欢迎来到Hibernate二级缓存示例教程。今天我们将深入了解Hibernate EHCache,这是最流行的Hibernate二级缓存提供商。
Hibernate二级缓存
 在大型应用程序中使用Hibernate的主要好处之一是它对缓存的支持,从而减少数据库查询并提高性能。在先前的示例中,我们研究了Hibernate一级缓存,今天我们将使用Hibernate EHCache实现来研究Hibernate二级缓存。Hibernate二级缓存提供程序包括EHCache和Infinispan,但EHCache更受欢迎,我们将在示例项目中使用它。然而,在我们转向项目之前,我们应该了解缓存对象的不同策略。
在大型应用程序中使用Hibernate的主要好处之一是它对缓存的支持,从而减少数据库查询并提高性能。在先前的示例中,我们研究了Hibernate一级缓存,今天我们将使用Hibernate EHCache实现来研究Hibernate二级缓存。Hibernate二级缓存提供程序包括EHCache和Infinispan,但EHCache更受欢迎,我们将在示例项目中使用它。然而,在我们转向项目之前,我们应该了解缓存对象的不同策略。
- 只读:应该对始终读取但永远不更新的持久化对象使用此缓存策略。适用于读取和缓存应用程序配置以及永远不会更新的其他静态数据。这是性能最佳的最简单策略,因为不需要检查对象在数据库中是否已更新。
- 读写:这对于可以由Hibernate应用程序更新的持久对象来说是很好的。但是,如果数据通过后端或其他应用程序进行更新,则Hibernate将无法知道,数据可能会变得过时。因此,在使用此策略时,请确保您正在使用Hibernate API来更新数据。
- 非受限读写:如果应用程序只偶尔需要更新数据,并且不需要严格的事务隔离,则非严格读写缓存可能是合适的。
- 事务性:事务性缓存策略提供了对完全事务性缓存提供程序(如JBoss TreeCache)的支持。这样的缓存只能在JTA环境中使用,您必须指定hibernate.transaction.manager_lookup_class。
Hibernate EHCache
由于EHCache支持以上所有缓存策略,所以当您在Hibernate中寻找二级缓存时,它是最佳选择。我不会详细介绍EHCache,我的主要重点将是使其适用于Hibernate应用程序。在Eclipse或您喜爱的IDE中创建一个Maven项目,最终实现将如下图所示。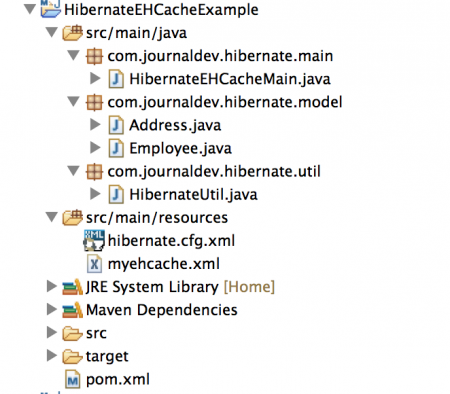 让我们逐个查看应用程序的每个组件。
让我们逐个查看应用程序的每个组件。
Hibernate EHCache Maven 依赖
对于 Hibernate 的二级缓存,我们需要在应用程序中添加 ehcache-core 和 hibernate-ehcache 依赖项。EHCache 使用 slf4j 进行日志记录,因此我还添加了 slf4j-simple 用于日志记录。我正在使用所有这些 API 的最新版本,有一点点可能是 hibernate-ehcache API 与 ehcache-core API 不兼容,如果出现这种情况,您需要检查 hibernate-ehcache 的 pom.xml 以找出正确的版本。我们最终的 pom.xml 如下所示。
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.journaldev.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>HibernateEHCacheExample</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<description>Hibernate Secondary Level Cache Example using EHCache implementation</description>
<dependencies>
<!-- Hibernate Core API -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>4.3.5.Final</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL Driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- EHCache Core APIs -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache-core</artifactId>
<version>2.6.9</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Hibernate EHCache API -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>4.3.5.Final</version>
</dependency>
<!-- EHCache uses slf4j for logging -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId>
<version>1.7.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Hibernate 二级缓存 – Hibernate EHCache 配置
默认情况下,Hibernate 的二级缓存是禁用的,因此我们需要启用它并添加一些配置来使其工作。我们的 hibernate.cfg.xml 文件如下所示。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration SYSTEM "classpath://org/hibernate/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">pankaj123</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/TestDB</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">pankaj</property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.current_session_context_class">thread</property>
<property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory</property>
<!-- For singleton factory -->
<!-- <property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.SingletonEhCacheRegionFactory</property>
-->
<!-- enable second level cache and query cache -->
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</property>
<property name="net.sf.ehcache.configurationResourceName">/myehcache.xml</property>
<mapping class="com.journaldev.hibernate.model.Employee" />
<mapping class="com.journaldev.hibernate.model.Address" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
关于 Hibernate 二级缓存配置的一些重要点是:
- hibernate.cache.region.factory_class 用于定义二级缓存的工厂类,我正在使用
org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory。如果要使工厂类为单例,应该使用org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.SingletonEhCacheRegionFactory类。如果你使用的是 Hibernate 3,对应的类将是net.sf.ehcache.hibernate.EhCacheRegionFactory和net.sf.ehcache.hibernate.SingletonEhCacheRegionFactory。 - hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache 用于启用二级缓存。
- hibernate.cache.use_query_cache 用于启用查询缓存,如果没有启用,HQL 查询结果将不会被缓存。
- net.sf.ehcache.configurationResourceName 用于定义 EHCache 配置文件的位置,这是一个可选参数,如果不存在,则 EHCache 将尝试在应用程序类路径中定位 ehcache.xml 文件。
Hibernate EHCache 配置文件
我们的 EHCache 配置文件 myehcache.xml 如下所示。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="ehcache.xsd" updateCheck="true"
monitoring="autodetect" dynamicConfig="true">
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir/ehcache" />
<defaultCache maxEntriesLocalHeap="10000" eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" diskSpoolBufferSizeMB="30"
maxEntriesLocalDisk="10000000" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU" statistics="true">
<persistence strategy="localTempSwap" />
</defaultCache>
<cache name="employee" maxEntriesLocalHeap="10000" eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="5" timeToLiveSeconds="10">
<persistence strategy="localTempSwap" />
</cache>
<cache name="org.hibernate.cache.internal.StandardQueryCache"
maxEntriesLocalHeap="5" eternal="false" timeToLiveSeconds="120">
<persistence strategy="localTempSwap" />
</cache>
<cache name="org.hibernate.cache.spi.UpdateTimestampsCache"
maxEntriesLocalHeap="5000" eternal="true">
<persistence strategy="localTempSwap" />
</cache>
</ehcache>
Hibernate EHCache 提供了许多选项,我不会详细介绍,但上面的一些重要配置是:
- diskStore:EHCache 将数据存储在内存中,但当内存溢出时,它开始将数据写入文件系统。我们使用此属性来定义 EHCache 将写入溢出数据的位置。
- defaultCache:这是一个强制性配置,当对象需要被缓存但没有为其定义缓存区域时使用。
- cache name=“employee”:我们使用缓存元素来定义区域及其配置。我们可以定义多个区域及其属性,同时在定义模型 bean 缓存属性时,我们也可以定义带有缓存策略的区域。缓存属性易于理解,名称清晰。
- 由于 EHCache 发出警告,缓存区域
org.hibernate.cache.internal.StandardQueryCache和org.hibernate.cache.spi.UpdateTimestampsCache被定义。
Hibernate 二级缓存 – 模型 Bean 缓存策略
我们使用org.hibernate.annotations.Cache注解来提供缓存配置。org.hibernate.annotations.CacheConcurrencyStrategy用于定义缓存策略,我们还可以定义用于模型 bean 的缓存区域。
package com.journaldev.hibernate.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import javax.persistence.PrimaryKeyJoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Cache;
import org.hibernate.annotations.CacheConcurrencyStrategy;
import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Parameter;
@Entity
@Table(name = "ADDRESS")
@Cache(usage=CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_ONLY, region="employee")
public class Address {
@Id
@Column(name = "emp_id", unique = true, nullable = false)
@GeneratedValue(generator = "gen")
@GenericGenerator(name = "gen", strategy = "foreign",
parameters = { @Parameter(name = "property", value = "employee") })
private long id;
@Column(name = "address_line1")
private String addressLine1;
@Column(name = "zipcode")
private String zipcode;
@Column(name = "city")
private String city;
@OneToOne
@PrimaryKeyJoinColumn
private Employee employee;
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getAddressLine1() {
return addressLine1;
}
public void setAddressLine1(String addressLine1) {
this.addressLine1 = addressLine1;
}
public String getZipcode() {
return zipcode;
}
public void setZipcode(String zipcode) {
this.zipcode = zipcode;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public Employee getEmployee() {
return employee;
}
public void setEmployee(Employee employee) {
this.employee = employee;
}
}
package com.journaldev.hibernate.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Cache;
import org.hibernate.annotations.CacheConcurrencyStrategy;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Cascade;
@Entity
@Table(name = "EMPLOYEE")
@Cache(usage=CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_ONLY, region="employee")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "emp_id")
private long id;
@Column(name = "emp_name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "emp_salary")
private double salary;
@OneToOne(mappedBy = "employee")
@Cascade(value = org.hibernate.annotations.CascadeType.ALL)
private Address address;
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
请注意,我正在使用与 HQL示例中相同的数据库设置,请您检查一下以创建数据库表并加载示例数据。
Hibernate SessionFactory实用程序类
我们有一个简单的实用程序类来配置Hibernate并获取 SessionFactory 单例实例。
package com.journaldev.hibernate.util;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
public class HibernateUtil {
private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
private static SessionFactory buildSessionFactory() {
try {
// 从hibernate.cfg.xml创建SessionFactory
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml");
System.out.println("Hibernate Configuration loaded");
ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry = new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(configuration.getProperties()).build();
System.out.println("Hibernate serviceRegistry created");
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
return sessionFactory;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
System.err.println("Initial SessionFactory creation failed." + ex);
ex.printStackTrace();
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
}
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
if(sessionFactory == null) sessionFactory = buildSessionFactory();
return sessionFactory;
}
}
我们的Hibernate二级缓存项目使用Hibernate EHCache已经准备就绪,让我们编写一个简单的程序来测试它。
Hibernate EHCache测试程序
package com.journaldev.hibernate.main;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.stat.Statistics;
import com.journaldev.hibernate.model.Employee;
import com.journaldev.hibernate.util.HibernateUtil;
public class HibernateEHCacheMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Temp Dir:"+System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir"));
// 初始化会话
SessionFactory sessionFactory = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
Statistics stats = sessionFactory.getStatistics();
System.out.println("Stats enabled="+stats.isStatisticsEnabled());
stats.setStatisticsEnabled(true);
System.out.println("Stats enabled="+stats.isStatisticsEnabled());
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Session otherSession = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Transaction otherTransaction = otherSession.beginTransaction();
printStats(stats, 0);
Employee emp = (Employee) session.load(Employee.class, 1L);
printData(emp, stats, 1);
emp = (Employee) session.load(Employee.class, 1L);
printData(emp, stats, 2);
// 清除一级缓存,以便使用二级缓存
session.evict(emp);
emp = (Employee) session.load(Employee.class, 1L);
printData(emp, stats, 3);
emp = (Employee) session.load(Employee.class, 3L);
printData(emp, stats, 4);
emp = (Employee) otherSession.load(Employee.class, 1L);
printData(emp, stats, 5);
// 释放资源
transaction.commit();
otherTransaction.commit();
sessionFactory.close();
}
private static void printStats(Statistics stats, int i) {
System.out.println("***** " + i + " *****");
System.out.println("Fetch Count="
+ stats.getEntityFetchCount());
System.out.println("Second Level Hit Count="
+ stats.getSecondLevelCacheHitCount());
System.out
.println("Second Level Miss Count="
+ stats
.getSecondLevelCacheMissCount());
System.out.println("Second Level Put Count="
+ stats.getSecondLevelCachePutCount());
}
private static void printData(Employee emp, Statistics stats, int count) {
System.out.println(count+":: Name="+emp.getName()+", Zipcode="+emp.getAddress().getZipcode());
printStats(stats, count);
}
}
`org.hibernate.stat.Statistics`提供了Hibernate SessionFactory的统计信息,我们正在使用它来打印获取计数和二级缓存的命中、未命中和放置计数。统计信息默认处于禁用状态以获得更好的性能,这就是为什么我在程序开始时启用它的原因。当我们运行上述程序时,会生成大量由Hibernate和EHCache API生成的输出,但我们只对我们正在打印的数据感兴趣。样本运行打印以下输出。
Temp Dir:/var/folders/h4/q73jjy0902g51wkw0w69c0600000gn/T/
Hibernate Configuration loaded
Hibernate serviceRegistry created
Stats enabled=false
Stats enabled=true
***** 0 *****
Fetch Count=0
Second Level Hit Count=0
Second Level Miss Count=0
Second Level Put Count=0
Hibernate: select employee0_.emp_id as emp_id1_1_0_, employee0_.emp_name as emp_name2_1_0_, employee0_.emp_salary as emp_sala3_1_0_, address1_.emp_id as emp_id1_0_1_, address1_.address_line1 as address_2_0_1_, address1_.city as city3_0_1_, address1_.zipcode as zipcode4_0_1_ from EMPLOYEE employee0_ left outer join ADDRESS address1_ on employee0_.emp_id=address1_.emp_id where employee0_.emp_id=?
1:: Name=Pankaj, Zipcode=95129
***** 1 *****
Fetch Count=1
Second Level Hit Count=0
Second Level Miss Count=1
Second Level Put Count=2
2:: Name=Pankaj, Zipcode=95129
***** 2 *****
Fetch Count=1
Second Level Hit Count=0
Second Level Miss Count=1
Second Level Put Count=2
3:: Name=Pankaj, Zipcode=95129
***** 3 *****
Fetch Count=1
Second Level Hit Count=2
Second Level Miss Count=1
Second Level Put Count=2
Hibernate: select employee0_.emp_id as emp_id1_1_0_, employee0_.emp_name as emp_name2_1_0_, employee0_.emp_salary as emp_sala3_1_0_, address1_.emp_id as emp_id1_0_1_, address1_.address_line1 as address_2_0_1_, address1_.city as city3_0_1_, address1_.zipcode as zipcode4_0_1_ from EMPLOYEE employee0_ left outer join ADDRESS address1_ on employee0_.emp_id=address1_.emp_id where employee0_.emp_id=?
4:: Name=Lisa, Zipcode=560100
***** 4 *****
Fetch Count=2
Second Level Hit Count=2
Second Level Miss Count=2
Second Level Put Count=4
5:: Name=Pankaj, Zipcode=95129
***** 5 *****
Fetch Count=2
Second Level Hit Count=4
Second Level Miss Count=2
Second Level Put Count=4
从输出中可以看出,统计信息首先被禁用,但我们启用它来检查我们的Hibernate二级缓存。输出的逐步解释如下:
- 在我们的应用程序中加载任何数据之前,所有统计信息都为0,这是预期的。
- 当我们第一次加载id=1的Employee时,它首先被搜索到一级缓存中,然后再到二级缓存中。如果在缓存中找不到,则执行数据库查询,因此获取计数变为1。一旦对象加载完成,它就会被保存到一级缓存和二级缓存中。因此,二级命中计数保持为0,未命中计数变为1。请注意,放置计数为2,这是因为Employee对象还包含Address,因此两个对象都保存到二级缓存中,并且计数增加到2。
- 接下来,我们再次加载id=1的员工,这次它存在于一级缓存中。因此,您不会看到任何数据库查询,所有其他二级缓存统计信息也保持不变。
- 下一步,我们使用
evict()方法从一级缓存中移除员工对象,现在当我们尝试加载它时,Hibernate在二级缓存中找到它。这就是为什么没有执行数据库查询,获取计数保持为1的原因。请注意,命中计数从0增加到2,因为员工和地址对象都是从二级缓存中读取的。二级缓存的未命中和放入计数保持在之前的值。 - 接下来,我们加载一个ID为3的员工,执行数据库查询,获取计数增加到2,未命中计数从1增加到2,放入计数从2增加到4。
- 接下来,我们尝试在另一个会话中加载ID为1的员工,由于Hibernate二级缓存在会话之间共享,它在二级缓存中被找到,不会执行数据库查询。获取计数、未命中计数和放入计数保持不变,而命中计数从2增加到4。
因此,很明显我们的Hibernate二级缓存;Hibernate EHCache;运行良好。Hibernate统计信息对于找到系统中的瓶颈并进行优化以减少获取计数并从缓存中加载更多数据非常有帮助。关于Hibernate EHCache示例就介绍到这里,希望它能帮助您在Hibernate应用程序中配置EHCache并通过Hibernate二级缓存获得更好的性能。您可以从下面的链接下载示例项目并使用其他统计数据进行更多学习。
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/hibernate-ehcache-hibernate-second-level-cache













