Abstraction is one of the core concepts of Object-Oriented Programming. Abstraction defines a model to create an application component. The implementation of abstraction depends on the language-specific features and processes.
1. What is Abstraction?
Abstraction is the process of hiding the internal details of an application from the outer world. Abstraction is used to describe things in simple terms. It’s used to create a boundary between the application and the client programs.
2. Abstraction in Real Life
Abstraction is present in almost all the real life machines.
- Your car is a great example of abstraction. You can start a car by turning the key or pressing the start button. You don’t need to know how the engine is getting started, what all components your car has. The car internal implementation and complex logic is completely hidden from the user.
- We can heat our food in Microwave. We press some buttons to set the timer and type of food. Finally, we get a hot and delicious meal. The microwave internal details are hidden from us. We have been given access to the functionality in a very simple manner.
3. Abstraction in OOPS
Objects are the building blocks of Object-Oriented Programming. An object contains some properties and methods. We can hide them from the outer world through access modifiers. We can provide access only for required functions and properties to the other programs. This is the general procedure to implement abstraction in OOPS.
4. What are the different types of abstraction?
There are two types of abstraction.
- Data Abstraction
- Process Abstraction
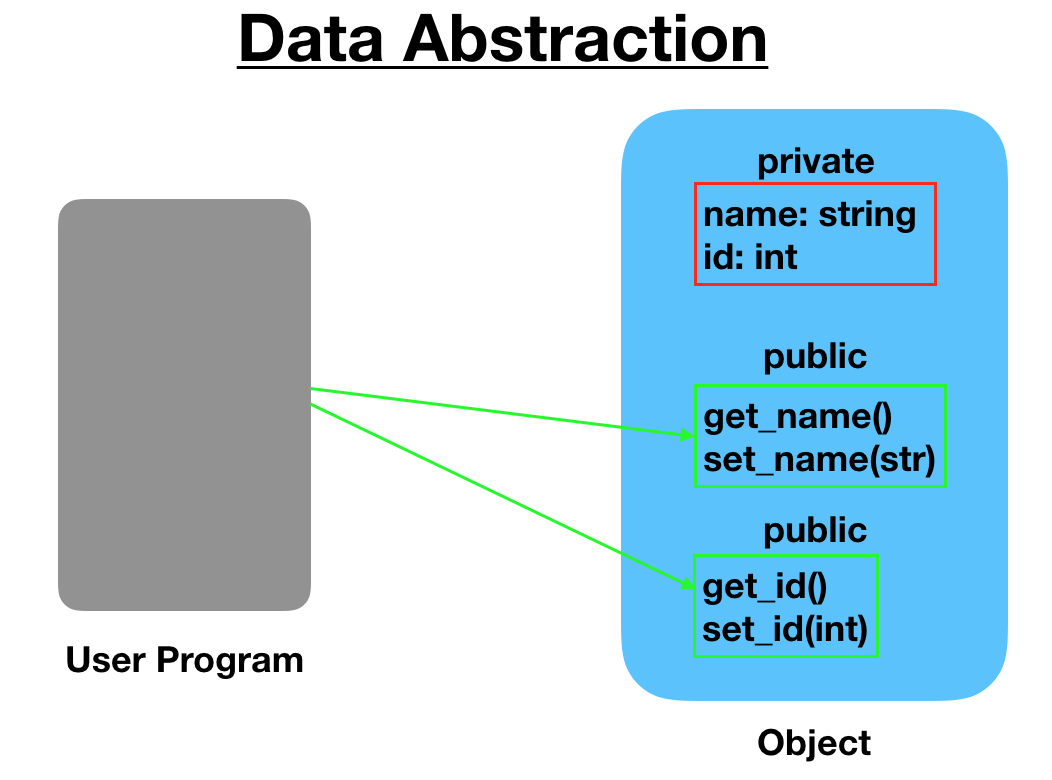
4.1) Data Abstraction
When the object data is not visible to the outer world, it creates data abstraction. If needed, access to the Objects’ data is provided through some methods.
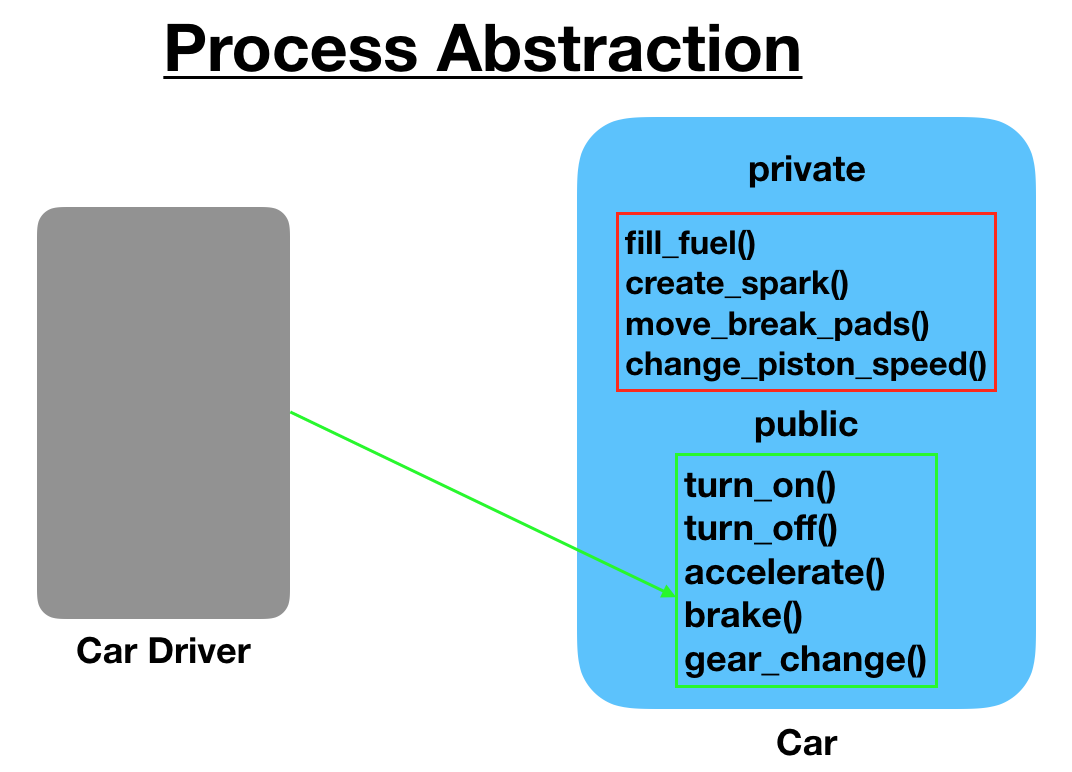
4.2) Process Abstraction
We don’t need to provide details about all the functions of an object. When we hide the internal implementation of the different functions involved in a user operation, it creates process abstraction.
5. Abstraction in Java
Abstraction in Java is implemented through interfaces and abstract classes. They are used to create a base implementation or contract for the actual implementation classes. Car.java: Base interface or abstract class
package com.journaldev.oops.abstraction;
public interface Car {
void turnOnCar();
void turnOffCar();
String getCarType();
}
ManualCar.java, AutomaticCar.java: implementation classes of Car.
package com.journaldev.oops.abstraction;
public class ManualCar implements Car {
private String carType = "Manual";
@Override
public void turnOnCar() {
System.out.println("turn on the manual car");
}
@Override
public void turnOffCar() {
System.out.println("turn off the manual car");
}
@Override
public String getCarType() {
return this.carType;
}
}
package com.journaldev.oops.abstraction;
public class AutomaticCar implements Car {
private String carType = "Automatic";
@Override
public void turnOnCar() {
System.out.println("turn on the automatic car");
}
@Override
public void turnOffCar() {
System.out.println("turn off the automatic car");
}
@Override
public String getCarType() {
return this.carType;
}
}
User Program: Let’s look at a test program where the Car functions will be used.
package com.journaldev.oops.abstraction;
public class CarTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car1 = new ManualCar();
Car car2 = new AutomaticCar();
car1.turnOnCar();
car1.turnOffCar();
System.out.println(car1.getCarType());
car2.turnOnCar();
car2.turnOffCar();
System.out.println(car2.getCarType());
}
}
The client program only knows about the Car and the functions that the Car provides. The internal implementation details are hidden from the client program. References: Wikipedia, Oracle Docs
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/what-is-abstraction-in-oops













