ようこそ、Spring 国際化(i18n)チュートリアルへ。世界中のユーザーを対象とした Web アプリケーションでは、国際化(i18n)またはローカリゼーション(L10n)がユーザーとのより良いインタラクションのために非常に重要です。ほとんどの Web アプリケーションフレームワークは、ユーザーのロケール設定に基づいてアプリケーションをローカライズする簡単な方法を提供しています。Spring も同様のパターンに従い、Spring インターセプター、ロケールリゾルバ、および異なるロケールのためのリソースバンドルを使用した国際化(i18n)に対する広範なサポートを提供しています。Java におけるi18nに関するいくつかの以前の記事もあります。
Spring国際化(i18n)
単純なSpring MVCプロジェクトを作成しましょう。ここでは、ユーザーロケールを取得するためにリクエストパラメータを使用し、それに基づいてロケール固有のリソースバンドルから応答ページのラベル値を設定します。

Spring i18n Maven構成
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.journaldev</groupId>
<artifactId>spring</artifactId>
<name>Springi18nExample</name>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>1.0.0-BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<java-version>1.6</java-version>
<org.springframework-version>4.0.2.RELEASE</org.springframework-version>
<org.aspectj-version>1.7.4</org.aspectj-version>
<org.slf4j-version>1.7.5</org.slf4j-version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
<exclusions>
<!-- Exclude Commons Logging in favor of SLF4j -->
<exclusion>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- AspectJ -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>${org.aspectj-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Logging -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.mail</groupId>
<artifactId>mail</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.jms</groupId>
<artifactId>jms</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.sun.jdmk</groupId>
<artifactId>jmxtools</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.sun.jmx</groupId>
<artifactId>jmxri</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- @Inject -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.inject</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.inject</artifactId>
<version>1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Servlet -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.7</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-eclipse-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.9</version>
<configuration>
<additionalProjectnatures>
<projectnature>org.springframework.ide.eclipse.core.springnature</projectnature>
</additionalProjectnatures>
<additionalBuildcommands>
<buildcommand>org.springframework.ide.eclipse.core.springbuilder</buildcommand>
</additionalBuildcommands>
<downloadSources>true</downloadSources>
<downloadJavadocs>true</downloadJavadocs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.6</source>
<target>1.6</target>
<compilerArgument>-Xlint:all</compilerArgument>
<showWarnings>true</showWarnings>
<showDeprecation>true</showDeprecation>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>exec-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.2.1</version>
<configuration>
<mainClass>org.test.int1.Main</mainClass>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
ほとんどのコードはSTSによって自動生成されていますが、Springのバージョンを最新の4.0.2.RELEASEに更新しました。他の依存関係のバージョンを削除または更新することもできますが、シンプルさのためにそのままにしています。
Springリソースバンドル
シンプルにするために、アプリケーションは2つのロケール、enとfrのみをサポートすると仮定しましょう。ユーザーのロケールが指定されていない場合、デフォルトのロケールとして英語を使用します。これらのロケール用のSpringリソースバンドルを作成しましょう。これらはJSPページで使用されます。messages_en.propertiesのコード:
label.title=Login Page
label.firstName=First Name
label.lastName=Last Name
label.submit=Login
messages_fr.propertiesのコード:
label.title=Connectez-vous page
label.firstName=Pr\u00E9nom
label.lastName=Nom
label.submit=Connexion
フランス語のロケールリソースバンドルでは特殊文字をUnicodeで使用していることに注意してください。これにより、クライアントリクエストに送信される応答HTMLで適切に解釈されます。さらに重要な点として、両方のリソースバンドルがアプリケーションのクラスパスにあり、その名前が「messages_{locale}.properties」のパターンになっていることに注意してください。これらが後でなぜ重要なのかを見ていきます。
Spring i18n コントローラークラス
当社のコントローラークラスは非常にシンプルです。ユーザーロケールをログに記録し、home.jspページを応答として返します。
package com.journaldev.spring;
import java.util.Locale;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
/**
* Handles requests for the application home page.
*/
@Controller
public class HomeController {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HomeController.class);
/**
* Simply selects the home view to render by returning its name.
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String home(Locale locale, Model model) {
logger.info("Welcome home! The client locale is {}.", locale);
return "home";
}
}
Spring i18n JSP ページ
私たちのhome.jspページのコードは以下のようになります。
<%@taglib uri="https://www.springframework.org/tags" prefix="spring"%>
<%@ page session="false"%>
<html>
<head>
<title><spring:message code="label.title" /></title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" action="login">
<table>
<tr>
<td><label> <strong><spring:message
code="label.firstName" /></strong>
</label></td>
<td><input name="firstName" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><label> <strong><spring:message
code="label.lastName" /></strong>
</label></td>
<td><input name="lastName" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<spring:message code="label.submit" var="labelSubmit"></spring:message>
<td colspan="2"><input type="submit" value="${labelSubmit}" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
唯一言及する価値があるのは、spring:messageを使用して指定されたコードでメッセージを取得することです。taglib jsp directiveを使用してSpringタグライブラリを設定してください。Springは適切なリソースバンドルメッセージをロードし、JSPページで使用できるようにします。
Spring 国際化 i18n – Bean設定ファイル
Spring Bean設定ファイルは、すべての魔法が起こる場所です。これはSpringフレームワークの美しさであり、私たちが些細なタスクのコーディングではなく、ビジネスロジックにもっと集中できるように助けてくれます。私たちのspring bean設定ファイルがどのように見えるか見てみましょう、そして私たちは一つ一つのbeanを見ていきます。servlet-context.xml コード:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:beans="https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="https://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- DispatcherServlet Context: defines this servlet's request-processing
infrastructure -->
<!-- Enables the Spring MVC @Controller programming model -->
<annotation-driven />
<!-- Handles HTTP GET requests for /resources/** by efficiently serving
up static resources in the ${webappRoot}/resources directory -->
<resources mapping="/resources/**" location="/resources/" />
<!-- Resolves views selected for rendering by @Controllers to .jsp resources
in the /WEB-INF/views directory -->
<beans:bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<beans:property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/" />
<beans:property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</beans:bean>
<beans:bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource">
<beans:property name="basename" value="classpath:messages" />
<beans:property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8" />
</beans:bean>
<beans:bean id="localeResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.CookieLocaleResolver">
<beans:property name="defaultLocale" value="en" />
<beans:property name="cookieName" value="myAppLocaleCookie"></beans:property>
<beans:property name="cookieMaxAge" value="3600"></beans:property>
</beans:bean>
<interceptors>
<beans:bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor">
<beans:property name="paramName" value="locale" />
</beans:bean>
</interceptors>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.journaldev.spring" />
</beans:beans>
-
annotation-drivenタグは、コントローラープログラミングモデルを有効にし、これがなければSpringは私たちのHomeControllerをクライアントリクエストのハンドラーとして認識しません。
-
context:component-scanは、Springが注釈付きコンポーネントを探し、自動的にSpring beanとして登録するパッケージを提供します。
-
messageSourceビーンは、アプリケーションのi18nを有効にするように構成されています。basenameプロパティは、リソースバンドルの場所を指定します。
classpath:messagesは、リソースバンドルがクラスパスにあり、messages_{locale}.propertiesという名前のパターンに従うことを意味します。defaultEncodingプロパティは、メッセージに使用されるエンコーディングを定義するために使用されます。 -
localeResolverビーンのタイプ
org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.CookieLocaleResolverは、クライアントリクエストにクッキーを設定し、その後のリクエストでユーザーロケールを簡単に認識できるようにします。たとえば、Webアプリケーションを初めて起動する際にユーザーにロケールの選択を求め、クッキーを使用してユーザーロケールを識別し、自動的にロケール固有の応答を送信できます。デフォルトのロケール、クッキーの名前、クライアントブラウザによってクッキーが期限切れになる前の最大年齢も指定できます。アプリケーションがユーザーセッションを維持する場合は、ユーザーセッション内のロケール属性を使用するためにorg.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolverをlocaleResolverとして使用できます。設定はCookieLocaleResolverと類似しています。<bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver"> <property name="defaultLocale" value="en" /> </bean>「localeResolver」が登録されていない場合、デフォルトでAcceptHeaderLocaleResolverが使用され、クライアントHTTPリクエストの
accept-languageヘッダーを確認してユーザーロケールを解決します。 -
org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptorインターセプターは、ユーザーリクエストをインターセプトしてユーザーのロケールを識別するように構成されています。パラメーター名は設定可能で、私たちはロケールのリクエストパラメーター名として「locale」を使用しています。このインターセプターがないと、ユーザーのロケールを変更して新しいロケール設定に基づいて応答を送信することができません。これはinterceptors要素の一部である必要があります。さもないと、Springはそれをインターセプターとして構成しません。
Springフレームワークに私たちのコンテキスト設定をロードするように指示する構成について疑問がある場合は、MVCアプリケーションのデプロイメント記述子に存在します。
<servlet>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/appServlet/servlet-context.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
私たちは、web.xmlの構成を変更することで、コンテキストファイルの場所や名前を変更できます。Springのi18nアプリケーションは準備ができており、任意のサーブレットコンテナに展開するだけです。通常、スタンドアロンのTomcatウェブサーバーのwebappsディレクトリにWARファイルとしてエクスポートします。以下は、異なるロケールでのアプリケーションホームページのスクリーンショットです。デフォルトのホームページ(enロケール): 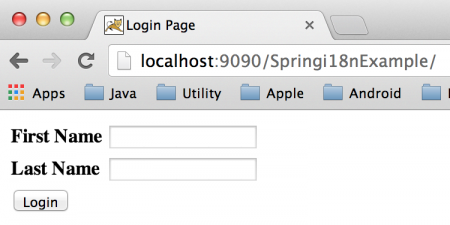 パラメータとしてロケールを渡す(frロケール):
パラメータとしてロケールを渡す(frロケール): 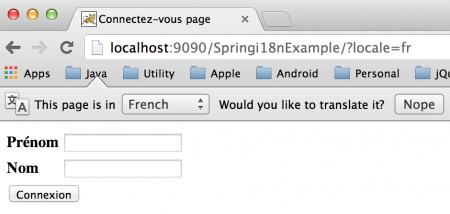 ロケールなしでの追加のリクエスト:
ロケールなしでの追加のリクエスト: 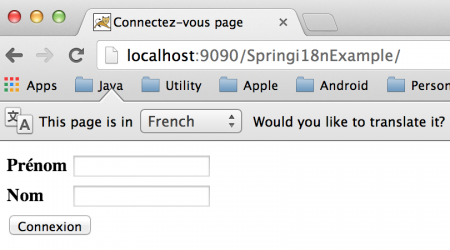 上記の画像でわかるように、クライアントリクエストでロケール情報を渡していませんが、アプリケーションはユーザーのロケールを特定しています。これは、Springビーン構成ファイルで構成したCookieLocaleResolverビーンのおかげです。ただし、ブラウザのクッキーデータを確認して確認できます。私はChromeを使用しており、以下の画像はアプリケーションによって保存されたクッキーデータを示しています。
上記の画像でわかるように、クライアントリクエストでロケール情報を渡していませんが、アプリケーションはユーザーのロケールを特定しています。これは、Springビーン構成ファイルで構成したCookieLocaleResolverビーンのおかげです。ただし、ブラウザのクッキーデータを確認して確認できます。私はChromeを使用しており、以下の画像はアプリケーションによって保存されたクッキーデータを示しています。 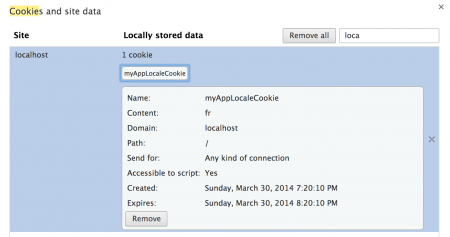 クッキーの有効期限が1時間、つまりcookieMaxAgeプロパティで設定された3600秒であることに注意してください。サーバーログを確認すると、ロケールがログに記録されていることがわかります。
クッキーの有効期限が1時間、つまりcookieMaxAgeプロパティで設定された3600秒であることに注意してください。サーバーログを確認すると、ロケールがログに記録されていることがわかります。
INFO : com.journaldev.spring.HomeController - Welcome home! The client locale is en.
INFO : com.journaldev.spring.HomeController - Welcome home! The client locale is fr.
INFO : com.journaldev.spring.HomeController - Welcome home! The client locale is fr.
それでSpring i18nの例題アプリケーションは以上です。以下のリンクから例題プロジェクトをダウンロードして、さらに詳しく学んでみてください。













