春季Bean范围允许我们更细粒度地控制bean实例的创建。有时,我们希望将bean实例创建为单例,但在其他情况下,我们可能希望它在每个请求时或在会话中创建一次。
Spring Bean范围
有五种Spring Bean范围:
- singleton – 仅为spring容器创建一个spring bean实例。这是默认的Spring Bean范围。在使用此范围时,请确保bean没有共享的实例变量,否则可能导致数据不一致的问题。
- prototype – 每次从spring容器请求bean时都会创建一个新实例。
- request – 这与prototype范围相同,但用于Web应用程序。将为每个HTTP请求创建一个bean的新实例。
- session – 容器将为每个HTTP会话创建一个新的bean实例。
- global-session – 用于为Portlet应用程序创建全局会话bean。
Spring Bean Singleton和Prototype作用域
Spring Bean的Singleton和Prototype作用域可以用于独立的Spring应用程序。让我们看看如何使用@Scope注解轻松配置这些作用域。假设我们有一个Java Bean类。
package com.journaldev.spring;
public class MyBean {
public MyBean() {
System.out.println("MyBean instance created");
}
}
让我们定义Spring配置类,在这里我们将定义从Spring容器获取MyBean实例的方法。
package com.journaldev.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
@Configuration
public class MyConfiguration {
@Bean
@Scope(value="singleton")
public MyBean myBean() {
return new MyBean();
}
}
注意,singleton是默认作用域,因此我们可以从上面的Bean定义中删除@Scope(value="singleton")。现在让我们创建一个主方法并测试Singleton作用域。
package com.journaldev.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class MySpringApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
ctx.register(MyConfiguration.class);
ctx.refresh();
MyBean mb1 = ctx.getBean(MyBean.class);
System.out.println(mb1.hashCode());
MyBean mb2 = ctx.getBean(MyBean.class);
System.out.println(mb2.hashCode());
ctx.close();
}
}
当执行上述程序时,我们将获得如下输出。
MyBean instance created
867988177
867988177
注意,两个MyBean实例具有相同的哈希码,并且构造函数仅调用一次,这意味着Spring容器始终返回MyBean的相同实例。现在让我们将作用域更改为prototype。
@Bean
@Scope(value="prototype")
public MyBean myBean() {
return new MyBean();
}
当执行主方法时,我们将得到以下输出。
MyBean instance created
867988177
MyBean instance created
443934570
很明显,每次从Spring容器请求时都会创建一个新的MyBean实例。现在让我们将作用域更改为request。
@Bean
@Scope(value="request")
public MyBean myBean() {
return new MyBean();
}
在这种情况下,我们将得到以下异常。
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: No Scope registered for scope name 'request'
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:347)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:224)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.resolveNamedBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:1015)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:339)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:334)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.getBean(AbstractApplicationContext.java:1107)
at com.journaldev.spring.MySpringApp.main(MySpringApp.java:12)
这是因为request、session和global-session范围对于独立应用程序不可用。
Spring Bean 请求和会话范围
对于 Spring Bean 请求和会话范围示例,我们将创建 Spring Boot web 应用程序。创建一个 Spring Boot starter 项目,并选择“web”,这样我们就可以将其作为 web 应用程序运行。 我们最终的项目将如下图所示。
我们最终的项目将如下图所示。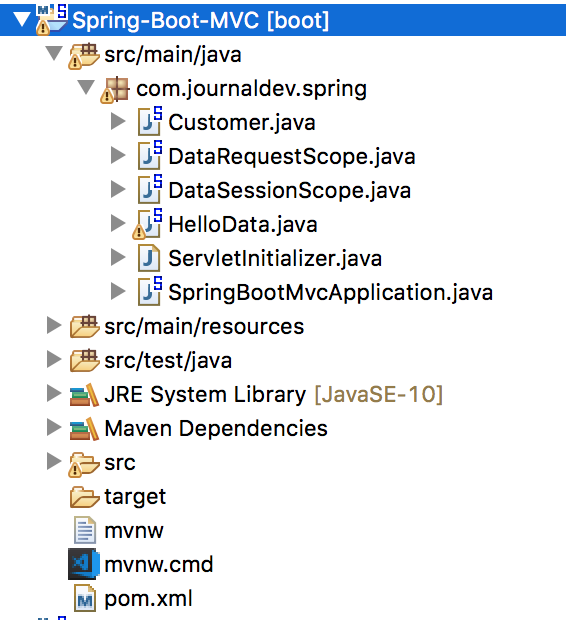
ServletInitializer 和 SpringBootMvcApplication 是自动生成的 Spring Boot 类。我们不需要在那里进行任何更改。这是我的 pom.xml 文件,请查看我们应用程序的依赖项。根据您使用的 Eclipse 版本,您的 pom.xml 文件可能略有不同。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.journaldev.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring-Boot-MVC</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>Spring-Boot-MVC</name>
<description>Spring Beans Scope MVC</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>10</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
让我们创建一些 Spring 组件,并将它们配置为 Spring 容器中的 Spring Bean,范围为request和session。
Spring Bean 请求范围
package com.journaldev.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ScopedProxyMode;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Scope(value = "request", proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS)
public class DataRequestScope {
private String name = "Request Scope";
public DataRequestScope() {
System.out.println("DataRequestScope Constructor Called");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
Spring Bean Session Scope
package com.journaldev.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ScopedProxyMode;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Scope(value = "session", proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS)
public class DataSessionScope {
private String name = "Session Scope";
public DataSessionScope() {
System.out.println("DataSessionScope Constructor Called at "+LocalDateTime.now());
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
Spring组件
现在让我们创建一个Spring组件,并使用Spring自动配置上述的bean。
package com.journaldev.spring;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Customer {
@Autowired
private DataRequestScope dataRequestScope;
@Autowired
private DataSessionScope dataSessionScope;
public DataRequestScope getDataRequestScope() {
return dataRequestScope;
}
public void setDataRequestScope(DataRequestScope dataRequestScope) {
this.dataRequestScope = dataRequestScope;
}
public DataSessionScope getDataSessionScope() {
return dataSessionScope;
}
public void setDataSessionScope(DataSessionScope dataSessionScope) {
this.dataSessionScope = dataSessionScope;
}
}
Spring Rest控制器
最后,让我们创建一个RestController类,并为测试目的配置一些API端点。
package com.journaldev.spring;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloData {
@Autowired
private Customer customer;
@RequestMapping("/nameRS")
public String helloRS() {
return customer.getDataRequestScope().getName();
}
@RequestMapping("/nameSSUpdated")
public String helloSSUpdated() {
customer.getDataSessionScope().setName("Session Scope Updated");
return customer.getDataSessionScope().getName();
}
@RequestMapping("/nameSS")
public String helloSS() {
return customer.getDataSessionScope().getName();
}
}
Spring Boot会话超时配置
最后,我们需要配置Spring Boot会话超时变量,在src/main/resources/application.properties中添加以下属性。
server.session.cookie.max-age= 1
server.session.timeout= 1
现在我们的Spring beans的会话范围将在一分钟内失效。只需将SpringBootMvcApplication类作为Spring Boot应用程序运行。您应该看到我们配置的端点的以下输出。
2018-05-23 17:02:25.830 INFO 6921 --- [main] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/nameRS]}" onto public java.lang.String com.journaldev.spring.HelloData.helloRS()
2018-05-23 17:02:25.831 INFO 6921 --- [main] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/nameSSUpdated]}" onto public java.lang.String com.journaldev.spring.HelloData.helloSSUpdated()
2018-05-23 17:02:25.832 INFO 6921 --- [main] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/nameSS]}" onto public java.lang.String com.journaldev.spring.HelloData.helloSS()
Spring Bean请求范围测试
打开任何浏览器并访问URL https://localhost:8080/nameRS,查看控制台输出。您应该在每个请求中看到 DataRequestScope Constructor Called 被打印出来。
Spring Bean会话范围测试
前往 https://localhost:8080/nameSS,你将得到以下输出。  现在前往
现在前往 https://localhost:8080/nameSSUpdated 以更新 DataSessionScope 名称值为 Session Scope Updated。 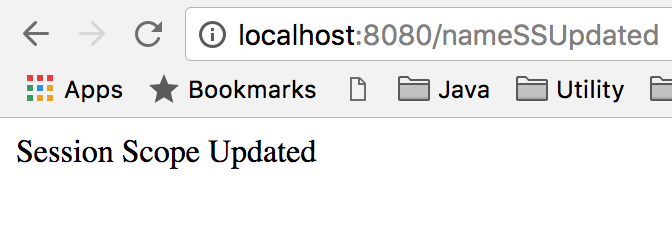 然后再次访问
然后再次访问 https://localhost:8080/nameSS,你应该看到已更新的值。 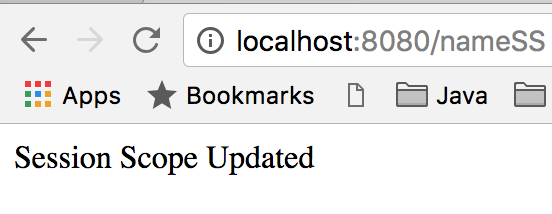 到此时,你应该在控制台输出中只看到一次
到此时,你应该在控制台输出中只看到一次 DataSessionScope Constructor Called at XXX。现在等待1分钟,以使我们的会话作用域bean失效。然后再次访问 https://localhost:8080/nameSS,你应该看到原始输出。此外,你应该检查控制台消息,查看容器再次创建DataSessionScope的情况。  这就是关于Spring Beans作用域教程的全部内容。
这就是关于Spring Beans作用域教程的全部内容。
你可以从我们的 GitHub存储库 下载Spring Beans Scope Spring Boot项目。
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/spring-bean-scopes













