVC pom.xml如下所示。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.journaldev</groupId>
<artifactId>spring</artifactId>
<name>Springi18nExample</name>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>1.0.0-BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<java-version>1.6</java-version>
<org.springframework-version>4.0.2.RELEASE</org.springframework-version>
<org.aspectj-version>1.7.4</org.aspectj-version>
<org.slf4j-version>1.7.5</org.slf4j-version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
<exclusions>
<!-- Exclude Commons Logging in favor of SLF4j -->
<exclusion>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- AspectJ -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>${org.aspectj-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Logging -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.mail</groupId>
<artifactId>mail</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.jms</groupId>
<artifactId>jms</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.sun.jdmk</groupId>
<artifactId>jmxtools</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.sun.jmx</groupId>
<artifactId>jmxri</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- @Inject -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.inject</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.inject</artifactId>
<version>1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Servlet -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.7</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-eclipse-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.9</version>
<configuration>
<additionalProjectnatures>
<projectnature>org.springframework.ide.eclipse.core.springnature</projectnature>
</additionalProjectnatures>
<additionalBuildcommands>
<buildcommand>org.springframework.ide.eclipse.core.springbuilder</buildcommand>
</additionalBuildcommands>
<downloadSources>true</downloadSources>
<downloadJavadocs>true</downloadJavadocs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.6</source>
<target>1.6</target>
<compilerArgument>-Xlint:all</compilerArgument>
<showWarnings>true</showWarnings>
<showDeprecation>true</showDeprecation>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>exec-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.2.1</version>
<configuration>
<mainClass>org.test.int1.Main</mainClass>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
大部分代码都是由STS自动生成的,除了我已将Spring版本更新为使用最新版本4.0.2.RELEASE。我们也可以移除依赖项或更新其他依赖项的版本,但出于简单起见,我将它们保留了下来。
Spring资源包
为简单起见,让我们假设我们的应用程序仅支持两种区域设置 – 英语和法语。如果未指定用户区域设置,则将使用英语作为默认区域设置。让我们为这两种区域设置创建 spring 资源包,这将在 JSP 页面中使用。 messages_en.properties 代码:
label.title=Login Page
label.firstName=First Name
label.lastName=Last Name
label.submit=Login
messages_fr.properties 代码:
label.title=Connectez-vous page
label.firstName=Pr\u00E9nom
label.lastName=Nom
label.submit=Connexion
请注意,我在法语区域设置的资源包中使用 Unicode 来表示特殊字符,以便在发送到客户端请求的响应 HTML 中正确解释它们。另一个重要的注意点是,这两个资源包都位于应用程序的类路径中,它们的名称的模式为“messages_{locale}.properties”。我们稍后将看到这些为什么很重要。
Spring i18n 控制器类
我们的控制器类非常简单,它只是记录用户区域设置并返回 home.jsp 页面作为响应。
package com.journaldev.spring;
import java.util.Locale;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
/**
* Handles requests for the application home page.
*/
@Controller
public class HomeController {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HomeController.class);
/**
* Simply selects the home view to render by returning its name.
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String home(Locale locale, Model model) {
logger.info("Welcome home! The client locale is {}.", locale);
return "home";
}
}
Spring i18n JSP 页面
我们的 home.jsp 页面代码如下。
<%@taglib uri="https://www.springframework.org/tags" prefix="spring"%>
<%@ page session="false"%>
<html>
<head>
<title><spring:message code="label.title" /></title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" action="login">
<table>
<tr>
<td><label> <strong><spring:message
code="label.firstName" /></strong>
</label></td>
<td><input name="firstName" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><label> <strong><spring:message
code="label.lastName" /></strong>
</label></td>
<td><input name="lastName" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<spring:message code="label.submit" var="labelSubmit"></spring:message>
<td colspan="2"><input type="submit" value="${labelSubmit}" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
唯一值得一提的部分是使用spring:message来检索具有给定代码的消息。确保使用taglib jsp指令配置Spring标签库。Spring负责加载适当的资源包消息,并使其可供JSP页面使用。
Spring国际化 i18n – Bean配置文件
Spring Bean配置文件是所有魔法发生的地方。这是Spring框架的美妙之处,因为它帮助我们更多地专注于业务逻辑,而不是为琐碎的任务编写代码。让我们看看我们的Spring Bean配置文件是什么样子的,我们将逐个查看每个bean。 servlet-context.xml 代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:beans="https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="https://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- DispatcherServlet Context: defines this servlet's request-processing
infrastructure -->
<!-- Enables the Spring MVC @Controller programming model -->
<annotation-driven />
<!-- Handles HTTP GET requests for /resources/** by efficiently serving
up static resources in the ${webappRoot}/resources directory -->
<resources mapping="/resources/**" location="/resources/" />
<!-- Resolves views selected for rendering by @Controllers to .jsp resources
in the /WEB-INF/views directory -->
<beans:bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<beans:property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/" />
<beans:property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</beans:bean>
<beans:bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource">
<beans:property name="basename" value="classpath:messages" />
<beans:property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8" />
</beans:bean>
<beans:bean id="localeResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.CookieLocaleResolver">
<beans:property name="defaultLocale" value="en" />
<beans:property name="cookieName" value="myAppLocaleCookie"></beans:property>
<beans:property name="cookieMaxAge" value="3600"></beans:property>
</beans:bean>
<interceptors>
<beans:bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor">
<beans:property name="paramName" value="locale" />
</beans:bean>
</interceptors>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.journaldev.spring" />
</beans:beans>
-
annotation-driven标签启用了Controller编程模型,没有它,Spring就不会将我们的HomeController识别为客户端请求的处理程序。
-
context:component-scan提供了Spring将查找已注释组件并自动将它们注册为Spring bean的包。
- `
`
messageSource` bean 被配置为启用应用程序的国际化(i18n)。`basename` 属性用于提供资源包的位置。 `
classpath:messages` 表示资源包位于类路径中,并且遵循 `messages_{locale}.properties` 的命名模式。`defaultEncoding` 属性用于定义消息的编码。`
-
localeResolver类型的
org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.CookieLocaleResolverbean 用于在客户端请求中设置一个cookie,以便后续请求可以轻松识别用户的区域设置。例如,我们可以要求用户在首次启动Web应用程序时选择区域设置,并通过使用cookie,我们可以识别用户的区域设置并自动发送区域特定的响应。我们还可以指定默认区域设置、cookie名称和cookie在客户端浏览器中过期和被删除之前的最大寿命。如果您的应用程序维护用户会话,那么您还可以使用org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver作为localeResolver,以在用户会话中使用一个区域设置属性。配置与CookieLocaleResolver类似。<bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver"> <property name="defaultLocale" value="en" /> </bean>如果我们没有注册任何“localeResolver”,则默认情况下将使用AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver,它通过检查客户端HTTP请求中的
accept-language头来解析用户区域设置。 -
org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor拦截器被配置为拦截用户请求并识别用户区域设置。参数名称是可配置的,我们正在使用请求参数名“locale”作为区域设置。没有这个拦截器,我们将无法更改用户的区域设置并根据用户的新区域设置发送响应。它需要成为拦截器元素的一部分,否则Spring将不会将其配置为拦截器。
如果您想知道告诉Spring框架加载我们的上下文配置的配置,它存在于我们MVC应用程序的部署描述符中。
<servlet>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/appServlet/servlet-context.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
我们可以通过更改web.xml配置来更改上下文文件的位置或名称。我们的Spring i18n应用程序已经准备就绪,只需将其部署到任何Servlet容器中。通常我将其导出为WAR文件,放在独立的Tomcat Web服务器的webapps目录中。以下是我们应用程序主页的不同地区的截图。默认主页(英文地区):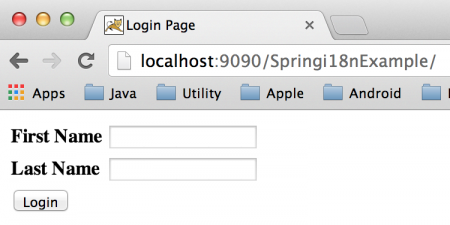 将地区作为参数传递(法文地区):
将地区作为参数传递(法文地区):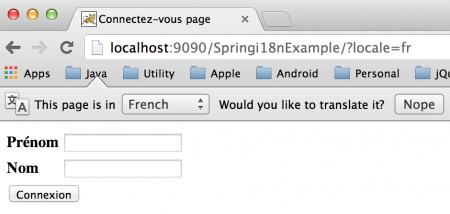 进一步的请求没有地区信息:
进一步的请求没有地区信息: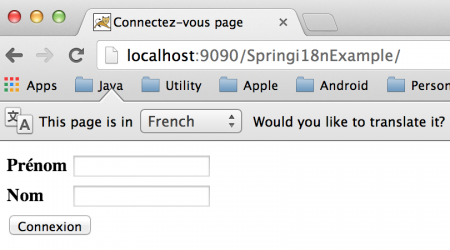 如您在上面的图片中所见,我们没有在客户端请求中传递地区信息,但我们的应用程序仍然能够识别用户的地区。现在你可能已经猜到,这是因为我们在Spring Bean配置文件中配置了CookieLocaleResolver bean。但是,您可以检查浏览器的Cookie数据来确认这一点。我正在使用Chrome,下面的图片显示了应用程序存储的Cookie数据。
如您在上面的图片中所见,我们没有在客户端请求中传递地区信息,但我们的应用程序仍然能够识别用户的地区。现在你可能已经猜到,这是因为我们在Spring Bean配置文件中配置了CookieLocaleResolver bean。但是,您可以检查浏览器的Cookie数据来确认这一点。我正在使用Chrome,下面的图片显示了应用程序存储的Cookie数据。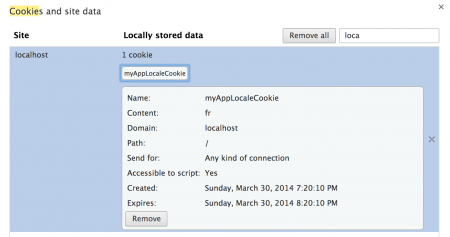 请注意,Cookie的过期时间为一小时,即3600秒,这是由cookieMaxAge属性配置的。如果您查看服务器日志,您会看到地区已被记录。
请注意,Cookie的过期时间为一小时,即3600秒,这是由cookieMaxAge属性配置的。如果您查看服务器日志,您会看到地区已被记录。
INFO : com.journaldev.spring.HomeController - Welcome home! The client locale is en.
INFO : com.journaldev.spring.HomeController - Welcome home! The client locale is fr.
INFO : com.journaldev.spring.HomeController - Welcome home! The client locale is fr.
这就是关于Spring i18n示例应用的全部内容,请从下面的链接下载示例项目,并进行操作以了解更多。













