ようこそSpring MVCの例へ。以前、Spring MVCチュートリアルで、Spring Tool Suiteを使用してSpring MVCアプリケーションを作成する方法を説明しました。しかし、今日は、MavenとEclipseを使用して基本的なhello world spring MVCアプリケーションを作成します。
Spring MVCの例
Spring MVCは、モデルビューコントローラーアーキテクチャに基づいています。以下のイメージは、高レベルでのSpring MVCのアーキテクチャを示しています。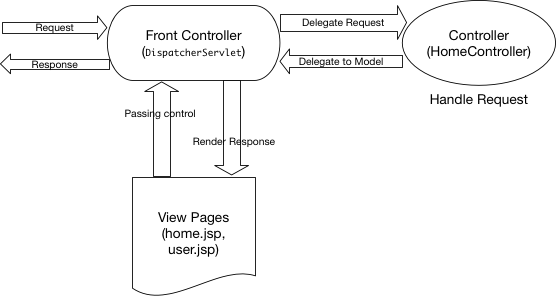
DispatcherServletは、すべてのリクエストを受け取り、処理を開始するフロントコントローラークラスです。これはweb.xmlファイルで構成する必要があります。その役割は、リクエストを適切なコントローラークラスに渡し、ビューページがレスポンスページをレンダリングしたときに応答を送信することです。 HomeController.javaは、当社のspring mvcの例アプリケーションでの唯一のコントローラークラスになります。 home.jsp、user.jspは、当社のspring mvc hello worldの例アプリケーションのビューページです。 User.javaは、当社のspring mvcの例のWebアプリケーションで唯一のモデルクラスになります。
Spring MVCの例 こんにちは 世界 エクリプス プロジェクト
以下の画像は、EclipseでのSpring MVCの例プロジェクトを示しています。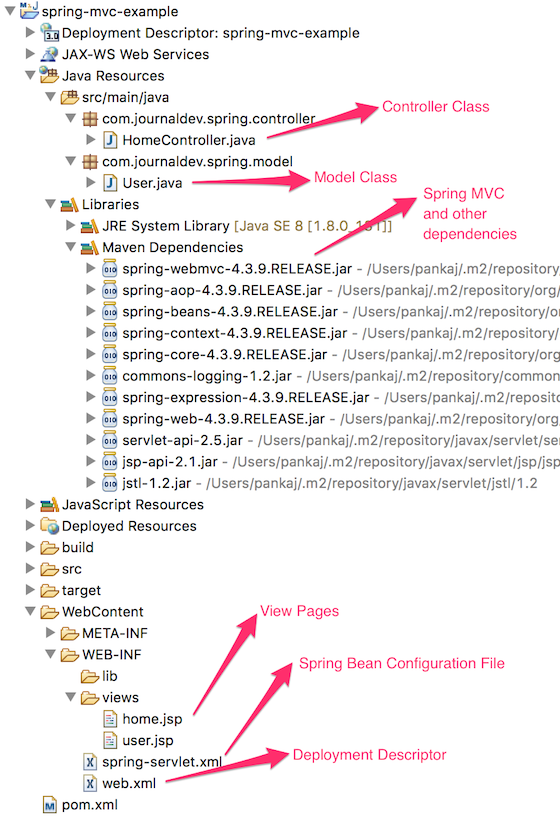 さあ始めましょう。ゼロからプロジェクトを作成しましょう。
さあ始めましょう。ゼロからプロジェクトを作成しましょう。
Spring MVCの例 Eclipseプロジェクトのセットアップ
 WebアプリケーションでMavenを依存関係の管理に使用したい場合、まず動的Webアプリケーションを作成し、それをMavenプロジェクトに変換する必要があります。以下の画像は、これを行い、プロジェクトの骨組みを整える方法を示しています。プロジェクトエクスプローラーウィンドウで右クリックし、「新規 -> Dynamic Web Project」をクリックします(以下の画像参照)。
WebアプリケーションでMavenを依存関係の管理に使用したい場合、まず動的Webアプリケーションを作成し、それをMavenプロジェクトに変換する必要があります。以下の画像は、これを行い、プロジェクトの骨組みを整える方法を示しています。プロジェクトエクスプローラーウィンドウで右クリックし、「新規 -> Dynamic Web Project」をクリックします(以下の画像参照)。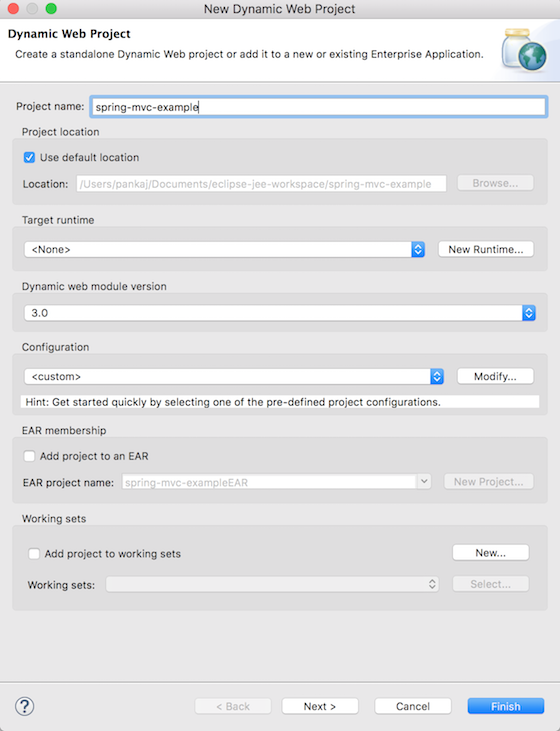 次に表示されるポップアップページで、名前を「spring-mvc-example」と入力し、その他の設定は変更する必要はありません。
次に表示されるポップアップページで、名前を「spring-mvc-example」と入力し、その他の設定は変更する必要はありません。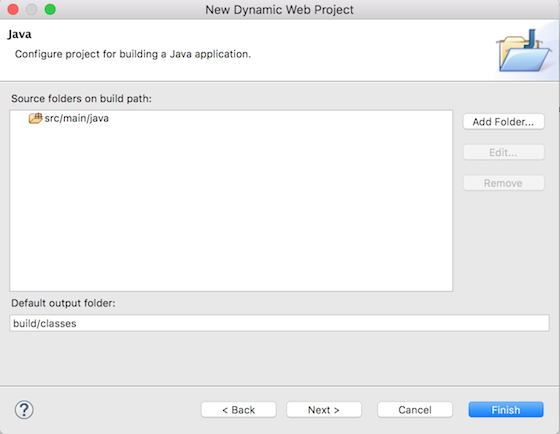 次のページで、ソースフォルダーを「src/main/java」として指定します。これを追加する前にリストから「src」フォルダーを削除する必要があるかもしれません。
次のページで、ソースフォルダーを「src/main/java」として指定します。これを追加する前にリストから「src」フォルダーを削除する必要があるかもしれません。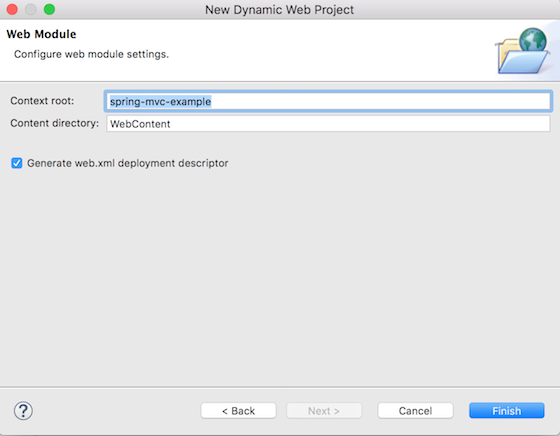 次はWebモジュールページで、アプリケーションのコンテキストルートを「spring-mvc-example」として指定し、「web.xmlデプロイ記述子を生成」オプションを確認してください。Finishをクリックすると、Eclipseのプロジェクトエクスプローラーに新しいDynamic Web Projectが作成されます。
次はWebモジュールページで、アプリケーションのコンテキストルートを「spring-mvc-example」として指定し、「web.xmlデプロイ記述子を生成」オプションを確認してください。Finishをクリックすると、Eclipseのプロジェクトエクスプローラーに新しいDynamic Web Projectが作成されます。
ダイナミックWebプロジェクトをMavenプロジェクトに変換する
Spring MVCの依存関係を簡単に管理するためにMavenを使用したいです。ですので、WebプロジェクトをMavenに変換しましょう。プロジェクトを右クリックし、「Configure -> Maven Projectに変換」を選択します。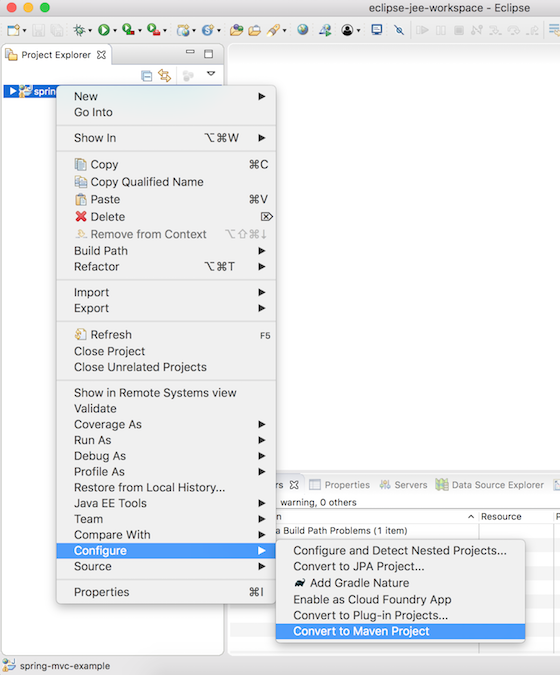 次に、以下に示すようにpom.xmlの設定を提供します。
次に、以下に示すようにpom.xmlの設定を提供します。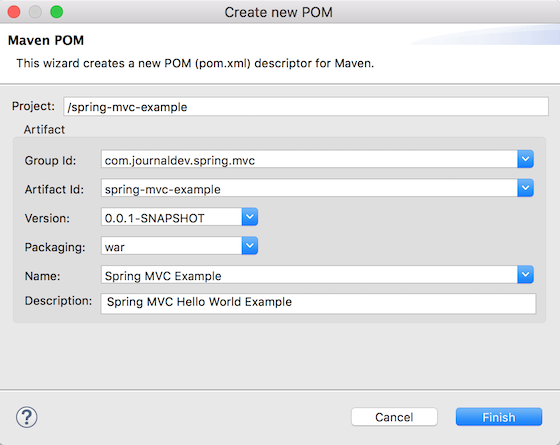 私たちのMavenウェブアプリケーションプロジェクトのスケルトンコードは準備ができています。これで、変更を加えてSpring MVCのハローワールドの例アプリケーションを作成できます。
私たちのMavenウェブアプリケーションプロジェクトのスケルトンコードは準備ができています。これで、変更を加えてSpring MVCのハローワールドの例アプリケーションを作成できます。
pom.xmlにSpring MVCの依存関係を追加
pom.xmlにspring-webとspring-webmvcの依存関係を追加する必要があります。また、servlet-api、jsp-api、およびjstlの依存関係も追加してください。最終的なpom.xmlファイルは以下のようになります。
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.journaldev.spring.mvc</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-mvc-example</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>Spring MVC Example</name>
<description>Spring MVC Hello World Example</description>
<!-- Add Spring Web and MVC dependencies -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>4.3.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>4.3.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Servlet -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.6.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
<configuration>
<warSourceDirectory>WebContent</warSourceDirectory>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName> <!-- added to remove Version from WAR file -->
</build>
</project>
ビルドの中でfinalName構成を注意してください。プロジェクトがEclipseによってビルドされると、すべてのJARがMavenの依存関係セクションに表示されることに注意してください。
Spring MVCディスパッチャーサーブレットをフロントコントローラーとして
Spring MVCフレームワークをWebアプリケーションに追加する必要があります。そのためには、以下に示すようにweb.xmlでDispatcherServletを構成する必要があります。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="https://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="https://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee https://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<display-name>spring-mvc-example</display-name>
<!-- Add Spring MVC DispatcherServlet as front controller -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>spring</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>spring</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
contextConfigLocation init-paramは、Spring Bean構成ファイルの場所を提供するために使用されます。
Spring MVCの例のBean構成ファイル
次のステップは、次に示すようにSpring Bean構成ファイルspring-servlet.xmlを作成することです。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:beans="https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="https://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- DispatcherServlet Context: defines this servlet's request-processing
infrastructure -->
<!-- Enables the Spring MVC @Controller programming model -->
<annotation-driven />
<context:component-scan base-package="com.journaldev.spring" />
<!-- Resolves views selected for rendering by @Controllers to .jsp resources
in the /WEB-INF/views directory -->
<beans:bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<beans:property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/" />
<beans:property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</beans:bean>
</beans:beans>
3つの重要な構成があります。
annotation-drivenは、@Controllerアノテーションを使用してコントローラークラスを検索するようにDispatcherServletに指示します。context:component-scanは、DispatcherServletがコントローラークラスを探す場所を指定します。InternalResourceViewResolverビーン構成を使用して、ビューページの場所と使用されるサフィックスを指定します。コントローラークラスのメソッドはビューページの名前を返し、その後、レスポンスをレンダリングするために使用するビューページを特定するためにサフィックスが追加されます。
Spring MVCコントローラークラス
ホームページ用の「/」とユーザーページ用の「/user」の2つのURIに応答する単一のコントローラークラスがあります。
package com.journaldev.spring.controller;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Locale;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import com.journaldev.spring.model.User;
@Controller
public class HomeController {
/**
* Simply selects the home view to render by returning its name.
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String home(Locale locale, Model model) {
System.out.println("Home Page Requested, locale = " + locale);
Date date = new Date();
DateFormat dateFormat = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.LONG, DateFormat.LONG, locale);
String formattedDate = dateFormat.format(date);
model.addAttribute("serverTime", formattedDate);
return "home";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String user(@Validated User user, Model model) {
System.out.println("User Page Requested");
model.addAttribute("userName", user.getUserName());
return "user";
}
}
シンプルさのために、log4jなどのロギングフレームワークは使用していません。
Spring MVCモデルクラス
単一の変数とそのgetter-setterメソッドを持つ単純なモデルクラスがあります。これは単純なPOJOクラスです。
package com.journaldev.spring.model;
public class User {
private String userName;
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
}
Spring MVCビューページ
以下に定義された2つのビューページがあります。home.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri="https://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<%@ page session="false"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Home</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello world!</h1>
<P>The time on the server is ${serverTime}.</p>
<form action="user" method="post">
<input type="text" name="userName"><br> <input
type="submit" value="Login">
</form>
</body>
</html>
user.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "https://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>User Home Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Hi ${userName}</h3>
</body>
</html>
注意してください、Spring MVCはフォーム変数をモデルクラスの変数にマッピングするため、両方の場所に同じ変数名があるのです。これで、Spring MVCの例題プロジェクトが展開されてテストする準備が整いました。
Spring MVC Eclipseプロジェクトの展開
私たちは、EclipseのWARファイルとしてエクスポートするオプションを使用して、それを直接実行中のTomcatサーバーのwebappsディレクトリに展開できます。ただし、プロジェクトをビルドしてから、お気に入りのサーブレットコンテナの展開ディレクトリにコピーするために、コマンドラインも使用できます。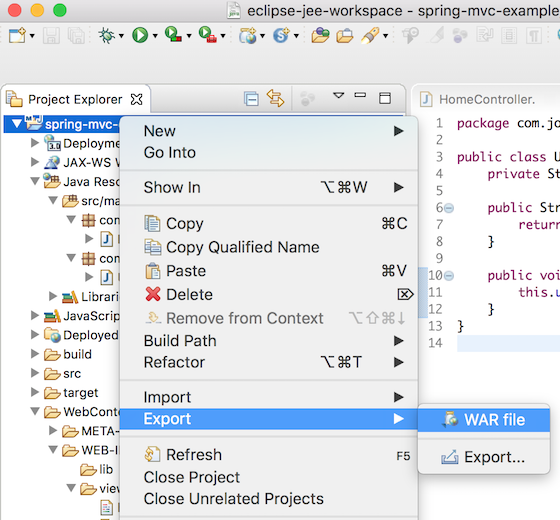
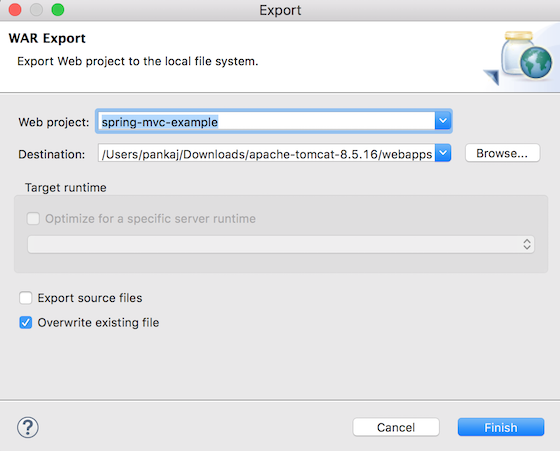
Spring MVCの例題テスト
一度Spring MVCプロジェクトが展開されると、ホームページにはhttps://localhost:8080/spring-mvc-example/からアクセスできます。Tomcatポートとコンテキストルートを適切に変更してください。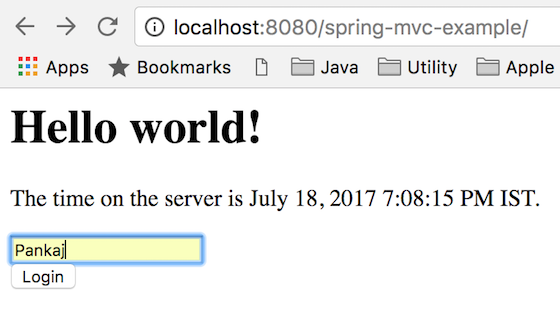
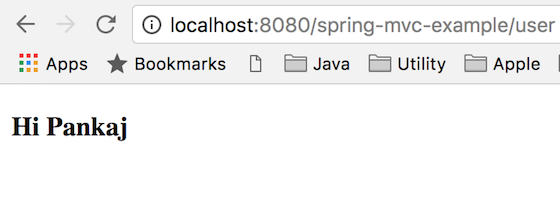 これでSpring MVCの例はすべてです。できるだけシンプルに保つように努めましたが、何か問題が発生した場合はコメントでお知らせください。お手伝いさせていただきます。最終的なSpring MVCの例プロジェクトは以下のリンクからダウンロードできます。
これでSpring MVCの例はすべてです。できるだけシンプルに保つように努めましたが、何か問題が発生した場合はコメントでお知らせください。お手伝いさせていただきます。最終的なSpring MVCの例プロジェクトは以下のリンクからダウンロードできます。
参考文献:公式ページ
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/spring-mvc-example













