Welcome to the Java Web Services Tutorial. Here we will learn about web services, useful concepts in web services and then different types of API we have in Java to create web services.
What is a Web Service
In simple words, services that can be accessed over network are called web services. So how does it differ from web application, they are also services that are accessed over network. There are few attributes that clarifies this difference.
- Web applications are meant for users and to be accessed in browser having human readable format whereas web services are meant for applications to access data in the format of XML, JSON etc.
- Web applications always use HTTP/HTTPS protocol whereas traditional web services use SOAP protocol. Recently REST is getting popularity that is an architecture style and almost all times run on HTTP/HTTPS protocol.
- Web applications are not meant for reusability whereas this is one of the benefit of web services. A single web service can be used by different kinds of applications.
- Web application can access web services to access some data or to perform some tasks, web services can’t access web applications to fetch some data.
- Web applications are capable to maintain user session, web services are stateless.
I hope above differences are good enough to clear any confusion with web applications and web services. Both are different concepts and meant for different purpose.
Types of Web Services
There are two types of web services.
- SOAP: SOAP stands for Simple Object Access Protocol. SOAP is an XML based industry standard protocol for designing and developing web services. Since it’s XML based, it’s platform and language independent. So our server can be based on JAVA and client can be on .NET, PHP etc. and vice versa.
- REST: REST is an architectural style for developing web services. It’s getting popularity recently because it has small learning curve when compared to SOAP. Resources are core concepts of Restful web services and they are uniquely identified by their URIs.
Java Web Services
Java provides it’s own API to create both SOAP as well as REST web services.
- JAX-WS: JAX-WS stands for Java API for XML Web Services. JAX-WS is XML based Java API to build web services server and client application.
- JAX-RS: Java API for RESTful Web Services (JAX-RS) is the Java API for creating REST web services. JAX-RS uses annotations to simplify the development and deployment of web services.
Both of these APIs are part of standard JDK installation, so we don’t need to add any jars to work with them. Both of these APIs use annotations very heavily.
Hello World JAX-WS Application
Let’s create a very simple Hello World JAX-WS application. TestService.java
package com.journaldev.jaxws.service;
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.jws.soap.SOAPBinding;
import javax.xml.ws.Endpoint;
@WebService
@SOAPBinding(style = SOAPBinding.Style.DOCUMENT)
public class TestService {
@WebMethod
public String sayHello(String msg){
return "Hello "+msg;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Endpoint.publish("https://localhost:8888/testWS", new TestService());
}
}
That’s it. Just run this application and our Hello World JAX-WS SOAP web service is published. Below image shows the invocation of this JAX-WS web service through SOAP UI.  That’s it for a very basic tutorial of JAX-WS web service. Below are some of the articles you should read for better understanding of SOAP web services and JAX-WS.
That’s it for a very basic tutorial of JAX-WS web service. Below are some of the articles you should read for better understanding of SOAP web services and JAX-WS.
- JAX-WS Tutorial
- JAX-WS Web Service Deployment on Tomcat
- SOAP Web Service Example using Eclipse and Apache Axis
- Apache Axis 2 Web Services Tutorial
Hello World JAX-RS Application
Jersey is the reference implementation of JAX-RS API, it’s not part of standard JDK and we have to include all the required jars. Best way is to use Maven build, so create a simple Dynamic web project and then convert it to Maven in Eclipse. Here is the final pom.xml file having required dependencies.
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>JAX-RS-HelloWorld</groupId>
<artifactId>JAX-RS-HelloWorld</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.jersey</groupId>
<artifactId>jersey-server</artifactId>
<version>1.19</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.jersey</groupId>
<artifactId>jersey-servlet</artifactId>
<version>1.19</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<sourceDirectory>src</sourceDirectory>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
<configuration>
<warSourceDirectory>WebContent</warSourceDirectory>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.3</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.7</source>
<target>1.7</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Now add Jersey servlet to our deployment descriptor web.xml as front controller.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="https://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee https://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
id="WebApp_ID" version="3.1">
<display-name>JAX-RS-HelloWorld</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Jersey REST Service</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.sun.jersey.spi.container.servlet.ServletContainer</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>com.sun.jersey.config.property.packages</param-name>
<param-value>com.journaldev.jaxrs.service</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Jersey REST Service</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Above two steps are required for initial setup, below is our Hello World JAX-RS service class.
package com.journaldev.jaxrs.service;
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
@Path("/test")
public class TestService {
@GET
@Path("/hello/{msg}")
public String sayHello(@PathParam(value="msg") String msg){
return "Hello "+msg;
}
}
Just export it as WAR file and then access it in the browser as shown in below image. 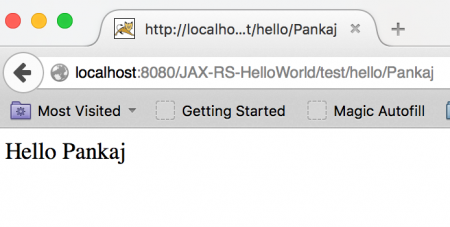 You can change the last part of URL and returned message will change accordingly. You can see how easy it was to create RESTful web service using JAX-RS API. However there is more to it, follow below articles to learn more.
You can change the last part of URL and returned message will change accordingly. You can see how easy it was to create RESTful web service using JAX-RS API. However there is more to it, follow below articles to learn more.
That’s all for a quick introduction of java web services, finally if you are preparing for any interview then go through Web Services Interview Questions. References: JAX-WS Oracle Page, JAX-RS Oracle Page
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/java-web-services-tutorial













