Struts2は、Javaでウェブアプリケーションを開発するための有名なフレームワークの1つです。最近、私は多くのStruts2チュートリアルを書いたばかりで、この投稿では、面接で役立ついくつかの重要なStruts2の面接質問と回答をリストアップしています。
Struts2の面接質問

- Struts2とは何ですか?
- Struts1とStruts2の違いは何ですか、またはStruts2がStruts1よりも優れている点は何ですか?
- Struts2のコアコンポーネントは何ですか?
- Struts2のインターセプターとは何ですか?
- Struts2インターセプターによって実装されているデザインパターンは何ですか?
- Struts2でアクションクラスを作成する異なる方法は何ですか?
- Struts2のアクションとインターセプターはスレッドセーフですか?
- Struts2のフロントコントローラーはどのクラスですか?
- Struts2のインターセプターの利点は何ですか?
- ValueStackとOGNLとは何ですか?
- Struts2で導入された便利な注釈をいくつか挙げてください。
- 使用した重要なStruts2定数をいくつか提供してください。
- Struts2のアクションマッピングでの名前空間の利用目的は何ですか?
- リクエストパラメータをアクションクラスのJava Beanプロパティにマッピングするのはどのインターセプターですか?
- i18nサポートを担当するインターセプターはどれですか?
- アクションクラスでActionインターフェースとActionSupportクラスの使用にはどのような違いがあり、どちらをお勧めですか?
- アクションクラスでServlet APIのリクエスト、レスポンス、HttpSessionなどのオブジェクトを取得する方法は?
- execAndWaitインターセプターの利用目的は何ですか?
- Struts2でのトークンインターセプターの利用目的は何ですか?
- Struts2アプリケーションでlog4jを統合する方法は?
- 異なるStruts2タグは何ですか?それらをどのように使用できますか?
- Struts2のカスタムタイプコンバーターとは何ですか?
- 独自のインターセプターを作成し、それをアクションにマッピングする方法は?
- インターセプターのライフサイクルとは何ですか?
- インターセプタースタックとは何ですか?
- struts-defaultパッケージとは何ですか、そしてその利点は何ですか?
- Struts2アクションURIのデフォルトの接尾辞は何ですか、そしてそれを変更する方法はありますか?
- 結果ページのデフォルトの場所はどこですか、そしてそれを変更する方法はありますか?
- Struts2アプリケーションでファイルをアップロードする方法は?
- Struts2アプリケーションを開発する際に従うべきベストプラクティスは何ですか?
- Struts2でアプリケーションがスローした例外をどのように処理できますか?
Struts2 インタビューの質問と回答
-
Struts2とは何ですか?
Apache Struts2は、Javaでウェブアプリケーションを構築するためのオープンソースフレームワークです。Struts2はOpenSymphony WebWorkフレームワークをベースにしています。Struts1から大幅に改善され、より柔軟で使いやすく拡張性が向上しています。Struts2の中核コンポーネントは、アクション、インターセプター、および結果ページです。Struts2は、struts.xmlを介してアクションクラスを作成し構成するための多くの方法を提供しています。また、アノテーションを使用して構成することもできます。一般的なタスクのための独自のインターセプターを作成することができます。Struts2には多くのタグが付属しており、OGNL式言語を使用しています。独自のタイプコンバータを作成して結果ページをレンダリングすることができます。結果ページはJSPとFreeMarkerテンプレートを使用できます。
-
Struts1とStruts2の違いは何ですか、またはStruts2はStruts1よりも優れていますか?
Struts2はStruts1の不具合を克服し、より柔軟で拡張可能にするために設計されています。いくつかの顕著な違いは次のとおりです:
コンポーネント Struts1 Struts2 アクションクラス Struts1のアクションクラスはAbstract Classを強制的に拡張する必要があり、拡張不可能です。 Struts2のアクションクラスは柔軟で、Actionインターフェースを実装したり、ActionSupportクラスを拡張したり、単にexecute()メソッドを持つことができます。 スレッドセーフ Struts1のアクションクラスはシングルトンであり、スレッドセーフではありません。これにより、マルチスレッドの副作用を回避するために開発者側で追加の注意が必要です。 Struts2のアクションクラスはリクエストごとにインスタンス化されるため、マルチスレッドはありません。これにより、スレッドセーフになります。 Servlet APIの結合 Struts1のAPIはServlet APIと密接に結合しており、リクエストおよびレスポンスオブジェクトがアクションクラスのexecute()メソッドに渡されます。 Struts2のAPIはServlet APIと緩やかに結合しており、フォームビーンデータをアクションクラスのJavaビーンプロパティに自動的にマップします。ただし、Servlet APIクラスへの参照が必要な場合は、そのための*Awareインターフェースがあります。 テスト Struts1のアクションクラスはServlet APIの結合のためにテストが難しいです。 Struts2のアクションクラスは通常のJavaクラスのようであり、インスタンス化してプロパティを設定することで簡単にテストできます。 リクエストパラメータのマッピング Struts1では、リクエストパラメータを保持するActionFormクラスを作成し、struts構成ファイルで構成する必要があります。 Struts2のリクエストパラメータマッピングは動的に行われ、アクションクラスにJavaビーンプロパティが必要であり、またはModelDrivenインターフェースを実装してマッピングに使用するJavaビーンクラス名を提供する必要があります。 タグサポート Struts1はJSTLタグを使用しており、したがって制限されています。 Struts2はOGNLを使用し、さまざまな種類のUI、コントロール、データタグを提供しています。より汎用性が高く、使いやすいです。 バリデーション Struts1は手動のvalidate()メソッドをサポートしています。 Struts2は手動のバリデーションとバリデーションフレームワークの統合の両方をサポートしています。 ビューのレンダリング Struts1は標準のJSP技術を使用して、ビューページにビーン値を提供しています。 Struts2はValueStackを使用してリクエストパラメータと属性を保存し、それらにアクセスするためにOGNLとStruts2タグを使用できます。 モジュールサポート Struts1のモジュールは設計が複雑で、独立したプロジェクトのように見えます。 Struts2はパッケージに対して”namespace”構成を提供し、簡単にモジュールを作成できます。 -
Struts2のコアコンポーネントは何ですか?
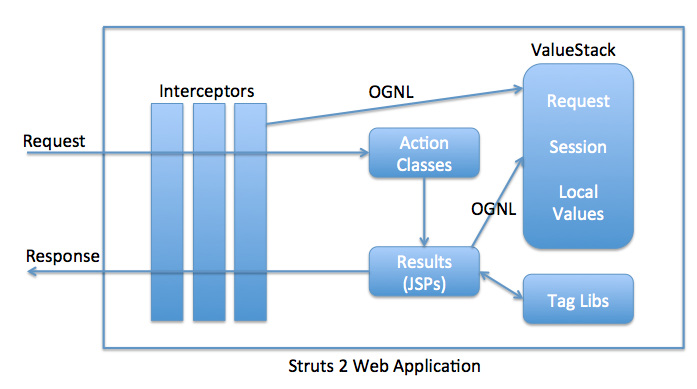
Struts2のコアコンポーネントは次のとおりです:
- Actionクラス
- インターセプター
- 結果ページ、FreeMarkerテンプレートのJSP
- ValueStack、OGNL、およびタグライブラリ
-
Struts2のインターセプターとは何ですか?
インターセプターはStruts2フレームワークの中核です。Struts2のインターセプターは、アクションクラスにリクエストパラメータを渡したり、Servlet APIリクエスト、レスポンス、セッションをアクションクラスに利用可能にしたり、バリデーション、i18nサポートなど、フレームワークによって行われるほとんどの処理を担当しています。ActionInvocationは、アクションクラスとインターセプターをカプセル化し、それらを順番に実行する責任があります。ActionInvocationで最も重要なメソッドはinvoke()メソッドであり、このメソッドはインターセプターチェーンを追跡し、次のインターセプターまたはアクションを呼び出します。これは、Java EEフレームワークにおける責任連鎖パターンの最良の例の1つです。
-
Struts2のインターセプタはどのデザインパターンを実装していますか?
Struts2 interceptors are based on intercepting filters design pattern. The invocation of interceptors in interceptor stack closely resembles Chain of Responsibility design pattern.
Struts2 provide different ways to create action classes.
1. By implementing Action interface
2. Using Struts2 @Action annotation
3. By extending ActionSupport class
4. Any normal java class with execute() method returning String can be configured as Action class.
Struts2 Action classes are thread safe because an object is instantiated for every request to handle it. Struts2 interceptors are singleton classes and a new thread is created to handle the request, so it's not thread safe and we need to implement them carefully to avoid any issues with shared data.
`org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter` is the Front Controller class in Struts2 and every request processing starts from this class. Earlier versions of Struts2 uses `org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.FilterDispatcher` as Front Controller class.
Some of the benefits of interceptors are:
- Interceptor plays a crucial role in achieving high level of separation of concerns.
- Struts2 interceptors are configurable, we can configure it for any action we want.
- We can create our own custom interceptors to perform some common tasks such as request params logging, authentication etc. This helps us in taking care of common tasks at a single location, achieving low maintenance cost.
- We can create interceptors stack to use with different actions.
ValueStack is the storage area where the application data is stored by Struts2 for processing the client requests. The data is stored in `ActionContext` objects that use ThreadLocal to have values specific to the particular request thread. Object-Graph Navigation Language (OGNL) is a powerful Expression Language that is used to manipulate data stored on the ValueStack. As you can see in architecture diagram, both interceptors and result pages can access data stored on ValueStack using OGNL.
Some of the important annotations introduced in Struts2 are:
1. @Action to create action class
2. @Actions to configure single class for multiple actions
3. @Namespace and @Namespaces for creating different modules
4. @Result for result pages
5. @ResultPath for configuring result pages location
Some of the Struts2 constants that I have used are:
1. **struts.devMode** to run our application in development mode. This mode does reload properties files and provides extra logging and debugging feature. It's very useful while developing our application but we should turn it off while moving our code to production.
2. **struts.convention.result.path** to configure the location of result pages. By default Struts2 look for result pages at {WEBAPP-ROOT}/{Namespace}/ and we can change the location with this constant.
3. **struts.custom.i18n.resources** to define global resource bundle for i18n support.
4. **struts.action.extension** to configure the URL suffix to for Struts2 application. Default suffix is .action but sometimes we might want to change it to .do or something else.
We can configure above constants in the struts.xml file like below.
```
<constant name="struts.devMode" value="true"></constant>
<constant name="struts.action.extension" value="action,do"></constant>
<constant name="struts.custom.i18n.resources" value="global"></constant>
<constant name="struts.convention.result.path" value="/"></constant>
```
Struts2 namespace configuration allows us to create modules easily. We can use namespace to separate our action classes based on their functionality, for example admin, user, customer etc.
`com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ParametersInterceptor` interceptor is responsible for mapping request parameters to the Action class java bean properties. This interceptor is configured in struts-default package with name "params". This interceptor is part of basicStack and defaultStack interceptors stack.
`com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.I18nInterceptor` interceptor is responsible for i18n support in Struts2 applications. This interceptor is configured in struts-default package with name "i18n" and it's part of i18nStack and defaultStack.
We can implement Action interface to create our action classes. This interface has a single method execute() that we need to implement. The only benefit of using this interface is that it contains some constants that we can use for result pages, these constants are SUCCESS, ERROR, NONE, INPUT and LOGIN. ActionSupport class is the default implementation of Action interface and it also implements interfaces related to Validation and i18n support. ActionSupport class implements Action, Validateable, ValidationAware, TextProvider and LocaleProvider interfaces. We can override the validate() method of ActionSupport class to include field level validation login in our action classes. Depending on the requirements, we can use any of the approaches to creating Struts 2 action classes, my favorite is ActionSupport class because it helps in writing validation and i18n logic easily in action classes.
Struts2 action classes don't provide direct access to Servlet API components such as Request, Response, and Session. However, sometimes we need these access in action classes such as checking HTTP method or setting cookies in response. That's why Struts2 API provides a bunch of \*Aware interfaces that we can implement to access these objects. Struts2 API uses dependency injection to inject Servlet API components in action classes. Some of the important Aware interfaces are SessionAware, ApplicationAware, ServletRequestAware, and ServletResponseAware. You can read more about them in How to get [Servlet API Session in Struts2 Action Classes](/community/tutorials/get-servlet-session-request-response-context-attributes-struts-2-action) tutorial.
Struts2 provides execAndWait interceptor for long running action classes. We can use this interceptor to return an intermediate response page to the client and once the processing is finished, final response is returned to the client. This interceptor is defined in the struts-default package and implementation is present in `ExecuteAndWaitInterceptor` class. Check out [Struts2 execAndWait interceptor example](/community/tutorials/struts2-execandwait-interceptor-example-for-long-running-actions) to learn more about this interceptor and how to use it.
One of the major problems with web applications is the double form submission. If not taken care, double form submission could result in charging double amount to customer or updating database values twice. We can use a token interceptor to solve the double form submission problem. This interceptor is defined in the struts-default package but it's not part of any interceptor stack, so we need to include it manually in our action classes. Read more at [Struts2 token interceptor](/community/tutorials/struts2-token-interceptor-example) example.
Struts2 provides easy integration of log4j API for logging purpose, all we need to have is log4j configuration file in the WEB-INF/classes directory. You can check out the sample project at [Struts2 Log4j integration](/community/tutorials/struts2-and-log4j-integration-example-project).
Struts2 provides a lot of custom tags that we can use in result pages to create views for client request. These tags are broadly divided into three categories- Data tags, Control tags and UI tags. We can use these tags by adding these in JSP pages using taglib directive.
```
<%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s" %>
```
Some of the important Data tags are property, set, push, bean, action, include, i18n and text tag. Read more at [Struts2 Data Tags](/community/tutorials/struts-2-data-tags-example-tutorial). Control tags are used for manipulation and navigation of data from a collection. Some of the important Control tags are if-elseif-else, iterator, append, merge, sort, subset and generator tag. Read more at [Struts2 Control Tags](/community/tutorials/struts-2-control-tags-example-tutorial). Struts2 UI tags are used to generate HTML markup language, binding HTML form data to action classes properties, type conversion, validation, and i18n support. Some of the important UI tags are form, textfield, password, textarea, checkbox, select, radio and submit tag. Read more about them at [Struts2 UI Tags](/community/tutorials/struts-2-ui-tags-form-checkbox-radio-select-submit).
Struts2 support OGNL expression language and it performs two important tasks in Struts 2 – data transfer and type conversion. OGNL is flexible and we can easily extend it to create our own custom converter class. Creating and configuring custom type converter class is very easy. The first step is to fix the input format for the custom class. The second step is to implement the converter class. Type converter classes should implement `com.opensymphony.xwork2.conversion.TypeConverter` interface. Since in web application, we always get the request in form of String and send the response in the form of String, Struts 2 API provides a default implementation of TypeConverter interface, StrutsTypeConverter. StrutsTypeConverter contains two abstract methods – convertFromString to convert String to Object and convertToString to convert Object to String. For implementation details, read [Struts2 OGNL Example Tutorial](/community/tutorials/struts2-ognl).
We can implement `com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.Interceptor` interface to create our own interceptor. Once the interceptor class is ready, we need to define that in struts.xml package where we want to use it. We can also create interceptor stack with our custom interceptor and defaultStack interceptors. After that we can configure it for action classes where we want to use our interceptor. One of the best example of using custom interceptor is to validate session, read more about it at [Struts2 Interceptor Tutorial](/community/tutorials/struts-2-interceptor-example).
Interceptor interface defines three methods - init(), destroy() and intercept(). init and destroy are the life cycle methods of an interceptor. Interceptors are Singleton classes and Struts2 initialize a new thread to handle each request. init() method is called when interceptor instance is created and we can initialize any resources in this method. destroy() method is called when application is shutting down and we can release any resources in this method. intercept() is the method called every time client request comes through the interceptor.
An interceptor stack helps us to group together multiple interceptors in a package for further use. struts-default package creates some of the mostly used interceptor stack - basicStack and defaultStack. We can create our own interceptor stack at the start of the package and then configure our action classes to use it.
struts-default is an abstract package that defines all the Struts2 interceptors and commonly used interceptor stack. It is advisable to extend this package while configuring our application package to avoid configuring interceptors again. This is provided to help developers by eliminating the trivial task of configuring interceptor and result pages in our application.
The default URI suffix for Struts2 action is .action, in Struts1 default suffix was .do. We can change this suffix by defining struts.action.extension constant value in our Struts2 configuration file as:
```
<constant name="struts.action.extension" value="action,do"></constant>
```
By default Struts2 looks for result pages in {WEBAPP-ROOT}/{Namespace}/ directory but sometimes we want to keep result pages in another location, we can provide struts.convention.result.path constant value in Struts2 configuration file to change the result pages location. Another way is to use @ResultPath annotation in action classes to provide the result pages location.
File Upload is one of the common tasks in a web application. That's why Struts2 provides built-in support for file upload through FileUploadInterceptor. This interceptor is configured in the struts-default package and provide options to set the maximum size of a file and file types that can be uploaded to the server. Read more about FileUpload interceptor at [Struts2 File Upload Example](/community/tutorials/struts-2-file-upload-example).
Some of the best practices while developing Struts2 application are:
1. Always try to extend struts-default package while creating your package to avoid code redundancy in configuring interceptors.
2. For common tasks across the application, such as logging request params, try to use interceptors.
3. Always keep action classes java bean properties in a separate bean for code reuse and implement ModelDriven interface.
4. If you have custom interceptor that you will use in multiple actions, create interceptor stack for that and then use it.
5. Try to divide your application in different modules with namespace configuration based on functional areas.
6. Try to use Struts2 tags in result pages for code clarify, if needed create your own type converters.
7. Use development mode for faster development, however make sure production code doesn't run in dev mode.
8. Use Struts2 i18n support for resource bundles and to support localization.
9. Struts2 provides a lot of places where you can have resource bundles but try to keep one global resource bundle and one for action class to avoid confusion.
10. struts-default package configures all the interceptors and creates different interceptor stacks. Try to use only what is needed, for example if you don't have localization requirement, you can avoid i18n interceptor.
Struts2 provides a very robust framework for exception handling. We can specify global results in packages and then map specific exceptions to these result pages. The exception mapping can be done at the global package level as well as the action level. It's a good idea to have exception result pages to provide some information to the user when some unexpected exception occurs that is not processed by the application. The sample configuration in the struts.xml file looks like below.
```
<package name="user" namespace="/" extends="struts-default">
<global-results>
<result name="exception">/exception.jsp</result>
<result name="runtime_exception">/runtime_exception.jsp</result>
<result name="error">/error.jsp</result>
</global-results>
<global-exception-mappings>
<exception-mapping exception="java.lang.Exception" result="exception"></exception-mapping>
<exception-mapping exception="java.lang.Error" result="error"></exception-mapping>
<exception-mapping exception="java.lang.RuntimeException" result="runtime_exception"></exception-mapping>
</global-exception-mappings>
<action name="myaction" class="com.journaldev.struts2.exception.MyAction">
</action>
<action name="myspecialaction" class="com.journaldev.struts2.exception.MySpecialAction">
<exception-mapping exception="java.io.IOException" result="login"></exception-mapping>
<result name="login">/error.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
```
Read more at [Struts2 Exception Handling Example](/community/tutorials/struts2-exception-handling-example-tutorial).
それがStruts2の面接の質問と回答のすべてです。もし見落とした重要な質問があれば、コメントでお知らせください。
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/struts2-interview-questions-and-answers













