日期命令是一个外部的 bash 程序,允许设置或显示系统日期和时间。它还提供了几种格式选项。日期命令在所有 Linux 发行版中默认安装。
$ which date $ type -a date
在终端中键入日期命令,将显示当前日期和时间。
$ date
更改 Linux 系统日期和时间
使用日期命令,可以修改系统日期、时间和时区,并且更改必须与硬件时钟同步。
$ date --set="Thu Nov 12 13:06:59 IST 2020" $ hwclock --systohc
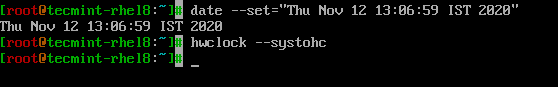
格式化选项
A good place to get the list of formatting options will be the man page.
$ man date
让我们看看我们将使用的一些最常见的格式化选项。
日期命令的两个重要部分是使用格式 +% 和 -date 选项。
现在让我们对date命令应用一些格式。要应用格式,请添加加号(+),然后跟随%formatter,如示例所示。
在Linux中处理日期
让我们看看如何在一个称为’date.sh‘的简单shell脚本中使用与日期相关的格式化程序。
# PRINT YEAR,MONTH,DAY AND DATE... echo "We are in the year = $(date +%Y)" echo "We are in the year = $(date +%y)" # Difference between %Y and %y is %Y will print 4 digits while %y will print the last 2 digits of the year. echo "We are in the month = $(date +%m)" echo "We are in the month = $(date +%b)" echo "We are in the month = $(date +%B)" # Difference between %B and %b is, %B will print full month name while %b will print abbreviated month name. echo "Current Day of the month = $(date +%d)" echo "Current Day of the week = $(date +%A)" echo "Current Day of the week = $(date +%a)" # Difference between %A and %a is, %A will print full Weekday name while %a will print abbreviated weekday name. # Instead of formatting to get the date, we can use %D which will print the date as %m/%d/%y or %F which prints in %Y-%M-%d format. echo "Date using %D = $(date +%D)" echo "Date using %F = $(date +%F)"
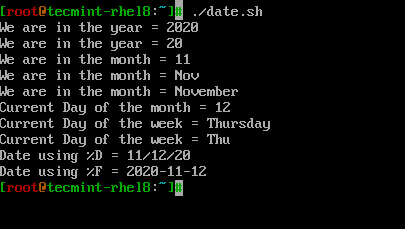
在Linux中处理时间
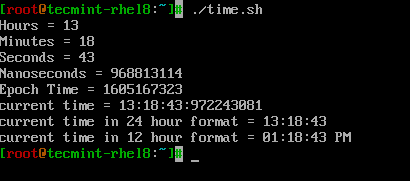
让我们看看如何在一个称为’time.sh‘的简单shell脚本中使用时间相关的格式化程序。
# PRINT HOURS, MINS, SECONDS, NANO SECONDS echo Hours = $(date +%H) echo Minutes = $(date +%M) echo Seconds = $(date +%S) echo Nanoseconds = $(date +%N) echo Epoch Time = $(date +%s) echo "current time = $(date +%H:%M:%S:%N)" # can also use %T which displays Time in HH:MM:SS format. echo "current time in 24 hour format = $(date +%T)" # can also use %r to display time in 12 hour format. echo "current time in 12 hour format = $(date +%r)"
使用–date或-d标志
使用--date或-d标志可以将输入作为字符串传递,date命令知道如何巧妙处理它。
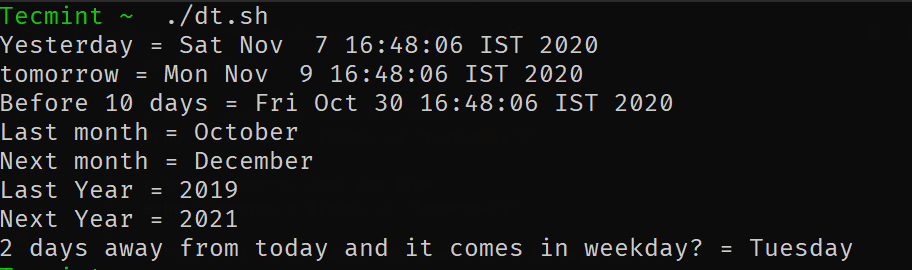
让我们看一些例子来理解它是如何工作的。
# Print yesterday's date and time. echo "Yesterday = $(date -d "Yesterday")" # Print Tomorrow date and time. echo "tomorrow = $(date -d "tomorrow")" # Find what is the date and time before 10 days from now. echo "Before 10 days = $(date -d "tomorrow -10 days")" # Find last month and next month echo "Last month = $(date -d "last month" "%B")" echo "Next month = $(date -d "next month" "%B")" # Find last year and next year echo "Last Year = $(date -d "last year" "+%Y")" echo "Next Year = $(date -d "next year" "+%Y")" # Forecast the weekday echo "2 days away from today and it comes on weekdays? = $(date -d "Today +2 days" "+%A")
常见操作
计算给定日期之间的天数。
$ echo $(( ( $(date -d "2020-11-10" "+%s") - $(date -d "2020-11-01" "+%s") ) / 86400))
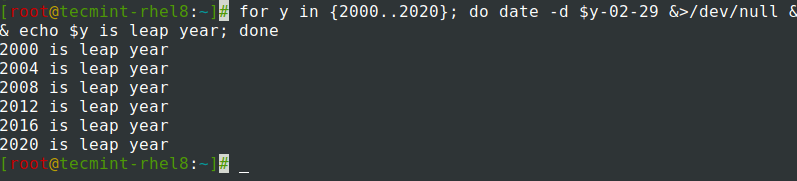
查找给定年份是否为闰年。
$ for y in {2000..2020}; do date -d $y-02-29 &>/dev/null && echo $y is leap year; done
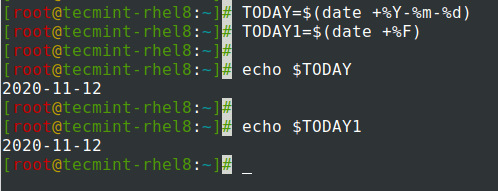
将date命令的输出分配给变量。
$ TODAY=$(date +%Y-%m-%d) OR $ TODAY1=$(date +%F) $ echo $TODAY $ echo $TODAY1
创建带有日期添加到文件名中的日志文件。
在创建日志文件、备份文件或文本文件时添加日期和时间是一个常见的操作,我们经常会遇到。让我们举个例子,为了备份,我们创建了一个shell脚本。
这个脚本将从00:00到23:59备份,并计划每天在第二天的00:00运行。我们想要使用昨天的日期格式创建日志文件。
CUSTOM_FORMAT=$(date --date "Yesterday" "+%d-%y-%H:%M")
LOG_FILE=/var/log/custom_application/application_${CUSTOM_FORMAT}.log
echo "Script started" >> ${LOG_FILE}
...
CODE BLOCKS
...
echo "Script completed" >> ${LOG_FILE}
这篇文章就到这里了。在本文中,我们已经看到了如何在Linux中使用bash日期和时间。欢迎留下您的反馈。
Source:
https://www.tecmint.com/change-linux-system-date-and-time/













