JUnit5チュートリアル
このJUnitチュートリアルでは、例を使用してJUnit5の基礎と新機能を紹介します。Javaの世界では、JUnitはJavaコードに対してユニットテストを実装するために使用される人気のあるフレームワークの一つです。JUnitは主に開発者がJVM上で自分自身でコードをテストするのに役立ちます。
JUnit5のアーキテクチャ
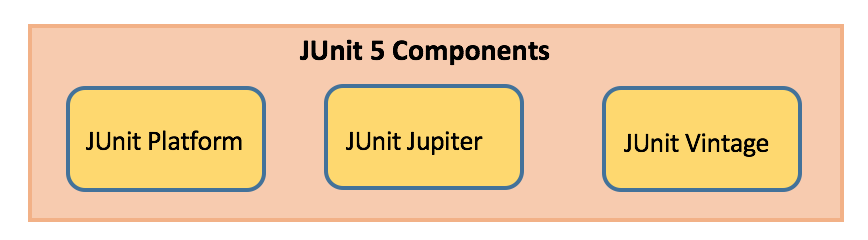
JUnitプラットフォーム
- JUnitプラットフォーム上でテストフレームワークを起動します。
- JUnitプラットフォーム上で実行されるテストフレームワークを構築するために使用されるTestEngine APIを持っています。
JUnit Jupiter
- テストを書くための新しいプログラミングモデルと拡張モデルの組み合わせです。
- 新しい注釈の追加、例えば
@BeforeEach、@AfterEach、@AfterAll、@BeforeAllなど。
JUnit Vintage
- この新しいプラットフォームで以前のJUnitバージョン3および4のテストを実行するためのサポートを提供します。
JUnit Maven Dependencies
プロジェクトのpom.xmlファイルに以下の依存関係を追加して、JUnit5ベースのテストケースを実装します。
- JUnit 5 ライブラリ
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>5.1.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-runner</artifactId>
<version> 1.1.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
- JUnit5 Maven Surefireプロバイダーは、IDEがJUnit5のサポートを持っていない場合に単体テストを実行するために使用します(IDEがサポートしている場合、このポイントは不要です)
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.19.1</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-surefire-provider</artifactId>
<version>1.0.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>
JUnit5の新機能
ランタイムでJava 8以上が必要ですが、以前のJavaバージョンでコンパイルされたコードをテストすることもできます。さまざまな新機能が導入されています。
JUnitアノテーション
以下には、一般的に使用されるいくつかのアノテーションが示されています:
| Annotation | Description |
|---|---|
| @Test | Denotes a test method |
| @DisplayName | Declares a custom display name for the test class or test method |
| @BeforeEach | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed before each test method |
| @AfterEach | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed after each test method |
| @BeforeAll | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed before all test methods |
| @AfterAll | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed after all test methods |
| @Disable | Used to disable a test class or test method |
| @Nested | Denotes that the annotated class is a nested, non-static test class |
| @Tag | Declare tags for filtering tests |
| @ExtendWith | Register custom extensions |
package com.journaldev;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Disabled;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class JUnit5Sample1Test {
@BeforeAll
static void beforeAll() {
System.out.println("**--- Executed once before all test methods in this class ---**");
}
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
System.out.println("**--- Executed before each test method in this class ---**");
}
@Test
void testMethod1() {
System.out.println("**--- Test method1 executed ---**");
}
@DisplayName("Test method2 with condition")
@Test
void testMethod2() {
System.out.println("**--- Test method2 executed ---**");
}
@Test
@Disabled("implementation pending")
void testMethod3() {
System.out.println("**--- Test method3 executed ---**");
}
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
System.out.println("**--- Executed after each test method in this class ---**");
}
@AfterAll
static void afterAll() {
System.out.println("**--- Executed once after all test methods in this class ---**");
}
}
上記のJUnitテストクラスを実行するには、Eclipse -> 実行 -> JUnitテストで実行できます。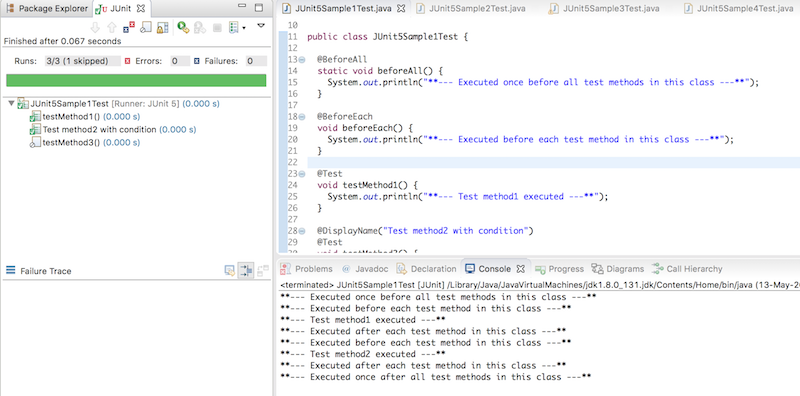
JUnitアサーション
すべてのテストメソッドは、アサーションを使用して条件が真であるか評価される必要があります。JUnit Jupiterのアサーションは、org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertionsクラスに格納されています。すべてのメソッドは静的です。
| Assertion | Description |
|---|---|
| assertEquals(expected, actual) | Fails when expected does not equal actual |
| assertFalse(expression) | Fails when expression is not false |
| assertNull(actual) | Fails when actual is not null |
| assertNotNull(actual) | Fails when actual is null |
| assertAll() | Group many assertions and every assertion is executed even if one or more of them fails |
| assertTrue(expression) | Fails if expression is not true |
| assertThrows() | Class to be tested is expected to throw an exception |
@Test
void testAssertEqual() {
assertEquals("ABC", "ABC");
assertEquals(20, 20, "optional assertion message");
assertEquals(2 + 2, 4);
}
@Test
void testAssertFalse() {
assertFalse("FirstName".length() == 10);
assertFalse(10 > 20, "assertion message");
}
@Test
void testAssertNull() {
String str1 = null;
String str2 = "abc";
assertNull(str1);
assertNotNull(str2);
}
@Test
void testAssertAll() {
String str1 = "abc";
String str2 = "pqr";
String str3 = "xyz";
assertAll("numbers",
() -> assertEquals(str1,"abc"),
() -> assertEquals(str2,"pqr"),
() -> assertEquals(str3,"xyz")
);
//以下のコードのコメントを解除し、各アサートの実行を理解してください。
/*assertAll("numbers",
() -> assertEquals(str1,"abc"),
() -> assertEquals(str2,"pqr1"),
() -> assertEquals(str3,"xyz1")
);*/
}
@Test
void testAssertTrue() {
assertTrue("FirstName".startsWith("F"));
assertTrue(10 {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Argument Exception occured");
});
assertEquals("Illegal Argument Exception occured", exception.getMessage());
}
JUnit5のインポート
JUnitのテストクラスにはorg.junit.jupiter.api.Testのインポート文を使用し、org.junit.Testは使用しません。また、テストメソッドはpublicである必要はありませんし、ローカルパッケージにする必要もありません。
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
JUnit5のAssumptions
Assumptionsは、org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptionsクラスの静的メソッドです。指定された条件が満たされている場合にのみテストが実行され、それ以外の場合は中止されます。中止されたテストはビルドの失敗を引き起こしません。Assumptionsが失敗すると、org.opentest4j.TestAbortedExceptionがスローされ、テストはスキップされます。
| Assumptions | Description |
|---|---|
| assumeTrue | Execute the body of lamda when the positive condition hold else test will be skipped |
| assumeFalse | Execute the body of lamda when the negative condition hold else test will be skipped |
| assumingThat | Portion of the test method will execute if an assumption holds true and everything after the lambda will execute irrespective of the assumption in assumingThat() holds |
@Test
void testAssumeTrue() {
boolean b = 'A' == 'A';
assumeTrue(b);
assertEquals("Hello", "Hello");
}
@Test
@DisplayName("test executes only on Saturday")
public void testAssumeTrueSaturday() {
LocalDateTime dt = LocalDateTime.now();
assumeTrue(dt.getDayOfWeek().getValue() == 6);
System.out.println("further code will execute only if above assumption holds true");
}
@Test
void testAssumeFalse() {
boolean b = 'A' != 'A';
assumeFalse(b);
assertEquals("Hello", "Hello");
}
@Test
void testAssumeFalseEnvProp() {
System.setProperty("env", "prod");
assumeFalse("dev".equals(System.getProperty("env")));
System.out.println("further code will execute only if above assumption hold");
}
@Test
void testAssumingThat() {
System.setProperty("env", "test");
assumingThat("test".equals(System.getProperty("env")),
() -> {
assertEquals(10, 10);
System.out.println("perform below assertions only on the test env");
});
assertEquals(20, 20);
System.out.println("perform below assertions on all env");
}
JUnitのネストされたテストクラス
ネストされたテストでは、ネストしたクラスを作成し、そのすべてのテストメソッドを実行できます。内部クラスは非静的である必要があります。内部クラスに@Nestedアノテーションを付けるだけで、その内部のすべてのテストメソッドが実行されます。
@BeforeAll
static void beforeAll() {
System.out.println("**--- JUnit5Sample4Test :: beforeAll :: Executed once before all test methods ---**");
}
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
System.out.println("**--- JUnit5Sample4Test :: beforeEach :: Executed before each test method ---**");
}
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
System.out.println("**--- JUnit5Sample4Test :: afterEach :: Executed after each test method ---**");
}
@AfterAll
static void afterAll() {
System.out.println("**--- JUnit5Sample4Test :: afterAll :: Executed after all test method ---**");
}
@Nested
class InnerClass {
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
System.out.println("**--- InnerClass :: beforeEach :: Executed before each test method ---**");
}
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
System.out.println("**--- InnerClass :: afterEach :: Executed after each test method ---**");
}
@Test
void testMethod1() {
System.out.println("**--- InnerClass :: testMethod1 :: Executed test method1 ---**");
}
@Nested
class InnerMostClass {
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
System.out.println("**--- InnerMostClass :: beforeEach :: Executed before each test method ---**");
}
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
System.out.println("**--- InnerMostClass :: afterEach :: Executed after each test method ---**");
}
@Test
void testMethod2() {
System.out.println("**--- InnerMostClass :: testMethod2 :: Executed test method2 ---**");
}
}
}
JUnitのテスト例外
特定の条件の下でメソッドが例外をスローすることが期待される状況があります。assertThrowsは、指定された例外がスローされない場合にテストを失敗させます。
Throwable exception = assertThrows(IllegalArgumentException.class, () -> {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Argument Exception occured");
});
assertEquals("Illegal Argument Exception occured", exception.getMessage());
JUnitテストの実行
ユニットテストはさまざまな方法で実行できますが、以下の2つの方法があります:
- Eclipse IDE Oxygen.3a (4.7.3a) Releaseを使用し、実行するテストファイルを開きます。ファイルを右クリックし、「実行」を選択してから「JUnitテスト」を選択します。
- Windowsコマンドプロンプトでmvn testコマンドを使用します。
概要
JUnit5およびその新機能についていくつかの例を示しました。また、JUnitのアノテーション、アサーション、アサンプション、例外の使用方法やネストされたテストクラスの作成方法も説明しました。
完全なサンプルプロジェクトは、GitHubリポジトリからダウンロードできます。
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/junit5-tutorial













