날짜 명령어는 외부 bash 프로그램으로, 시스템 날짜와 시간을 설정하거나 표시할 수 있습니다. 또한 여러 가지 형식 옵션을 제공합니다. 날짜 명령어는 모든 리눅스 배포판에 기본으로 설치되어 있습니다.
$ which date $ type -a date
터미널에 날짜 명령어를 입력하면 현재 날짜와 시간이 표시됩니다.
$ date
리눅스 시스템 날짜와 시간 변경
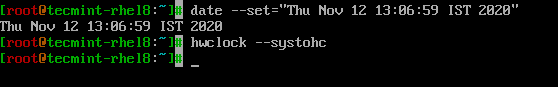
날짜 명령어를 사용하여 시스템 날짜, 시간 및 시간대를 수정할 수 있으며 변경 내용은 하드웨어 클록과 동기화해야 합니다.
$ date --set="Thu Nov 12 13:06:59 IST 2020" $ hwclock --systohc
형식 옵션
A good place to get the list of formatting options will be the man page.
$ man date
사용할 일반적인 형식 옵션 중 일부를 살펴보겠습니다.
- 형식을 적용하려면 “+” 다음에 “형식 지정자“를 사용합니다.
- GNU\LINUX의 형식 옵션 목록은 연결된 맨 페이지를 참조하십시오.
- BSD의 형식 옵션 목록은 연결된 맨 페이지를 참조하십시오.
날짜 명령어의 두 가지 중요한 부분은 형식 +%와 -date 옵션입니다.
이제 date 명령어에 일부 서식을 적용해봅시다. 서식을 적용하려면 예시에 표시된대로 플러스 기호 (+) 다음에 %formatter를 추가하면 됩니다.
리눅스에서 날짜 다루기
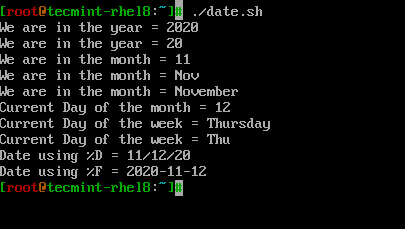
간단한 셸 스크립트인 ‘date.sh‘에서 날짜 관련 서식을 사용하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
# PRINT YEAR,MONTH,DAY AND DATE... echo "We are in the year = $(date +%Y)" echo "We are in the year = $(date +%y)" # Difference between %Y and %y is %Y will print 4 digits while %y will print the last 2 digits of the year. echo "We are in the month = $(date +%m)" echo "We are in the month = $(date +%b)" echo "We are in the month = $(date +%B)" # Difference between %B and %b is, %B will print full month name while %b will print abbreviated month name. echo "Current Day of the month = $(date +%d)" echo "Current Day of the week = $(date +%A)" echo "Current Day of the week = $(date +%a)" # Difference between %A and %a is, %A will print full Weekday name while %a will print abbreviated weekday name. # Instead of formatting to get the date, we can use %D which will print the date as %m/%d/%y or %F which prints in %Y-%M-%d format. echo "Date using %D = $(date +%D)" echo "Date using %F = $(date +%F)"
리눅스에서 시간 다루기
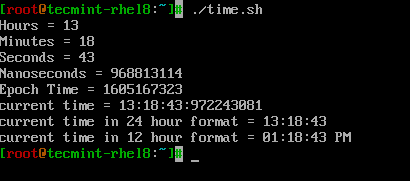
간단한 셸 스크립트인 ‘time.sh‘에서 시간 관련 서식을 사용하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
# PRINT HOURS, MINS, SECONDS, NANO SECONDS echo Hours = $(date +%H) echo Minutes = $(date +%M) echo Seconds = $(date +%S) echo Nanoseconds = $(date +%N) echo Epoch Time = $(date +%s) echo "current time = $(date +%H:%M:%S:%N)" # can also use %T which displays Time in HH:MM:SS format. echo "current time in 24 hour format = $(date +%T)" # can also use %r to display time in 12 hour format. echo "current time in 12 hour format = $(date +%r)"
–date 또는 -d 플래그와 함께
--date 또는 -d 플래그를 사용하여 입력을 문자열로 전달하면 date 명령어가 스마트하게 처리하는 방법을 알 수 있습니다.
작동 방식을 이해하기 위해 몇 가지 예제를 살펴보겠습니다.
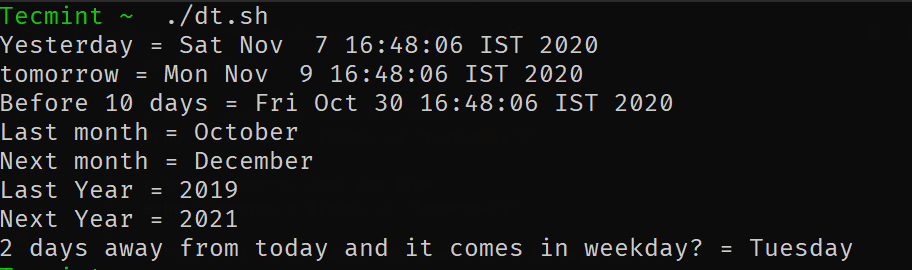
# Print yesterday's date and time. echo "Yesterday = $(date -d "Yesterday")" # Print Tomorrow date and time. echo "tomorrow = $(date -d "tomorrow")" # Find what is the date and time before 10 days from now. echo "Before 10 days = $(date -d "tomorrow -10 days")" # Find last month and next month echo "Last month = $(date -d "last month" "%B")" echo "Next month = $(date -d "next month" "%B")" # Find last year and next year echo "Last Year = $(date -d "last year" "+%Y")" echo "Next Year = $(date -d "next year" "+%Y")" # Forecast the weekday echo "2 days away from today and it comes on weekdays? = $(date -d "Today +2 days" "+%A")
일반적인 작업
주어진 두 날짜 사이의 일 수 계산.
$ echo $(( ( $(date -d "2020-11-10" "+%s") - $(date -d "2020-11-01" "+%s") ) / 86400))
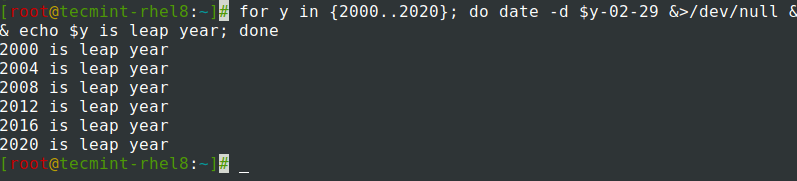
주어진 연도가 윤년인지 확인.
$ for y in {2000..2020}; do date -d $y-02-29 &>/dev/null && echo $y is leap year; done
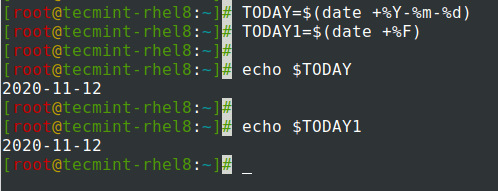
date 명령어의 출력을 변수에 할당.
$ TODAY=$(date +%Y-%m-%d) OR $ TODAY1=$(date +%F) $ echo $TODAY $ echo $TODAY1
파일 이름에 날짜를 추가하여 로그 파일 생성.
로그 파일, 백업 또는 텍스트 파일을 생성할 때 날짜와 시간을 추가하는 것은 우리가 가장 자주 마주치게 될 일반 작업입니다. 예를 들어 백업을 만들기 위해 셸 스크립트를 만들었다고 가정해봅시다.
이 스크립트는 00:00부터 23:59까지 백업을 수행하고 다음 날 00:00에 매일 실행되도록 예약되어 있습니다. 어제의 날짜 형식으로 로그 파일을 생성하려고 합니다.
CUSTOM_FORMAT=$(date --date "Yesterday" "+%d-%y-%H:%M")
LOG_FILE=/var/log/custom_application/application_${CUSTOM_FORMAT}.log
echo "Script started" >> ${LOG_FILE}
...
CODE BLOCKS
...
echo "Script completed" >> ${LOG_FILE}
그것이 이 기사에 대한 전부입니다. 이 기사에서는 Linux에서 bash 날짜와 시간을 사용하는 방법을 살펴보았습니다. 피드백을 알려주세요.
Source:
https://www.tecmint.com/change-linux-system-date-and-time/













