Struts2 is een van de beroemde frameworks voor het ontwikkelen van webapplicaties in Java. Onlangs heb ik veel Struts2 tutorials geschreven en in deze post, som ik enkele belangrijke Struts2 sollicitatievragen met antwoorden op om je te helpen bij het solliciteren.
Struts2 Sollicitatievragen

- Wat is Struts2?
- Wat zijn de verschillen tussen Struts1 en Struts2 of hoe is Struts2 beter dan Struts1?
- Wat zijn de kerncomponenten van Struts2?
- Wat is een interceptor in Struts2?
- Welk ontwerppatroon wordt geïmplementeerd door interceptors in Struts2?
- Op welke verschillende manieren kun je actieklassen maken in Struts2?
- Zijn Struts2 acties en interceptors threadsafe?
- Welke klasse is de Front Controller in Struts2?
- Wat zijn de voordelen van interceptors in Struts2?
- Wat is ValueStack en OGNL?
- Noem enkele nuttige annotaties geïntroduceerd in Struts2?
- Geef enkele belangrijke Struts2-constanten die je hebt gebruikt?
- Wat is het gebruik van namespace in actie-mapping in Struts2?
- Welke interceptor is verantwoordelijk voor het koppelen van verzoekparameters aan eigenschappen van actieklasse Java Bean?
- Welke interceptor is verantwoordelijk voor i18n-ondersteuning?
- Wat is het verschil tussen het gebruik van de Action-interface en de ActionSupport-klasse voor onze actieklassen, welke zou je verkiezen?
- Hoe kunnen we Servlet API Request, Response, HttpSession enz. Objecten krijgen in actieklassen?
- Wat is het gebruik van execAndWait-interceptor?
- Wat is het gebruik van de token-interceptor in Struts2?
- Hoe kunnen we log4j integreren in een Struts2-toepassing?
- Wat zijn de verschillende Struts2-tags? Hoe kunnen we ze gebruiken?
- Wat is een aangepaste typeconverteerder in Struts2?
- Hoe kunnen we onze eigen interceptor schrijven en deze koppelen aan een actie?
- Wat is de levenscyclus van een interceptor?
- Wat is een interceptor-stack?
- Wat is het struts-default-pakket en wat zijn de voordelen ervan?
- Wat is de standaard achtervoegsel voor Struts2 action URI en hoe kunnen we dit wijzigen?
- Wat is de standaardlocatie van resultaatpagina’s en hoe kunnen we dit wijzigen?
- Hoe kunnen we bestanden uploaden in een Struts2-toepassing?
- Wat zijn de best practices om te volgen bij het ontwikkelen van een Struts2-toepassing?
- Hoe kunnen we uitzonderingen afgehandelen die door de toepassing in Struts2 worden gegenereerd?
Struts2 Interviewvragen en antwoorden
-
Wat is Struts2?
Apache Struts2 is een open-sourceframework om webapplicaties te bouwen in Java. Struts2 is gebaseerd op het OpenSymphony WebWork-framework. Het is aanzienlijk verbeterd ten opzichte van Struts1, wat het flexibeler, eenvoudiger te gebruiken en uit te breiden maakt. De kerncomponenten van Struts2 zijn Actie, Interceptors en Result-pagina’s. Struts2 biedt vele manieren om Actieklassen te maken en deze te configureren via struts.xml of via annotaties. We kunnen onze eigen interceptors maken voor veelvoorkomende taken. Struts2 wordt geleverd met veel tags en maakt gebruik van de OGNL-expression language. We kunnen onze eigen type-converters maken om resultaatpagina’s weer te geven. Resultaatpagina’s kunnen JSP’s en FreeMarker-templates zijn.
-
Wat zijn de verschillen tussen Struts1 en Struts2 of hoe is Struts2 beter dan Struts1?
Struts2 is ontworpen om de tekortkomingen van Struts1 te overwinnen en het flexibeler en uitbreidbaar te maken. Enkele opmerkelijke verschillen zijn:
Componenten Struts1 Struts2 Actionklassen Struts1-actieklassen zijn verplicht om een abstracte klasse uit te breiden, wat het niet uitbreidbaar maakt. Struts2-actieklassen zijn flexibel en we kunnen ze maken door de Action-interface te implementeren, de ActionSupport-klasse uit te breiden of gewoon door een execute() methode te hebben. Draadsbeveiliging Struts1 Action-klassen zijn Singleton en niet thread-safe, wat extra zorg aan de kant van de ontwikkelaar vereist om eventuele neveneffecten als gevolg van multithreading te voorkomen. Struts2-actieklassen worden per verzoek geïnstantieerd, dus er is geen multithreading en maakt ze thread-safe. Servlet API-koppeling Struts1-API’s zijn sterk gekoppeld met Servlet API en de Request- en Response-objecten worden doorgegeven aan de execute()-methode van actieklassen. Struts2-API is losjes gekoppeld met Servlet API en koppelt automatisch de formuliergegevens aan de eigenschappen van de actieklasse java bean die we meestal gebruiken. Als we echter verwijzingen naar Servlet API-klassen nodig hebben, zijn er *Aware-interfaces voor dat. Testen Struts1-actieklassen zijn moeilijk te testen vanwege de koppeling met Servlet API. Struts2-actieklassen zijn als normale Java-klassen en we kunnen ze gemakkelijk testen door ze te instantiëren en hun eigenschappen in te stellen. Koppeling van verzoekparameters Struts1 vereist dat we ActionForm-klassen maken om verzoekparameters vast te houden en we moeten deze configureren in het struts-configuratiebestand. Struts2-verzoekparameters worden dynamisch gekoppeld en alles wat we nodig hebben, zijn Java Bean-eigenschappen in actieklassen of de ModelDriven-interface implementeren om de naam van de Java Bean-klasse op te geven die moet worden gebruikt voor mapping. Tagondersteuning Struts1 maakt gebruik van JSTL-tags en is dus beperkt. Struts2 maakt gebruik van OGNL en biedt verschillende soorten UI-, Control- en Datatags. Het is veelzijdiger en gemakkelijker te gebruiken. Validatie Struts1 ondersteunt validatie via de handmatige validate()-methode Struts2 ondersteunt zowel handmatige validatie als integratie met het validatiekader. Weergave van weergaven Struts1 maakt gebruik van standaard JSP-technologie om bean-waarden naar JSP-pagina’s voor weergaven te verstrekken. Struts2 gebruikt ValueStack om verzoekparameters en attributen op te slaan en we kunnen OGNL en Struts2-tags gebruiken om er toegang toe te krijgen. Ondersteuning voor modules Struts1-modules zijn complex om te ontwerpen en lijken op afzonderlijke projecten Struts2 biedt “namespace” -configuratie voor pakketten om eenvoudig modules te maken. -
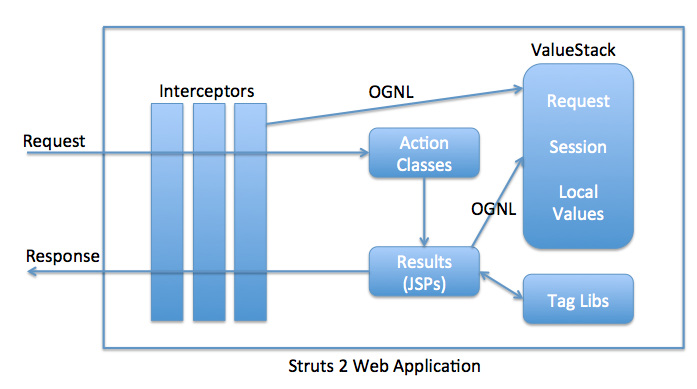
Wat zijn de kerncomponenten van Struts2?
De kerncomponenten van Struts2 zijn:
- Actionklassen
- Interceptors
- Resultaatpagina’s, JSP of FreeMarker-templates
- ValueStack, OGNL en Tag Libraries
-
Wat is een interceptor in Struts2?
Interceptors vormen het fundament van het Struts2-framework. Struts2-interceptors zijn verantwoordelijk voor het grootste deel van de verwerking die door het framework wordt uitgevoerd, zoals het doorgeven van request parameters aan actieklassen, het beschikbaar stellen van Servlet API-request, -response en -sessie aan actieklassen, validatie, i18n-ondersteuning, enz. ActionInvocation is verantwoordelijk voor het encapsuleren van actieklassen en interceptors en voor het afvuren ervan in volgorde. De belangrijkste methode voor gebruik in ActionInvocation is de invoke() methode die de interceptor-keten bijhoudt en de volgende interceptor of actie aanroept. Dit is een van de beste voorbeelden van het keten van verantwoordelijkheidspatroon in Java EE-frameworks.
-
Welk ontwerppatroon wordt geïmplementeerd door Struts2 interceptors?
Struts2 interceptors are based on intercepting filters design pattern. The invocation of interceptors in interceptor stack closely resembles Chain of Responsibility design pattern.
Struts2 provide different ways to create action classes.
1. By implementing Action interface
2. Using Struts2 @Action annotation
3. By extending ActionSupport class
4. Any normal java class with execute() method returning String can be configured as Action class.
Struts2 Action classes are thread safe because an object is instantiated for every request to handle it. Struts2 interceptors are singleton classes and a new thread is created to handle the request, so it's not thread safe and we need to implement them carefully to avoid any issues with shared data.
`org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter` is the Front Controller class in Struts2 and every request processing starts from this class. Earlier versions of Struts2 uses `org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.FilterDispatcher` as Front Controller class.
Some of the benefits of interceptors are:
- Interceptor plays a crucial role in achieving high level of separation of concerns.
- Struts2 interceptors are configurable, we can configure it for any action we want.
- We can create our own custom interceptors to perform some common tasks such as request params logging, authentication etc. This helps us in taking care of common tasks at a single location, achieving low maintenance cost.
- We can create interceptors stack to use with different actions.
ValueStack is the storage area where the application data is stored by Struts2 for processing the client requests. The data is stored in `ActionContext` objects that use ThreadLocal to have values specific to the particular request thread. Object-Graph Navigation Language (OGNL) is a powerful Expression Language that is used to manipulate data stored on the ValueStack. As you can see in architecture diagram, both interceptors and result pages can access data stored on ValueStack using OGNL.
Some of the important annotations introduced in Struts2 are:
1. @Action to create action class
2. @Actions to configure single class for multiple actions
3. @Namespace and @Namespaces for creating different modules
4. @Result for result pages
5. @ResultPath for configuring result pages location
Some of the Struts2 constants that I have used are:
1. **struts.devMode** to run our application in development mode. This mode does reload properties files and provides extra logging and debugging feature. It's very useful while developing our application but we should turn it off while moving our code to production.
2. **struts.convention.result.path** to configure the location of result pages. By default Struts2 look for result pages at {WEBAPP-ROOT}/{Namespace}/ and we can change the location with this constant.
3. **struts.custom.i18n.resources** to define global resource bundle for i18n support.
4. **struts.action.extension** to configure the URL suffix to for Struts2 application. Default suffix is .action but sometimes we might want to change it to .do or something else.
We can configure above constants in the struts.xml file like below.
```
<constant name="struts.devMode" value="true"></constant>
<constant name="struts.action.extension" value="action,do"></constant>
<constant name="struts.custom.i18n.resources" value="global"></constant>
<constant name="struts.convention.result.path" value="/"></constant>
```
Struts2 namespace configuration allows us to create modules easily. We can use namespace to separate our action classes based on their functionality, for example admin, user, customer etc.
`com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ParametersInterceptor` interceptor is responsible for mapping request parameters to the Action class java bean properties. This interceptor is configured in struts-default package with name "params". This interceptor is part of basicStack and defaultStack interceptors stack.
`com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.I18nInterceptor` interceptor is responsible for i18n support in Struts2 applications. This interceptor is configured in struts-default package with name "i18n" and it's part of i18nStack and defaultStack.
We can implement Action interface to create our action classes. This interface has a single method execute() that we need to implement. The only benefit of using this interface is that it contains some constants that we can use for result pages, these constants are SUCCESS, ERROR, NONE, INPUT and LOGIN. ActionSupport class is the default implementation of Action interface and it also implements interfaces related to Validation and i18n support. ActionSupport class implements Action, Validateable, ValidationAware, TextProvider and LocaleProvider interfaces. We can override the validate() method of ActionSupport class to include field level validation login in our action classes. Depending on the requirements, we can use any of the approaches to creating Struts 2 action classes, my favorite is ActionSupport class because it helps in writing validation and i18n logic easily in action classes.
Struts2 action classes don't provide direct access to Servlet API components such as Request, Response, and Session. However, sometimes we need these access in action classes such as checking HTTP method or setting cookies in response. That's why Struts2 API provides a bunch of \*Aware interfaces that we can implement to access these objects. Struts2 API uses dependency injection to inject Servlet API components in action classes. Some of the important Aware interfaces are SessionAware, ApplicationAware, ServletRequestAware, and ServletResponseAware. You can read more about them in How to get [Servlet API Session in Struts2 Action Classes](/community/tutorials/get-servlet-session-request-response-context-attributes-struts-2-action) tutorial.
Struts2 provides execAndWait interceptor for long running action classes. We can use this interceptor to return an intermediate response page to the client and once the processing is finished, final response is returned to the client. This interceptor is defined in the struts-default package and implementation is present in `ExecuteAndWaitInterceptor` class. Check out [Struts2 execAndWait interceptor example](/community/tutorials/struts2-execandwait-interceptor-example-for-long-running-actions) to learn more about this interceptor and how to use it.
One of the major problems with web applications is the double form submission. If not taken care, double form submission could result in charging double amount to customer or updating database values twice. We can use a token interceptor to solve the double form submission problem. This interceptor is defined in the struts-default package but it's not part of any interceptor stack, so we need to include it manually in our action classes. Read more at [Struts2 token interceptor](/community/tutorials/struts2-token-interceptor-example) example.
Struts2 provides easy integration of log4j API for logging purpose, all we need to have is log4j configuration file in the WEB-INF/classes directory. You can check out the sample project at [Struts2 Log4j integration](/community/tutorials/struts2-and-log4j-integration-example-project).
Struts2 provides a lot of custom tags that we can use in result pages to create views for client request. These tags are broadly divided into three categories- Data tags, Control tags and UI tags. We can use these tags by adding these in JSP pages using taglib directive.
```
<%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s" %>
```
Some of the important Data tags are property, set, push, bean, action, include, i18n and text tag. Read more at [Struts2 Data Tags](/community/tutorials/struts-2-data-tags-example-tutorial). Control tags are used for manipulation and navigation of data from a collection. Some of the important Control tags are if-elseif-else, iterator, append, merge, sort, subset and generator tag. Read more at [Struts2 Control Tags](/community/tutorials/struts-2-control-tags-example-tutorial). Struts2 UI tags are used to generate HTML markup language, binding HTML form data to action classes properties, type conversion, validation, and i18n support. Some of the important UI tags are form, textfield, password, textarea, checkbox, select, radio and submit tag. Read more about them at [Struts2 UI Tags](/community/tutorials/struts-2-ui-tags-form-checkbox-radio-select-submit).
Struts2 support OGNL expression language and it performs two important tasks in Struts 2 – data transfer and type conversion. OGNL is flexible and we can easily extend it to create our own custom converter class. Creating and configuring custom type converter class is very easy. The first step is to fix the input format for the custom class. The second step is to implement the converter class. Type converter classes should implement `com.opensymphony.xwork2.conversion.TypeConverter` interface. Since in web application, we always get the request in form of String and send the response in the form of String, Struts 2 API provides a default implementation of TypeConverter interface, StrutsTypeConverter. StrutsTypeConverter contains two abstract methods – convertFromString to convert String to Object and convertToString to convert Object to String. For implementation details, read [Struts2 OGNL Example Tutorial](/community/tutorials/struts2-ognl).
We can implement `com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.Interceptor` interface to create our own interceptor. Once the interceptor class is ready, we need to define that in struts.xml package where we want to use it. We can also create interceptor stack with our custom interceptor and defaultStack interceptors. After that we can configure it for action classes where we want to use our interceptor. One of the best example of using custom interceptor is to validate session, read more about it at [Struts2 Interceptor Tutorial](/community/tutorials/struts-2-interceptor-example).
Interceptor interface defines three methods - init(), destroy() and intercept(). init and destroy are the life cycle methods of an interceptor. Interceptors are Singleton classes and Struts2 initialize a new thread to handle each request. init() method is called when interceptor instance is created and we can initialize any resources in this method. destroy() method is called when application is shutting down and we can release any resources in this method. intercept() is the method called every time client request comes through the interceptor.
An interceptor stack helps us to group together multiple interceptors in a package for further use. struts-default package creates some of the mostly used interceptor stack - basicStack and defaultStack. We can create our own interceptor stack at the start of the package and then configure our action classes to use it.
struts-default is an abstract package that defines all the Struts2 interceptors and commonly used interceptor stack. It is advisable to extend this package while configuring our application package to avoid configuring interceptors again. This is provided to help developers by eliminating the trivial task of configuring interceptor and result pages in our application.
The default URI suffix for Struts2 action is .action, in Struts1 default suffix was .do. We can change this suffix by defining struts.action.extension constant value in our Struts2 configuration file as:
```
<constant name="struts.action.extension" value="action,do"></constant>
```
By default Struts2 looks for result pages in {WEBAPP-ROOT}/{Namespace}/ directory but sometimes we want to keep result pages in another location, we can provide struts.convention.result.path constant value in Struts2 configuration file to change the result pages location. Another way is to use @ResultPath annotation in action classes to provide the result pages location.
File Upload is one of the common tasks in a web application. That's why Struts2 provides built-in support for file upload through FileUploadInterceptor. This interceptor is configured in the struts-default package and provide options to set the maximum size of a file and file types that can be uploaded to the server. Read more about FileUpload interceptor at [Struts2 File Upload Example](/community/tutorials/struts-2-file-upload-example).
Some of the best practices while developing Struts2 application are:
1. Always try to extend struts-default package while creating your package to avoid code redundancy in configuring interceptors.
2. For common tasks across the application, such as logging request params, try to use interceptors.
3. Always keep action classes java bean properties in a separate bean for code reuse and implement ModelDriven interface.
4. If you have custom interceptor that you will use in multiple actions, create interceptor stack for that and then use it.
5. Try to divide your application in different modules with namespace configuration based on functional areas.
6. Try to use Struts2 tags in result pages for code clarify, if needed create your own type converters.
7. Use development mode for faster development, however make sure production code doesn't run in dev mode.
8. Use Struts2 i18n support for resource bundles and to support localization.
9. Struts2 provides a lot of places where you can have resource bundles but try to keep one global resource bundle and one for action class to avoid confusion.
10. struts-default package configures all the interceptors and creates different interceptor stacks. Try to use only what is needed, for example if you don't have localization requirement, you can avoid i18n interceptor.
Struts2 provides a very robust framework for exception handling. We can specify global results in packages and then map specific exceptions to these result pages. The exception mapping can be done at the global package level as well as the action level. It's a good idea to have exception result pages to provide some information to the user when some unexpected exception occurs that is not processed by the application. The sample configuration in the struts.xml file looks like below.
```
<package name="user" namespace="/" extends="struts-default">
<global-results>
<result name="exception">/exception.jsp</result>
<result name="runtime_exception">/runtime_exception.jsp</result>
<result name="error">/error.jsp</result>
</global-results>
<global-exception-mappings>
<exception-mapping exception="java.lang.Exception" result="exception"></exception-mapping>
<exception-mapping exception="java.lang.Error" result="error"></exception-mapping>
<exception-mapping exception="java.lang.RuntimeException" result="runtime_exception"></exception-mapping>
</global-exception-mappings>
<action name="myaction" class="com.journaldev.struts2.exception.MyAction">
</action>
<action name="myspecialaction" class="com.journaldev.struts2.exception.MySpecialAction">
<exception-mapping exception="java.io.IOException" result="login"></exception-mapping>
<result name="login">/error.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
```
Read more at [Struts2 Exception Handling Example](/community/tutorials/struts2-exception-handling-example-tutorial).
Dat is alles voor de Struts2 sollicitatievraag en antwoorden, als je nog een belangrijke vraag tegenkomt die ik heb gemist, laat het me dan weten via opmerkingen.
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/struts2-interview-questions-and-answers













