JUnit5 教程
在这个 JUnit 教程中,我们将使用示例介绍 JUnit5 的基础知识和新功能。在 Java 的世界中,JUnit 是一个流行的框架,用于对 Java 代码进行单元测试。JUnit 主要帮助开发人员自己在 JVM 上测试他们的代码。
JUnit5 架构
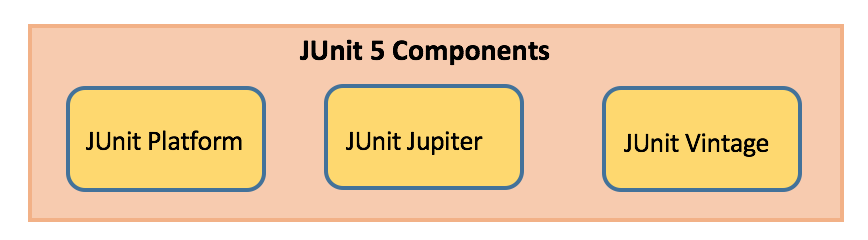
JUnit 平台
- 在 JVM 上启动测试框架
- 具有 TestEngine API,用于构建在 JUnit 平台上运行的测试框架
JUnit Jupiter
- 结合了用于编写测试的新编程模型和用于扩展的扩展模型
- 增加新的注解,如
@BeforeEach,@AfterEach,@AfterAll,@BeforeAll等。
JUnit Vintage
- 为在这个新平台上执行先前的JUnit版本3和4测试提供支持
JUnit Maven 依赖
要在项目中实现基于JUnit5的测试用例,请将以下依赖项添加到项目的pom.xml文件中:
- JUnit 5库
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>5.1.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-runner</artifactId>
<version> 1.1.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
- JUnit5 Maven Surefire提供程序,用于在IDE不支持JUnit5的情况下执行单元测试(如果IDE支持,则不需要此点)
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.19.1</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-surefire-provider</artifactId>
<version>1.0.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>
JUnit5新特性
运行时需要Java 8或更高版本。但仍然可以测试使用先前Java版本编译的代码。其中引入了各种新特性。
JUnit注解
下面列出了一些常用的注解:
| Annotation | Description |
|---|---|
| @Test | Denotes a test method |
| @DisplayName | Declares a custom display name for the test class or test method |
| @BeforeEach | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed before each test method |
| @AfterEach | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed after each test method |
| @BeforeAll | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed before all test methods |
| @AfterAll | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed after all test methods |
| @Disable | Used to disable a test class or test method |
| @Nested | Denotes that the annotated class is a nested, non-static test class |
| @Tag | Declare tags for filtering tests |
| @ExtendWith | Register custom extensions |
package com.journaldev;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Disabled;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class JUnit5Sample1Test {
@BeforeAll
static void beforeAll() {
System.out.println("**--- Executed once before all test methods in this class ---**");
}
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
System.out.println("**--- Executed before each test method in this class ---**");
}
@Test
void testMethod1() {
System.out.println("**--- Test method1 executed ---**");
}
@DisplayName("Test method2 with condition")
@Test
void testMethod2() {
System.out.println("**--- Test method2 executed ---**");
}
@Test
@Disabled("implementation pending")
void testMethod3() {
System.out.println("**--- Test method3 executed ---**");
}
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
System.out.println("**--- Executed after each test method in this class ---**");
}
@AfterAll
static void afterAll() {
System.out.println("**--- Executed once after all test methods in this class ---**");
}
}
我们可以在Eclipse中运行上述JUnit测试类,方法是Eclipse -> Run As -> JUnit Test。 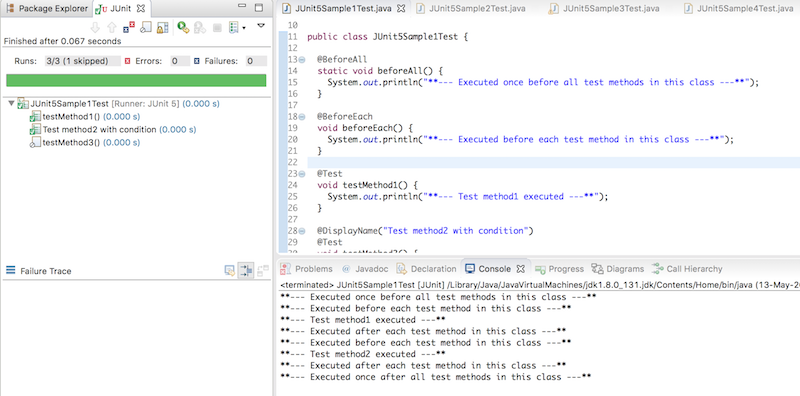
JUnit断言
每个测试方法都必须使用断言对条件进行评估,以便测试可以继续执行。JUnit Jupiter断言存储在org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions类中。所有方法都是静态的。
| Assertion | Description |
|---|---|
| assertEquals(expected, actual) | Fails when expected does not equal actual |
| assertFalse(expression) | Fails when expression is not false |
| assertNull(actual) | Fails when actual is not null |
| assertNotNull(actual) | Fails when actual is null |
| assertAll() | Group many assertions and every assertion is executed even if one or more of them fails |
| assertTrue(expression) | Fails if expression is not true |
| assertThrows() | Class to be tested is expected to throw an exception |
@Test
void testAssertEqual() {
assertEquals("ABC", "ABC");
assertEquals(20, 20, "optional assertion message");
assertEquals(2 + 2, 4);
}
@Test
void testAssertFalse() {
assertFalse("FirstName".length() == 10);
assertFalse(10 > 20, "assertion message");
}
@Test
void testAssertNull() {
String str1 = null;
String str2 = "abc";
assertNull(str1);
assertNotNull(str2);
}
@Test
void testAssertAll() {
String str1 = "abc";
String str2 = "pqr";
String str3 = "xyz";
assertAll("numbers",
() -> assertEquals(str1,"abc"),
() -> assertEquals(str2,"pqr"),
() -> assertEquals(str3,"xyz")
);
//取消下面的代码注释并了解每个断言的执行
/*assertAll("numbers",
() -> assertEquals(str1,"abc"),
() -> assertEquals(str2,"pqr1"),
() -> assertEquals(str3,"xyz1")
);*/
}
@Test
void testAssertTrue() {
assertTrue("FirstName".startsWith("F"));
assertTrue(10 {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Argument Exception occured");
});
assertEquals("Illegal Argument Exception occured", exception.getMessage());
}
JUnit5导入
其测试类需要org.junit.jupiter.api.Test导入语句,而不是org.junit.Test。此外,测试方法不需要是公共的,也不需要是本地包。
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
JUnit5 Assumptions
假设是org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions类中的静态方法。它们仅在满足指定条件时执行测试,否则测试将被中止。中止的测试不会导致构建失败。当假设失败时,将抛出org.opentest4j.TestAbortedException,并跳过测试。
| Assumptions | Description |
|---|---|
| assumeTrue | Execute the body of lamda when the positive condition hold else test will be skipped |
| assumeFalse | Execute the body of lamda when the negative condition hold else test will be skipped |
| assumingThat | Portion of the test method will execute if an assumption holds true and everything after the lambda will execute irrespective of the assumption in assumingThat() holds |
@Test
void testAssumeTrue() {
boolean b = 'A' == 'A';
assumeTrue(b);
assertEquals("Hello", "Hello");
}
@Test
@DisplayName("test executes only on Saturday")
public void testAssumeTrueSaturday() {
LocalDateTime dt = LocalDateTime.now();
assumeTrue(dt.getDayOfWeek().getValue() == 6);
System.out.println("further code will execute only if above assumption holds true");
}
@Test
void testAssumeFalse() {
boolean b = 'A' != 'A';
assumeFalse(b);
assertEquals("Hello", "Hello");
}
@Test
void testAssumeFalseEnvProp() {
System.setProperty("env", "prod");
assumeFalse("dev".equals(System.getProperty("env")));
System.out.println("further code will execute only if above assumption hold");
}
@Test
void testAssumingThat() {
System.setProperty("env", "test");
assumingThat("test".equals(System.getProperty("env")),
() -> {
assertEquals(10, 10);
System.out.println("perform below assertions only on the test env");
});
assertEquals(20, 20);
System.out.println("perform below assertions on all env");
}
JUnit嵌套测试类
嵌套测试允许创建嵌套类并执行其所有测试方法。内部类必须是非静态的。只需使用@Nested注解内部类,其中的所有测试方法都将被执行。
@BeforeAll
static void beforeAll() {
System.out.println("**--- JUnit5Sample4Test :: beforeAll :: Executed once before all test methods ---**");
}
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
System.out.println("**--- JUnit5Sample4Test :: beforeEach :: Executed before each test method ---**");
}
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
System.out.println("**--- JUnit5Sample4Test :: afterEach :: Executed after each test method ---**");
}
@AfterAll
static void afterAll() {
System.out.println("**--- JUnit5Sample4Test :: afterAll :: Executed after all test method ---**");
}
@Nested
class InnerClass {
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
System.out.println("**--- InnerClass :: beforeEach :: Executed before each test method ---**");
}
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
System.out.println("**--- InnerClass :: afterEach :: Executed after each test method ---**");
}
@Test
void testMethod1() {
System.out.println("**--- InnerClass :: testMethod1 :: Executed test method1 ---**");
}
@Nested
class InnerMostClass {
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
System.out.println("**--- InnerMostClass :: beforeEach :: Executed before each test method ---**");
}
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
System.out.println("**--- InnerMostClass :: afterEach :: Executed after each test method ---**");
}
@Test
void testMethod2() {
System.out.println("**--- InnerMostClass :: testMethod2 :: Executed test method2 ---**");
}
}
}
JUnit测试异常
在某些情况下,方法在特定条件下应该抛出异常。如果给定方法没有抛出指定的异常,assertThrows将使测试失败。
Throwable exception = assertThrows(IllegalArgumentException.class, () -> {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Argument Exception occured");
});
assertEquals("Illegal Argument Exception occured", exception.getMessage());
JUnit测试执行
单元测试可以以多种方式执行,以下是两种方式:
- 使用Eclipse IDE Oxygen.3a (4.7.3a)版本,打开要执行的测试文件。右键单击文件,选择“运行为”,然后选择JUnit测试。
- 在Windows命令提示符上使用mvn test命令
摘要
我们已经探讨了JUnit5及其新特性,并提供了一些示例。我们还了解了如何使用JUnit注解、断言、假设、异常以及编写嵌套测试类。
您可以从我们的GitHub存储库下载完整的示例项目。
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/junit5-tutorial













