Kotlin是由JetBrains推出的最新的JVM编程语言。Google已将其与Java一起指定为Android开发的官方语言。开发人员表示,它解决了Java编程中遇到的问题。我写了很多Kotlin教程,这里我提供一些重要的Kotlin面试问题。
Kotlin面试问题
这里我提供了一些Kotlin面试问题和答案,这将有助于你的Kotlin面试。这些Kotlin面试问题既适合初学者,也适合经验丰富的程序员。还有编码问题,可以帮助你提高编码技能。
-
Kotlin的目标平台是什么?Kotlin-Java的互操作性是如何实现的?
Java虚拟机(JVM)是Kotlin的目标平台。由于两者编译后都生成字节码,因此Kotlin与Java是100%可互操作的。因此,Kotlin代码可以从Java中调用,反之亦然。
-
如何在Kotlin中声明变量?声明与Java的对应方式有何不同?
Java和Kotlin变量声明有两个主要区别:
-
声明的类型 在Java中,声明如下:
String s = "Java String"; int x = 10;而在Kotlin中,声明如下:
val s: String = "Hi" var x = 5在Kotlin中,声明以
val和var开头,后跟可选类型。Kotlin可以使用类型推断自动检测类型。 -
默认值 在Java中可以这样写:
String s:而在Kotlin中以下变量声明是无效的。
val s: String
-
-
val 和 var 声明有什么区别?如何将 String 转换为 Int?
val变量不能被修改。它们类似于 Java 中的 final 修饰符。而var可以被重新赋值。重新赋值的值必须是相同的数据类型。fun main(args: Array<String>) { val s: String = "Hi" var x = 5 x = "6".toInt() }我们使用
toInt()方法将 String 转换为 Int。 -
在 Kotlin 中,什么是空安全和可空类型?猫王操作符是什么?
Kotlin非常重视空安全,这是一种防止可怕的空指针异常的方法,它使用可空类型,如
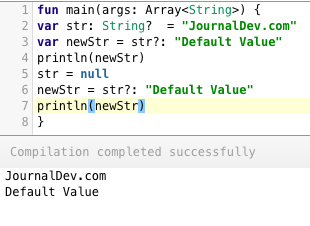
String?、Int?、Float?等。这些类型充当包装类型,可以容纳空值。可空值不能添加到另一个可空值或基本类型值中。要检索基本类型,我们需要使用安全调用来取消可空类型的包装。如果在取消包装时值为空,我们可以选择忽略或使用默认值。猫王操作符用于安全地取消可空值的包装。它表示为?:放在可空类型上。如果可空类型包含空值,则使用右侧的值。var str: String? = "JournalDev.com" var newStr = str?: "默认值" str = null newStr = str?: "默认值" -
什么是
const?它与val有什么不同?默认情况下,
val属性在运行时设置。在val上添加const修饰符会使其成为编译时常量。const不能与var一起使用,也不能单独使用。const不适用于局部变量。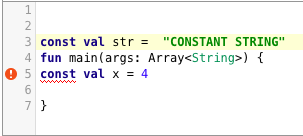
-
Kotlin允许我们使用诸如int、float、double等原始类型吗?
在语言级别上,我们不能使用上述类型。但编译后的JVM字节码当中确实有它们。
-
每个 Kotlin 程序的入口点是什么?
main函数是每个 Kotlin 程序的入口点。在 Kotlin 中,我们可以选择不在类内部编写 main 函数。在编译时,JVM 会隐式地将其封装在一个类中。以Array<String>形式传递的字符串用于检索命令行参数。 -
在取消可空值的情况下,
!!与?有什么不同?还有其他安全取消可空值的方法吗?!!用于强制取消可空类型以获取值。如果返回的值为空,将导致运行时崩溃。因此,!!操作符应仅在您绝对确定值不会为空时使用。否则,您将遇到可怕的空指针异常。另一方面,?是一个Elvis运算符,它执行安全调用。我们可以在可空值上使用lambda表达式let来安全取消,如下所示。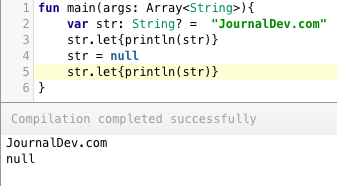 这里的let表达式执行安全调用以取消可空类型。
这里的let表达式执行安全调用以取消可空类型。 -
函数如何声明?为什么 Kotlin 函数被称为顶级函数?
fun sumOf(a: Int, b: Int): Int{ return a + b }函数的返回类型在
:之后定义。Kotlin 中的函数可以在 Kotlin 文件的根部声明。 -
Kotlin 中 == 和 === 运算符有什么区别?
\== is used to compare the values are equal or not. === is used to check if the references are equal or not.
- public
- internal
- protected
- private
`public` is the default visibility modifier.
```
class A{
}
class B : A(){
}
```
**NO**. By default classes are final in Kotlin. To make them non-final, you need to add the `open` modifier.
```
open class A{
}
class B : A(){
}
```
Constructors in Kotlin are of two types: **Primary** - These are defined in the class headers. They cannot hold any logic. There's only one primary constructor per class. **Secondary** - They're defined in the class body. They must delegate to the primary constructor if it exists. They can hold logic. There can be more than one secondary constructors.
```
class User(name: String, isAdmin: Boolean){
constructor(name: String, isAdmin: Boolean, age: Int) :this(name, isAdmin)
{
this.age = age
}
}
```
`init` is the initialiser block in Kotlin. It's executed once the primary constructor is instantiated. If you invoke a secondary constructor, then it works after the primary one as it is composed in the chain.
String interpolation is used to evaluate string templates. We use the symbol $ to add variables inside a string.
```
val name = "Journaldev.com"
val desc = "$name now has Kotlin Interview Questions too. ${name.length}"
```
Using `{}` we can compute an expression too.
By default, the constructor arguments are `val` unless explicitly set to `var`.
**NO**. Unlike Java, in Kotlin, new isn't a keyword. We can instantiate a class in the following way:
```
class A
var a = A()
val new = A()
```
when is the equivalent of `switch` in `Kotlin`. The default statement in a when is represented using the else statement.
```
var num = 10
when (num) {
0..4 -> print("value is 0")
5 -> print("value is 5")
else -> {
print("value is in neither of the above.")
}
}
```
`when` statments have a default break statement in them.
In Java, to create a class that stores data, you need to set the variables, the getters and the setters, override the `toString()`, `hash()` and `copy()` functions. In Kotlin you just need to add the `data` keyword on the class and all of the above would automatically be created under the hood.
```
data class Book(var name: String, var authorName: String)
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val book = Book("Kotlin Tutorials","Anupam")
}
```
Thus, data classes saves us with lot of code. It creates component functions such as `component1()`.. `componentN()` for each of the variables. [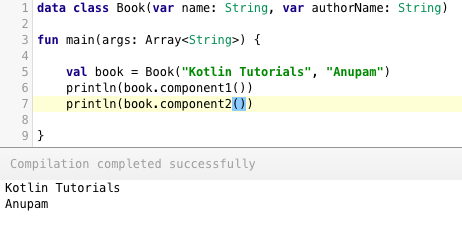](https://journaldev.nyc3.cdn.digitaloceanspaces.com/2018/04/kotlin-interview-questions-data-classes.png)
Destructuring Declarations is a smart way to assign multiple values to variables from data stored in objects/arrays. [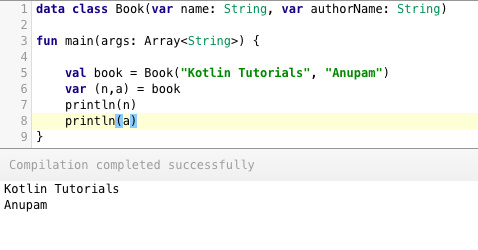](https://journaldev.nyc3.cdn.digitaloceanspaces.com/2018/04/kotlin-interview-questions-destructuring-declarations.png) Within paratheses, we've set the variable declarations. Under the hood, destructuring declarations create component functions for each of the class variables.
[Inline functions](/community/tutorials/kotlin-inline-function-reified) are used to save us memory overhead by preventing object allocations for the anonymous functions/lambda expressions called. Instead, it provides that functions body to the function that calls it at runtime. This increases the bytecode size slightly but saves us a lot of memory. [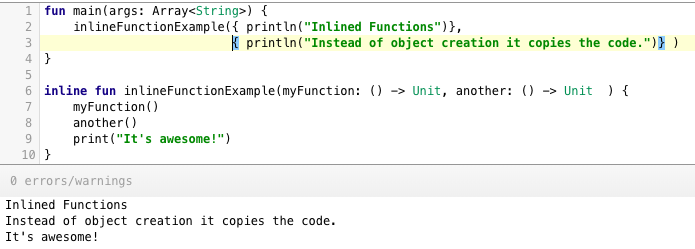](https://journaldev.nyc3.cdn.digitaloceanspaces.com/2018/04/kotlin-interview-questions-inline-functions.png) [infix functions](/community/tutorials/kotlin-functions) on the other are used to call functions without parentheses or brackets. Doing so, the code looks much more like a natural language. [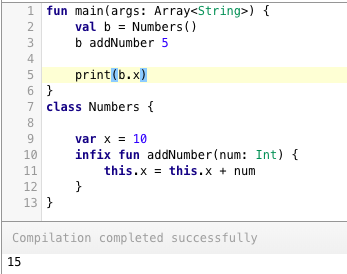](https://journaldev.nyc3.cdn.digitaloceanspaces.com/2018/04/kotlin-interview-questions-infix-notations.png)
Both are used to delay the property initializations in Kotlin `lateinit` is a modifier used with var and is used to set the value to the var at a later point. `lazy` is a method or rather say lambda expression. It's set on a val only. The val would be created at runtime when it's required.
```
val x: Int by lazy { 10 }
lateinit var y: String
```
To use the singleton pattern for our class we must use the keyword `object`
```
object MySingletonClass
```
An `object` cannot have a constructor set. We can use the init block inside it though.
**NO**. Kotlin doesn't have the static keyword. To create static method in our class we use the `companion object`. Following is the Java code:
```
class A {
public static int returnMe() { return 5; }
}
```
The equivalent Kotlin code would look like this:
```
class A {
companion object {
fun a() : Int = 5
}
}
```
To invoke this we simply do: `A.a()`.
```
val arr = arrayOf(1, 2, 3);
```
The type is Array<Int>.
这就是关于Kotlin面试问题和答案的全部内容。
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/kotlin-interview-questions