오늘은 하이버네이트에서의 일대일 매핑에 대해 알아보겠습니다. 우리는 주석과 XML 구성을 사용하여 하이버네이트 일대일 매핑 예제를 살펴볼 것입니다.
하이버네이트에서의 일대일 매핑
 대부분의 경우, 데이터베이스 테이블들은 서로 연관되어 있습니다. 일대일, 일대다 및 다대다와 같은 많은 형태의 연관 관계가 있습니다. 이러한 연관 관계는 단방향 및 양방향 매핑으로 나눌 수 있습니다. 오늘은 XML 구성 및 주석 구성을 사용하여 하이버네이트 일대일 매핑을 구현하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
대부분의 경우, 데이터베이스 테이블들은 서로 연관되어 있습니다. 일대일, 일대다 및 다대다와 같은 많은 형태의 연관 관계가 있습니다. 이러한 연관 관계는 단방향 및 양방향 매핑으로 나눌 수 있습니다. 오늘은 XML 구성 및 주석 구성을 사용하여 하이버네이트 일대일 매핑을 구현하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
하이버네이트 일대일 매핑 예제 데이터베이스 설정
먼저 데이터베이스 테이블에서 일대일 매핑을 설정해야합니다. 이 예제를 위해 두 개의 테이블을 만들 것입니다 – 거래(Transaction)와 고객(Customer). 이 두 테이블은 일대일 매핑을 갖습니다. 거래는 주 테이블이며, 고객 테이블에서는 일대일 매핑을 위해 외래 키를 사용할 것입니다. 이 튜토리얼에서 사용하는 데이터베이스는 MySQL이므로 MySQL 스크립트를 제공합니다. 다른 데이터베이스를 사용하는 경우 스크립트를 해당하는 데이터베이스에 맞게 변경해야합니다.
-- 거래 테이블 생성
CREATE TABLE `Transaction` (
`txn_id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`txn_date` date NOT NULL,
`txn_total` decimal(10,0) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`txn_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=16 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- 고객 테이블 생성
CREATE TABLE `Customer` (
`txn_id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL,
`cust_name` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`cust_email` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`cust_address` varchar(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
PRIMARY KEY (`txn_id`),
CONSTRAINT `customer_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`txn_id`) REFERENCES `Transaction` (`txn_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
위 두 테이블 간의 일대일 매핑의 Entity Relation Diagram (ERD)은 아래 이미지와 같습니다. 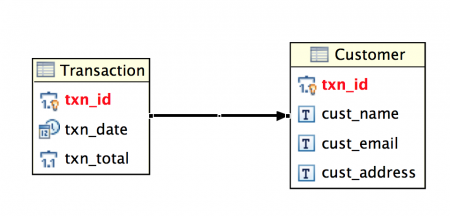 데이터베이스 설정이 완료되었으므로 이제 Hibernate 일대일 매핑 예제 프로젝트로 넘어갑시다.
데이터베이스 설정이 완료되었으므로 이제 Hibernate 일대일 매핑 예제 프로젝트로 넘어갑시다.
Hibernate 일대일 매핑 예제 프로젝트 구조
자바 IDE인 Eclipse에서 간단한 Maven 프로젝트를 생성합니다. 최종 프로젝트 구조는 아래 이미지와 같습니다. 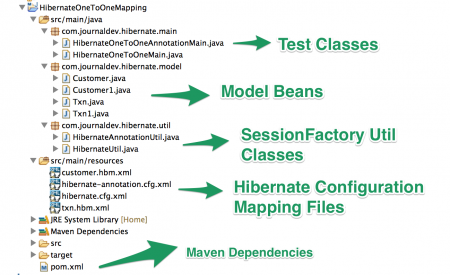 먼저 XML 기반의 Hibernate One to One 매핑 예제를 살펴보고, 그 다음에 어노테이션을 사용하여 같은 작업을 구현하겠습니다.
먼저 XML 기반의 Hibernate One to One 매핑 예제를 살펴보고, 그 다음에 어노테이션을 사용하여 같은 작업을 구현하겠습니다.
Hibernate Maven 종속성
최종 pom.xml 파일은 아래와 같습니다.
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.journaldev.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>HibernateOneToOneMapping</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>4.3.5.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
종속성은 Hibernate와 MySQL Java 드라이버를 위한 것입니다. Hibernate 최신 버전 4.3.5.Final과 MySQL 데이터베이스 서버 버전(5.0.5)에 맞는 MySQL Java 드라이버를 사용하고 있습니다. Hibernate 4에서는 JBoss 로깅을 사용하며, 이는 전이적 종속성으로 자동으로 가져옵니다. 프로젝트의 Maven 종속성에서 확인할 수 있습니다. Hibernate 이전 버전을 사용하는 경우 slf4j 종속성을 추가해야 할 수도 있습니다.
Hibernate One to One 매핑 모델 클래스
Hibernate One to One 매핑을 위한 데이터베이스 테이블을 반영하는 모델 클래스는 아래와 같습니다.
package com.journaldev.hibernate.model;
import java.util.Date;
public class Txn {
private long id;
private Date date;
private double total;
private Customer customer;
@Override
public String toString(){
return id+", "+total+", "+customer.getName()+", "+customer.getEmail()+", "+customer.getAddress();
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Date getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(Date date) {
this.date = date;
}
public double getTotal() {
return total;
}
public void setTotal(double total) {
this.total = total;
}
public Customer getCustomer() {
return customer;
}
public void setCustomer(Customer customer) {
this.customer = customer;
}
}
package com.journaldev.hibernate.model;
public class Customer {
private long id;
private String name;
private String email;
private String address;
private Txn txn;
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public Txn getTxn() {
return txn;
}
public void setTxn(Txn txn) {
this.txn = txn;
}
}
위의 모델 클래스는 getter-setter 메서드를 가진 간단한 POJO 클래스 또는 자바 빈으로 XML 기반 구성을 사용하고 있습니다. 혼동을 피하기 위해 클래스 이름을 Txn으로 사용하고 있으며 Hibernate API에는 클래스 이름이 Transaction입니다.
Hibernate One to One 매핑 구성
Txn 및 Customer 테이블을 위한 Hibernate One to One 매핑 구성 파일을 작성해보겠습니다. txn.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"https://hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.journaldev.hibernate.model.Txn" table="TRANSACTION" >
<id name="id" type="long">
<column name="txn_id" />
<generator class="identity" />
</id>
<property name="date" type="date">
<column name="txn_date" />
</property>
<property name="total" type="double">
<column name="txn_total" />
</property>
<one-to-one name="customer" class="com.journaldev.hibernate.model.Customer"
cascade="save-update" />
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
위에서 주목해야 할 중요한 점은 customer 속성에 대한 Hibernate one-to-one 요소입니다. customer.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"https://hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd" >
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.journaldev.hibernate.model.Customer" table="CUSTOMER">
<id name="id" type="long">
<column name="txn_id" />
<generator class="foreign">
<param name="property">txn</param>
</generator>
</id>
<one-to-one name="txn" class="com.journaldev.hibernate.model.Txn"
constrained="true"></one-to-one>
<property name="name" type="string">
<column name="cust_name"></column>
</property>
<property name="email" type="string">
<column name="cust_email"></column>
</property>
<property name="address" type="string">
<column name="cust_address"></column>
</property>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
generator class=”foreign”은 Hibernate 외래 키 구현에 사용되는 중요한 부분입니다.
Hibernate 구성 파일
다음은 XML 기반 Hibernate 매핑 구성을 위한 Hibernate 구성 파일입니다. hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"https://hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">pankaj123</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/TestDB</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">pankaj</property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.current_session_context_class">thread</property>
<property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property>
<mapping resource="txn.hbm.xml"/>
<mapping resource="customer.hbm.xml"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
Hibernate 구성 파일은 데이터베이스 연결 속성과 Hibernate 매핑 리소스를 가지고 있습니다.
Hibernate SessionFactory 유틸리티
여기에는 Hibernate SessionFactory 인스턴스를 생성하기 위한 유틸리티 클래스가 있습니다.
package com.journaldev.hibernate.util;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
public class HibernateUtil {
private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
private static SessionFactory buildSessionFactory() {
try {
// hibernate.cfg.xml에서 SessionFactory 생성
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml");
System.out.println("Hibernate Configuration loaded");
ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry = new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(configuration.getProperties()).build();
System.out.println("Hibernate serviceRegistry created");
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
return sessionFactory;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
System.err.println("Initial SessionFactory creation failed." + ex);
ex.printStackTrace();
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
}
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
if(sessionFactory == null) sessionFactory = buildSessionFactory();
return sessionFactory;
}
}
이것으로 끝입니다. 이제 하이버네이트의 일대일 매핑 XML 기반 구성을 테스트하는 테스트 프로그램을 작성해 보겠습니다.
Hibernate 일대일 매핑 XML 구성 테스트 프로그램
하이버네이트 일대일 매핑 예제 테스트 프로그램에서는 먼저 Txn 객체를 만들고 저장합니다. 데이터베이스에 저장된 후 생성된 ID를 사용하여 Txn 객체를 검색하고 출력합니다.
package com.journaldev.hibernate.main;
import java.util.Date;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import com.journaldev.hibernate.model.Customer;
import com.journaldev.hibernate.model.Txn;
import com.journaldev.hibernate.util.HibernateUtil;
public class HibernateOneToOneMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Txn txn = buildDemoTransaction();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
Session session = null;
Transaction tx = null;
try{
//세션 가져오기
sessionFactory = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
System.out.println("Session created");
//트랜잭션 시작
tx = session.beginTransaction();
//모델 객체 저장
session.save(txn);
//트랜잭션 커밋
tx.commit();
System.out.println("Transaction ID="+txn.getId());
//저장된 트랜잭션 데이터 가져오기
printTransactionData(txn.getId(), sessionFactory);
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("Exception occured. "+e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(!sessionFactory.isClosed()){
System.out.println("Closing SessionFactory");
sessionFactory.close();
}
}
}
private static void printTransactionData(long id, SessionFactory sessionFactory) {
Session session = null;
Transaction tx = null;
try{
//세션 가져오기
sessionFactory = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
//트랜잭션 시작
tx = session.beginTransaction();
//모델 객체 저장
Txn txn = (Txn) session.get(Txn.class, id);
//트랜잭션 커밋
tx.commit();
System.out.println("Transaction Details=\n"+txn);
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("Exception occured. "+e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static Txn buildDemoTransaction() {
Txn txn = new Txn();
txn.setDate(new Date());
txn.setTotal(100);
Customer cust = new Customer();
cust.setAddress("Bangalore, India");
cust.setEmail("[email protected]");
cust.setName("Pankaj Kumar");
txn.setCustomer(cust);
cust.setTxn(txn);
return txn;
}
}
이제 위의 일대일 매핑을 하는 하이버네이트 테스트 프로그램을 실행하면 다음과 같은 출력이 나옵니다.
Hibernate Configuration loaded
Hibernate serviceRegistry created
Session created
Hibernate: insert into TRANSACTION (txn_date, txn_total) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into CUSTOMER (cust_name, cust_email, cust_address, txn_id) values (?, ?, ?, ?)
Transaction ID=19
Hibernate: select txn0_.txn_id as txn_id1_1_0_, txn0_.txn_date as txn_date2_1_0_, txn0_.txn_total as txn_tota3_1_0_,
customer1_.txn_id as txn_id1_0_1_, customer1_.cust_name as cust_nam2_0_1_, customer1_.cust_email as cust_ema3_0_1_,
customer1_.cust_address as cust_add4_0_1_ from TRANSACTION txn0_ left outer join CUSTOMER customer1_ on
txn0_.txn_id=customer1_.txn_id where txn0_.txn_id=?
Transaction Details=
19, 100.0, Pankaj Kumar, [email protected], Bangalore, India
Closing SessionFactory
위에서 확인할 수 있듯이, 잘 작동하고 트랜잭션 ID를 사용하여 두 테이블에서 데이터를 검색할 수 있습니다. 데이터를 가져오기 위해 Hibernate 내부에서 사용하는 SQL을 확인하고, 두 테이블에서 데이터를 가져오기 위해 조인을 사용하고 있습니다.
Hibernate 일대일 매핑 주석
위 섹션에서는 Hibernate 일대일 매핑에 XML 기반 구성을 사용하는 방법을 알아보았으므로, 이제 JPA와 Hibernate 주석을 사용하여 동일한 결과를 얻는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
Hibernate 구성 파일
hibernate-annotation.cfg.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"https://hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">pankaj123</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/TestDB</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">pankaj</property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.current_session_context_class">thread</property>
<property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property>
<mapping class="com.journaldev.hibernate.model.Txn1"/>
<mapping class="com.journaldev.hibernate.model.Customer1"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
Hibernate 구성은 간단합니다. 주석을 사용하여 사용할 두 개의 모델 클래스 – Txn1 및 Customer1이 있음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
Hibernate 일대일 매핑 주석 예제 모델 클래스
하이버네이트의 일 대 일 매핑 주석 구성에는 모델 클래스가 가장 중요합니다. 모델 클래스가 어떻게 보이는지 살펴보겠습니다.
package com.journaldev.hibernate.model;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Cascade;
@Entity
@Table(name="TRANSACTION")
public class Txn1 {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="txn_id")
private long id;
@Column(name="txn_date")
private Date date;
@Column(name="txn_total")
private double total;
@OneToOne(mappedBy="txn")
@Cascade(value=org.hibernate.annotations.CascadeType.SAVE_UPDATE)
private Customer1 customer;
@Override
public String toString(){
return id+", "+total+", "+customer.getName()+", "+customer.getEmail()+", "+customer.getAddress();
}
//Getter-Setter 메소드, 가독성을 위해 생략
}
대부분의 주석은 하이버네이트가 제공하는 Java Persistence API에서 가져온 것입니다. 그러나 cascading에 대해서는 하이버네이트 주석 org.hibernate.annotations.Cascade 및 enum org.hibernate.annotations.CascadeType을 사용해야 합니다.
package com.journaldev.hibernate.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import javax.persistence.PrimaryKeyJoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Parameter;
@Entity
@Table(name="CUSTOMER")
public class Customer1 {
@Id
@Column(name="txn_id", unique=true, nullable=false)
@GeneratedValue(generator="gen")
@GenericGenerator(name="gen", strategy="foreign", parameters={@Parameter(name="property", value="txn")})
private long id;
@Column(name="cust_name")
private String name;
@Column(name="cust_email")
private String email;
@Column(name="cust_address")
private String address;
@OneToOne
@PrimaryKeyJoinColumn
private Txn1 txn;
//Getter-Setter 메소드
}
id를 생성하는 대신 txn에서 사용되도록 @GenericGenerator를 사용해야 함에 유의하세요.
하이버네이트 SessionFactory 유틸리티 클래스
SessionFactory 생성은 하이버네이트 매핑을 제공하는 방식과 독립적입니다. SessionFactory를 생성하기 위한 유틸리티 클래스는 다음과 같습니다.
package com.journaldev.hibernate.util;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
public class HibernateAnnotationUtil {
private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
private static SessionFactory buildSessionFactory() {
try {
// hibernate-annotation.cfg.xml에서 SessionFactory 생성
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.configure("hibernate-annotation.cfg.xml");
System.out.println("Hibernate Annotation Configuration loaded");
ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry = new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(configuration.getProperties()).build();
System.out.println("Hibernate Annotation serviceRegistry created");
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
return sessionFactory;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
System.err.println("Initial SessionFactory creation failed." + ex);
ex.printStackTrace();
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
}
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
if(sessionFactory == null) sessionFactory = buildSessionFactory();
return sessionFactory;
}
}
하이버네이트 일 대 일 매핑 주석 예제 테스트 프로그램
다음은 하이버네이트 일 대 일 매핑 주석 예제를 위한 간단한 테스트 프로그램입니다.
package com.journaldev.hibernate.main;
import java.util.Date;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import com.journaldev.hibernate.model.Customer1;
import com.journaldev.hibernate.model.Txn1;
import com.journaldev.hibernate.util.HibernateAnnotationUtil;
public class HibernateOneToOneAnnotationMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Txn1 txn = buildDemoTransaction();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
Session session = null;
Transaction tx = null;
try{
//세션 가져오기
sessionFactory = HibernateAnnotationUtil.getSessionFactory();
session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
System.out.println("Session created using annotations configuration");
//트랜잭션 시작
tx = session.beginTransaction();
//모델 객체 저장
session.save(txn);
//트랜잭션 커밋
tx.commit();
System.out.println("Annotation Example. Transaction ID="+txn.getId());
//저장된 트랜잭션 데이터 가져오기
printTransactionData(txn.getId(), sessionFactory);
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("Exception occured. "+e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(sessionFactory != null && !sessionFactory.isClosed()){
System.out.println("Closing SessionFactory");
sessionFactory.close();
}
}
}
private static void printTransactionData(long id, SessionFactory sessionFactory) {
Session session = null;
Transaction tx = null;
try{
//세션 가져오기
sessionFactory = HibernateAnnotationUtil.getSessionFactory();
session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
//트랜잭션 시작
tx = session.beginTransaction();
//모델 객체 저장
Txn1 txn = (Txn1) session.get(Txn1.class, id);
//트랜잭션 커밋
tx.commit();
System.out.println("Annotation Example. Transaction Details=\n"+txn);
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("Exception occured. "+e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static Txn1 buildDemoTransaction() {
Txn1 txn = new Txn1();
txn.setDate(new Date());
txn.setTotal(100);
Customer1 cust = new Customer1();
cust.setAddress("San Jose, USA");
cust.setEmail("[email protected]");
cust.setName("Pankaj Kr");
txn.setCustomer(cust);
cust.setTxn(txn);
return txn;
}
}
위 프로그램을 실행할 때의 출력 스니펫입니다.
Hibernate Annotation Configuration loaded
Hibernate Annotation serviceRegistry created
Session created using annotations configuration
Hibernate: insert into TRANSACTION (txn_date, txn_total) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into CUSTOMER (cust_address, cust_email, cust_name, txn_id) values (?, ?, ?, ?)
Annotation Example. Transaction ID=20
Hibernate: select txn1x0_.txn_id as txn_id1_1_0_, txn1x0_.txn_date as txn_date2_1_0_, txn1x0_.txn_total as txn_tota3_1_0_,
customer1x1_.txn_id as txn_id1_0_1_, customer1x1_.cust_address as cust_add2_0_1_, customer1x1_.cust_email as cust_ema3_0_1_,
customer1x1_.cust_name as cust_nam4_0_1_ from TRANSACTION txn1x0_ left outer join CUSTOMER customer1x1_ on
txn1x0_.txn_id=customer1x1_.txn_id where txn1x0_.txn_id=?
Annotation Example. Transaction Details=
20, 100.0, Pankaj Kr, [email protected], San Jose, USA
Closing SessionFactory
출력이 하이버네이트의 일대일 XML 기반 구성과 유사하다는 것에 유의하십시오. 이것으로 하이버네이트 일대일 매핑 예제에 대한 설명이 끝났습니다. 더 배우기 위해 아래 링크에서 최종 프로젝트를 다운로드하여 실험해 볼 수 있습니다.
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/hibernate-one-to-one-mapping-example-annotation













