 Java队列是在java.util包中提供的一个接口,它扩展了java.util.Collection接口。就像Java列表一样,Java队列是一个有序元素(或对象)的集合,但它执行插入和删除操作的方式不同。我们可以使用队列在处理这些元素之前存储它们。
Java队列是在java.util包中提供的一个接口,它扩展了java.util.Collection接口。就像Java列表一样,Java队列是一个有序元素(或对象)的集合,但它执行插入和删除操作的方式不同。我们可以使用队列在处理这些元素之前存储它们。
Java队列
在本节中,我们将讨论关于Java队列的一些重要点:
- java.util.Queue接口是java.util.Collection接口的子类型。
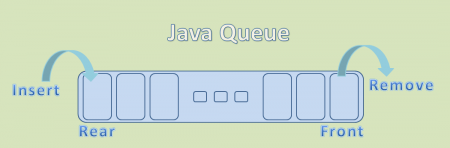
- 就像现实生活中的队列(例如,在银行或ATM中),队列将元素插入队列的末尾并从队列的开头删除。
- Java队列表示一个有序的元素列表。
- Java队列遵循FIFO顺序插入和删除其元素。FIFO代表先进先出。
- Java队列支持Collection接口的所有方法。
- 最常用的队列实现是LinkedList、ArrayBlockingQueue和PriorityQueue。
- BlockingQueues不接受null元素。如果执行任何与null相关的操作,它会抛出NullPointerException。
- BlockingQueues用于实现基于生产者/消费者的应用程序。
- BlockingQueues是线程安全的。
- 所有在java.util包中可用的队列都是无界队列,而在java.util.concurrent包中可用的队列是有界队列。
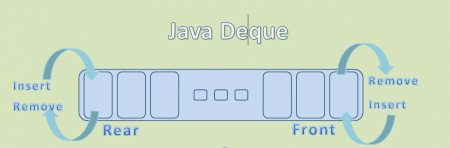
- 所有双端队列都不是线程安全的。
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue是基于链接节点的无界线程安全队列。
- 所有队列都支持在队列尾部插入和在队列头部移除,除了双端队列。
- 双端队列是队列,但它们支持在两端插入和移除元素。
Java队列类图
Java Queue接口扩展了Collection接口。Collection接口扩展了Iterable接口。一些常用的队列实现类包括LinkedList,PriorityQueue,ArrayBlockingQueue,DelayQueue,LinkedBlockingQueue,PriorityBlockingQueue等。AbstractQueue提供了Queue接口的骨架实现,以减少实现Queue的工作量。
Java队列方法
在本节中,我们将讨论一些有用且经常使用的Java队列方法:
- int size(): 获取集合中元素的数量。
- boolean isEmpty(): 检查集合是否为空。
- boolean contains(Object o): 如果此集合包含指定的元素,则返回 true。
- Iterator iterator(): 返回该集合中元素的迭代器。元素以无特定顺序返回。
- boolean removeAll(Collection c): 从该集合中移除包含在指定集合中的所有元素(可选操作)。
- boolean retainAll(Collection c): 仅保留在该集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。
- void clear(): 从集合中移除所有元素。
- E remove(): Retrieves and removes the head of this queue.
- E poll(): Retrieves and removes the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty.
- E peek(): Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty.
- boolean offer(E e): 如果可以在不违反容量限制的情况下立即将指定元素插入此队列,则插入并返回 true。
- E element(): Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue.
- boolean add(E e): 如果可以在不违反容量限制的情况下立即将指定元素插入此队列,则插入并在成功时返回 true;如果当前没有可用空间,则抛出 IllegalStateException。
- Object[] toArray(): 返回包含此集合中所有元素的数组。如果此集合对其迭代器返回的元素顺序有任何保证,该方法必须以相同顺序返回元素。
Java 队列基础
由于Java队列扩展了Java集合,因此它也支持所有集合接口操作。让我们在下面的示例中探索一些简单的操作:
package com.journaldev.queue;
import java.util.*;
public class QueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add("one");
queue.add("two");
queue.add("three");
queue.add("four");
System.out.println(queue);
queue.remove("three");
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println("Queue Size: " + queue.size());
System.out.println("Queue Contains element 'two' or not? : " + queue.contains("two"));
// 清空队列
queue.clear();
}
}
输出:-
[one, two, three, four]
[one, two, four]
Queue Size: 3
Queue Contains element 'two' or not? : true
Java数组转换为队列
在这里,我们可以通过一个简单的示例来探索如何使用“Collections.addAll()”方法将Java数组转换为队列。
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayToQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String nums[] = {"one","two","three","four","five"};
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Collections.addAll(queue, nums);
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
输出:-当我们运行上述程序时,我们将获得以下输出:
[one, two, three, four, five]
Java队列转换为数组
在这里,我们将通过一个简单的示例来探索如何使用“toArray()”将Java队列转换为Java数组。
import java.util.*;
public class QueueToArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add("one");
queue.add("two");
queue.add("three");
queue.add("four");
queue.add("five");
String strArray[] = queue.toArray(new String[queue.size()]);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strArray));
}
}
输出:-当我们运行上述程序时,我们将获得以下输出:
[one, two, three, four, five]
Java队列常见操作
Java队列支持集合接口支持的所有操作以及一些额外的操作。它以两种形式支持几乎所有操作。
- 一组操作在操作失败时抛出异常。
- 另一组操作在操作失败时返回特殊值。
以下表格简要解释了所有队列的常见操作。
| Operation | Throws exception | Special value |
|---|---|---|
| Insert | add(e) | offer(e) |
| Remove | remove() | poll() |
| Examine | element() | peek() |
我们将逐个讨论每个操作,并在接下来的部分中详细讨论它们,附带一些有用的示例。
Java队列插入操作
在本节中,我们将详细讨论Java队列插入操作,并附带一些有用的示例。如果此操作执行成功,它将返回“true”值。正如我们所知,队列支持两种形式的插入操作:
- Queue.add(e):
如果操作失败,它会抛出异常。- Queue.offer(e):
如果操作失败,它将返回一个特殊值。
注意: 这里的特殊值可以是“false”或“null”
队列add()操作
add()操作用于将新元素插入队列。如果成功执行插入操作,它将返回“true”值。否则,它会抛出java.lang.IllegalStateException。让我们开发一个简单的示例来演示此功能。
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class QueueAddOperation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2);
System.out.println(queue.add("one"));
System.out.println(queue.add("two"));
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println(queue.add("three"));
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
当我们运行以上程序时,我们将得到以下输出:
true
true
[one, two]
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full
由于我们的队列限制为两个元素,当我们尝试使用BlockingQueue.add()添加第三个元素时,它会抛出异常,如上所示。
队列offer()操作
offer()操作用于向队列插入新元素。如果成功执行插入操作,则返回“true”值。否则返回“false”值。让我们开发一个简单的示例来演示这个功能。
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class QueueOfferOperation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2);
System.out.println(queue.offer("one"));
System.out.println(queue.offer("two"));
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println(queue.offer("three"));
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
输出:当我们运行以上程序时,我们将得到以下输出:
true
true
[one, two]
false
[one, two]
由于我们的队列限制为两个元素,当我们尝试使用BlockingQueue.offer()操作添加第三个元素时,它会返回“false”值,如上所示。
Java队列删除操作
在本节中,我们将详细讨论Java队列删除操作,并提供一些有用的示例。如果删除操作成功执行,则返回队列的头元素。正如我们所知,队列支持两种形式的删除操作:
- Queue.remove():如果操作失败,则抛出异常。- Queue.poll():如果操作失败,则返回一个特殊值。
注意:- 这里特殊值可以是“false”或“null”
队列 remove() 操作
remove() 操作用于从队列头部删除一个元素。如果成功执行删除操作,它将返回队列的头元素。否则,它会抛出 java.util.NoSuchElementException 异常。让我们开发一个简单的示例来演示这个功能。
import java.util.*;
public class QueueRemoveOperation
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer("one");
queue.offer("two");
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println(queue.remove());
System.out.println(queue.remove());
System.out.println(queue.remove());
}
}
输出:当我们运行上面的程序时,将得到以下输出:
[one, two]
one
two
Exception in thread "main" java.util.NoSuchElementException
由于我们的队列只有两个元素,当我们尝试第三次调用 remove() 方法时,它会抛出如上所示的异常。注意:- Queue.remove(element) 用于从队列中删除指定的元素。如果成功执行删除操作,它将返回“true”值。否则,它将返回“false”值。
队列 poll() 操作
poll() 操作用于从队列头部删除一个元素。如果成功执行删除操作,它将返回队列的头元素。否则,它将返回“null”值。让我们开发一个简单的示例来演示这个功能。
import java.util.*;
public class QueuePollOperation
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer("one");
queue.offer("two");
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}
}
输出:-当我们运行以上程序时,我们将得到以下输出:
[one, two]
one
two
null
由于我们的队列只有两个元素,当我们尝试第三次调用poll()方法时,它会返回null值,如上所示。
Java队列检查操作
在本节中,我们将详细讨论Java队列检查操作,并附带一些有用的示例。如果此操作成功执行,它将返回队列的头元素,而不将其移除。正如我们所知,队列支持两种形式的检查操作:
- Queue.element():
如果操作失败,它会抛出异常。- Queue.peek():
如果操作失败,它将返回一个特殊值。
注意:-这里的特殊值可以是“false”或“null”
队列element()操作
element()操作用于从队列头部检索元素,而不将其移除。如果成功执行检查操作,它将返回队列的头元素。否则,它会抛出java.util.NoSuchElementException异常。让我们开发一个简单的示例来演示这个功能。
import java.util.*;
public class QueueElementOperation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add("one");
System.out.println(queue.element());
System.out.println(queue);
queue.clear();
System.out.println(queue.element());
}
}
输出:-当我们运行以上程序时,我们将得到以下输出:
one
[one]
Exception in thread "main" java.util.NoSuchElementException
如果我们尝试在空队列上调用element()方法,它会抛出异常,如上所示。
队列 peek() 操作
peek() 操作用于从队列头部检索元素,但不移除它。如果成功执行检查操作,则返回队列头部的元素。否则返回 null 值。让我们开发一个简单的示例来演示这个功能。
import java.util.*;
public class QueuePeekOperation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add("one");
System.out.println(queue.peek());
System.out.println(queue);
queue.clear();
System.out.println(queue.peek());
}
}
输出:-当我们运行上述程序时,我们将得到以下输出:
one
[one]
null
如果我们尝试在空队列上调用peek()方法,它会返回null值,但不会像上面所示抛出异常。
Java队列分类
在Java中,我们可以找到许多队列实现。我们可以将它们大致分类为以下两种类型:
- 有界队列
- 无界队列
有界队列是在创建时通过容量限制的队列,这意味着我们需要提供队列的最大大小。例如,ArrayBlockingQueue(见前面的例子)。无界队列是没有容量限制的队列,这意味着我们不应该提供队列的大小。例如,LinkedList(见前面的例子)。java.util包中可用的所有队列都是无界队列,而java.util.concurrent包中可用的队列都是有界队列。换句话说,我们可以广泛将它们分为以下两种类型:
- 阻塞队列
- 非阻塞队列
所有实现BlockingQueue接口的队列都是阻塞队列,其余的是非阻塞队列。阻塞队列会阻塞,直到完成任务或超时,而非阻塞队列则不会。一些队列是双端队列,而一些队列是优先队列。
阻塞队列操作
除了队列的两种操作形式外,阻塞队列还支持下面显示的两种形式的操作。
| Operation | Throws exception | Special value | Blocks | Times out |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insert | add(e) | offer(e) | put(e) | offer(e, time, unit) |
| Remove | remove() | poll() | take() | poll(time, unit) |
| Examine | element() | peek() | N/A | N/A |
一些操作会阻塞,直到完成任务,而另一些操作会阻塞,直到超时。这就是关于Java中队列的一个快速概述。希望这些Java队列示例能帮助你开始使用队列集合编程。如果你喜欢我的教程或有任何建议、问题或打字错误,请给我留言。谢谢。
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/java-queue













