Benvenuti alle domande e risposte dell’intervista JDBC. L’API JDBC viene utilizzata per connettersi a database relazionali ed eseguire query SQL da programmi Java. Negli ultimi articoli, abbiamo appreso dell’API JDBC e delle sue caratteristiche importanti. Questo articolo mira a fornire alcune delle importanti domande di intervista JDBC con risposte per aiutarti nell’intervista Java.
Domande di intervista JDBC

- Cos’è l’API JDBC e quando la usiamo?
- Quali sono i diversi tipi di driver JDBC?
- Come ci aiuta l’API JDBC a raggiungere il coupling flessibile tra il programma Java e l’API dei driver JDBC?
- Cosa è la connessione JDBC? Spiega i passaggi per ottenere una connessione al database in un semplice programma Java.
- A cosa serve la classe JDBC DriverManager?
- Come ottenere i dettagli del server del database in un programma Java?
- Cos’è lo statement JDBC?
- Qual è la differenza tra execute, executeQuery, executeUpdate?
- Cos’è PreparedStatement JDBC?
- Come impostare i valori NULL in PreparedStatement JDBC?
- Qual è l’uso del metodo getGeneratedKeys() in Statement?
- Quali sono i vantaggi di PreparedStatement rispetto a Statement?
- Qual è il limite di PreparedStatement e come superarlo?
- Cos’è ResultSet in JDBC?
- Quali sono i diversi tipi di ResultSet?
- Qual è l’uso dei metodi setFetchSize() e setMaxRows() in Statement?
- Come utilizzare l’API JDBC per chiamare le Stored Procedure?
- Cos’è l’elaborazione batch JDBC e quali sono i suoi vantaggi?
- Cos’è la gestione delle transazioni JDBC e perché ne abbiamo bisogno?
- Come eseguire il rollback di una transazione JDBC?
- Cos’è un Savepoint JDBC? Come si utilizza?
- Cos’è DataSource JDBC e quali sono i suoi vantaggi?
- Come ottenere il pooling delle connessioni JDBC utilizzando DataSource JDBC e JNDI in Apache Tomcat Server?
- Cos’è l’API Apache DBCP?
- Quali sono i livelli di isolamento della connessione JDBC?
- Cos’è RowSet JDBC? Quali sono i diversi tipi di RowSet?
- Cosa differisce tra ResultSet e RowSet?
- Quali sono le eccezioni JDBC comuni?
- Cosa sono i tipi di dati CLOB e BLOB in JDBC?
- Cosa significa “lettura sporca” in JDBC? Quale livello di isolamento previene la lettura sporca?
- Cosa significa “commit a due fasi”?
- Quali sono i diversi tipi di locking in JDBC?
- Cosa si intende per istruzioni DDL e DML?
- Qual è la differenza tra java.util.Date e java.sql.Date?
- Come inserire un’immagine o dati grezzi nel database?
- Cosa sono la lettura fantasma e quale livello di isolamento la previene?
- Cosa sono gli avvisi SQL? Come recuperare gli avvisi SQL nel programma JDBC?
- Come invocare una procedura memorizzata Oracle con oggetti di database come IN/OUT?
- Quando otteniamo java.sql.SQLException: Nessun driver adatto trovato?
- Quali sono le migliori pratiche JDBC?
Domande e Risposte sull’Intervista JDBC
-
Cos’è l’API JDBC e quando la utilizziamo?
Java DataBase Connectivity API ci consente di lavorare con database relazionali. Le interfacce e le classi dell’API JDBC fanno parte del pacchetto
java.sqlejavax.sql. Possiamo utilizzare l’API JDBC per ottenere la connessione al database, eseguire query SQL e stored procedure nel server del database e elaborare i risultati. L’API JDBC è progettata per consentire un accoppiamento lento tra il nostro programma Java e i driver JDBC effettivi che semplificano lo switching da un database all’altro. -
Quali sono i diversi tipi di driver JDBC?
Esistono quattro tipi di driver JDBC. Qualsiasi programma Java che interagisce con un database è composto da due parti: la prima parte è l’API JDBC e la seconda è il driver che svolge il lavoro effettivo.
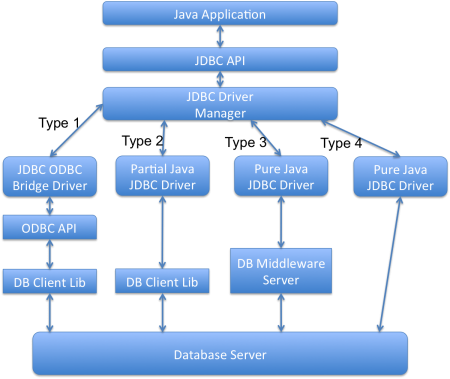
- JDBC-ODBC Bridge più driver ODBC (Tipo 1): Utilizza il driver ODBC per connettersi al database. Dobbiamo avere i driver ODBC installati per la connessione al database, motivo per cui questo driver è quasi obsoleto.
- Driver abilitato alla tecnologia Java API nativa (Tipo 2): Questo driver converte la classe JDBC nell’API client per i server di database. Dobbiamo avere installata l’API client del database. A causa della dipendenza aggiuntiva dai driver dell’API client del database, questo driver non è preferito.
- Driver Java puro per middleware del database (Tipo 3): Questo driver invia le chiamate JDBC a un server di middleware in grado di connettersi a diversi tipi di database. Dobbiamo avere un server di middleware installato per lavorare con questo driver. Ciò comporta chiamate di rete aggiuntive e prestazioni lente, motivo per cui questo driver JDBC non è ampiamente utilizzato.
- Driver Java puro diretto al database (Tipo 4): Questo driver converte le chiamate JDBC nel protocollo di rete compreso dal server del database. Questa soluzione è semplice e adatta per la connettività del database via rete. Tuttavia, per questa soluzione, dovremmo utilizzare driver specifici del database, ad esempio i file JAR OJDBC di Oracle per Oracle DB e MySQL Connector/J per i database MySQL.
-
Come la JDBC API ci aiuta a ottenere un accoppiamento scarso tra il programma Java e la JDBC Drivers API?
La JDBC API utilizza la Java Reflection API per ottenere un accoppiamento scarso tra i programmi Java e i driver JDBC. Se guardi un semplice esempio di JDBC, noterai che tutta la programmazione è fatta in termini di JDBC API e il driver entra in gioco solo quando viene caricato tramite reflection utilizzando il metodo
Class.forName(). Penso che questo sia uno dei migliori esempi di utilizzo della Reflection nelle classi core di Java per assicurarci che la nostra applicazione non lavori direttamente con la JDBC Drivers API, rendendo molto semplice il passaggio da un database all’altro. Per ulteriori informazioni, leggi di più nell’Esempio JDBC. -
Cosa è la connessione JDBC? Spiega i passaggi per ottenere una connessione al database in un semplice programma Java.
La connessione JDBC è simile a una sessione creata con il server del database. Puoi anche pensare che la connessione sia come una connessione Socket dal server del database. Creare una connessione JDBC è molto facile e richiede due passaggi:
- Registra e carica il driver: Utilizzando
Class.forName(), la classe del driver viene registrata nel DriverManager e caricata in memoria. - Usa il DriverManager per ottenere l’oggetto Connection: Otteniamo l’oggetto connessione da
DriverManager.getConnection()passando la stringa dell’URL del database, il nome utente e la password come argomenti.
Connection con = null; try{ // carica la classe del driver Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // crea la connessione ora con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/UserDB", "pankaj", "pankaj123"); }catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println("Controlla che il database sia acceso e le configurazioni siano corrette"); e.printStackTrace(); }catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("Includi il jar JDBC MySQL nel classpath"); e.printStackTrace(); } - Registra e carica il driver: Utilizzando
-
Che uso ha la classe JDBC DriverManager?
JDBC `DriverManager` is the factory class through which we get the Database Connection object. When we load the JDBC Driver class, it registers itself to the DriverManager, you can look up the JDBC Driver classes source code to check this. Then when we call `DriverManager.getConnection()` method by passing the database configuration details, DriverManager uses the registered drivers to get the Connection and return it to the caller program.
We can use `DatabaseMetaData` object to get the database server details. When the database connection is created successfully, we can get the meta data object by calling `getMetaData()` method. There are so many methods in DatabaseMetaData that we can use to get the database product name, it's version and configuration details.
```
DatabaseMetaData metaData = con.getMetaData();
String dbProduct = metaData.getDatabaseProductName();
```
JDBC API `Statement` is used to execute SQL queries in the database. We can create the Statement object by calling Connection `createStatement()` method. We can use Statement to execute static SQL queries by passing query through different execute methods such as execute(), executeQuery(), executeUpdate() etc. Since the query is generated in the java program, if the user input is not properly validated it can lead to SQL injection issue, more details can be found at [SQL Injection Example](/community/tutorials/jdbc-statement-vs-preparedstatement-sql-injection-example). By default, only one ResultSet object per Statement object can be open at the same time. Therefore, if we want to work with multiple ResultSet objects, then each must have been generated by different Statement objects. All execute() methods in the Statement interface implicitly close a statment's current ResultSet object if an open one exists.
Statement `execute(String query)` is used to execute any SQL query and it returns TRUE if the result is an ResultSet such as running Select queries. The output is FALSE when there is no ResultSet object such as running Insert or Update queries. We can use `getResultSet()` to get the ResultSet and `getUpdateCount()` method to retrieve the update count. Statement `executeQuery(String query)` is used to execute Select queries and returns the ResultSet. ResultSet returned is never null even if there are no records matching the query. When executing select queries we should use the executeQuery method so that if someone tries to execute insert/update statement it will throw java.sql.SQLException with message "executeQuery method cannot be used for update". Statement executeUpdate(String query) is used to execute Insert/Update/Delete (DML) statements or DDL statements that returns nothing. The output is int and equals the row count for SQL Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements. For DDL statements, the output is 0. You should use execute() method only when you are not sure about the type of statement else use executeQuery or executeUpdate method.
JDBC `PreparedStatement` object represents a precompiled SQL statement. We can use it's setter method to set the variables for the query. Since PreparedStatement is precompiled, it can then be used to efficiently execute this statement multiple times. PreparedStatement is better choice that Statement because it automatically escapes the special characters and avoid SQL injection attacks.
We can use PreparedStatement setNull() method to bind the null variable to a parameter. The setNull method takes index and SQL Types as argument, for example `ps.setNull(10, java.sql.Types.INTEGER);`.
Sometimes a table can have auto generated keys used to insert the unique column value for primary key. We can use Statement `getGeneratedKeys()` method to get the value of this auto generated key.
Some of the benefits of PreparedStatement over Statement are:
- PreparedStatement helps us in preventing SQL injection attacks because it automatically escapes the special characters.
- PreparedStatement allows us to execute dynamic queries with parameter inputs.
- PreparedStatement is faster than Statement. It becomes more visible when we reuse the PreparedStatement or use it’s batch processing methods for executing multiple queries.
- PreparedStatement helps us in writing object Oriented code with setter methods whereas with Statement we have to use String Concatenation to create the query. If there are multiple parameters to set, writing Query using String concatenation looks very ugly and error prone.
One of the limitation of PreparedStatement is that we can't use it directly with IN clause statements. Some of the alternative approaches to use PreparedStatement with IN clause are;
1. **Execute Single Queries** - very slow performance and not recommended
2. **Using Stored Procedure** - Database specific and hence not suitable for multiple database applications.
3. **Creating PreparedStatement Query dynamically** - Good approach but looses the benefit of cached PreparedStatement.
4. **Using NULL in PreparedStatement Query** - A good approach when you know the maximum number of variables inputs, can be extended to allow unlimited parameters by executing in parts.
A more detailed analysis can be found at [JDBC PreparedStatement IN clause alternatives](/community/tutorials/java-preparedstatement-in-clause-alternatives).
JDBC `ResultSet` is like a table of data representing a database result set, which is usually generated by executing a statement that queries the database. ResultSet object maintains a cursor pointing to its current row of data. Initially, the cursor is positioned before the first row. The next() method moves the cursor to the next row. If there are no more rows, next() method returns false and it can be used in a while loop to iterate through the result set. A default ResultSet object is not updatable and has a cursor that moves forward only. Thus, you can iterate through it only once and only from the first row to the last row. It is possible to produce ResultSet objects that are scrollable and/or updatable using below syntax.
```
Statement stmt = con.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,
ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);
```
A ResultSet object is automatically closed when the Statement object that generated it is closed, re-executed, or used to retrieve the next result from a sequence of multiple results. We can use ResultSet getter method with column name or index number starting from 1 to retrieve the column data.
There are different types of ResultSet objects that we can get based on the user input while creating the Statement. If you will look into the Connection methods, you will see that createStatement() and prepareStatement() method are overloaded to provide ResultSet type and concurrency as input argument. There are three types of ResultSet object.
1. **ResultSet.TYPE\_FORWARD\_ONLY**: This is the default type and cursor can only move forward in the result set.
2. **ResultSet.TYPE\_SCROLL\_INSENSITIVE**: The cursor can move forward and backward, and the result set is not sensitive to changes made by others to the database after the result set was created.
3. **ResultSet.TYPE\_SCROLL\_SENSITIVE**: The cursor can move forward and backward, and the result set is sensitive to changes made by others to the database after the result set was created.
Based on the concurrency there are two types of ResultSet object.
1. **ResultSet.CONCUR\_READ\_ONLY**: The result set is read only, this is the default concurrency type.
2. **ResultSet.CONCUR\_UPDATABLE**: We can use ResultSet update method to update the rows data.
We can use `setMaxRows(int i)` method to limit the number of rows that the database returns from the query. You can achieve the same thing using the SQL query itself. For example, in MySQL, we can use the [LIMIT](/community/tutorials/sql-limit-mysql-limit) clause to set the max rows that will be returned by the query. Understanding **fetchSize** can be tricky, for that you should know how Statement and ResultSet works. When we execute a query in the database, the result is obtained and maintained in the database cache and ResultSet is returned. ResultSet is the cursor that has the reference to the result in the database. Let's say we have a query that returns 100 rows and we have set fetchSize to 10, so in every database trip JDBC driver will fetch only 10 rows and hence there will be 10 trips to fetch all the rows. Setting optimal fetchSize is helpful when you need a lot of processing time for each row and number of rows in the result is huge. We can set fetchSize through Statement object but it can be overridden through ResultSet object setFetchSize() method.
Stored Procedures are group of SQL queries that are compiled in the database and can be executed from JDBC API. JDBC `CallableStatement` can be used to execute stored procedures in the database. The syntax to initialize CallableStatement is;
```
CallableStatement stmt = con.prepareCall("{call insertEmployee(?,?,?,?,?,?)}");
stmt.setInt(1, id);
stmt.setString(2, name);
stmt.setString(3, role);
stmt.setString(4, city);
stmt.setString(5, country);
//registrare il parametro OUT prima di chiamare la stored procedure
stmt.registerOutParameter(6, java.sql.Types.VARCHAR);
stmt.executeUpdate();
```
We need to register the OUT parameters before executing the CallableStatement. More details about this can be found at [JDBC CallableStatement Example](/community/tutorials/callablestatement-in-java-example).
Sometimes we need to run bulk queries of a similar kind for a database. For example, loading data from CSV files to relational database tables. As we know that we have the option to use Statement or PreparedStatement to execute queries. Apart from that JDBC API provides Batch Processing feature through which we can execute the bulk of queries in one go for a database. JDBC API supports batch processing through Statement and PreparedStatement `addBatch()` and `executeBatch()` methods. Batch Processing is faster than executing one statement at a time because the number of database calls is less. Read more at [JDBC Batch Processing Example](/community/tutorials/jdbc-batch-insert-update-mysql-oracle).
By default when we create a database connection, it runs in auto-commit mode. It means that whenever we execute a query and it’s completed, the commit is fired automatically. So every SQL query we fire is a transaction and if we are running some DML or DDL queries, the changes are getting saved into the database after every SQL statement finishes. Sometimes we want a group of SQL queries to be part of a transaction so that we can commit them when all the queries run fine and if we get an exception, we have a choice of rollback all the queries executed as part of the transaction. JDBC API provide method `setAutoCommit(boolean flag)` through which we can disable the auto commit feature of the connection. We should disable auto commit only when it’s required because the transaction will not be committed unless we call the commit() method on connection. Database servers uses table locks to achieve transaction management and it’s resource intensive process. So we should commit the transaction as soon as we are done with it. Read more with example program at [JDBC Transaction Management Example](/community/tutorials/java-jdbc-transaction-management-savepoint).
We can use Connection object `rollback()` method to rollback the transaction. It will rollback all the changes made by the transaction and release any database locks currently held by this Connection object.
Sometimes a transaction can be group of multiple statements and we would like to rollback to a particular point in the transaction. JDBC Savepoint helps us in creating checkpoints in a transaction and we can rollback to that particular checkpoint. Any savepoint created for a transaction is automatically released and become invalid when the transaction is committed, or when the entire transaction is rolled back. Rolling a transaction back to a savepoint automatically releases and makes invalid any other savepoints that were created after the savepoint in question. Read more at [JDBC Savepoint Example](/community/tutorials/java-jdbc-transaction-management-savepoint).
JDBC DataSource is the interface defined in `javax.sql` package and it is more powerful that DriverManager for database connections. We can use DataSource to create the database connection and Driver implementation classes does the actual work for getting connection. Apart from getting Database connection, DataSource provides some additional features such as:
- Caching of PreparedStatement for faster processing
- Connection timeout settings
- Logging features
- ResultSet maximum size threshold
- Connection Pooling in servlet container using JNDI support
Read more about DataSource at [JDBC DataSource Example](/community/tutorials/java-datasource-jdbc-datasource-example).
For web applications deployed in a servlet container, creating JDBC connection pool is very easy and involve only few steps.
1. Creating JDBC JNDI resource in the container configuration files, usually server.xml or context.xml. For example `server.xml`
```
<Resource name="jdbc/MyDB"
global="jdbc/MyDB"
auth="Container"
type="javax.sql.DataSource"
driverClassName="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/UserDB"
username="pankaj"
password="pankaj123"
maxActive="100"
maxIdle="20"
minIdle="5"
maxWait="10000"/>
```
`context.xml`
```
<ResourceLink name="jdbc/MyLocalDB"
global="jdbc/MyDB"
auth="Container"
type="javax.sql.DataSource" />
```
2. In web application, using InitialContext to look up the JNDI resource configured in the first step and then get the connection.
```
Context ctx = new InitialContext();
DataSource ds = (DataSource) ctx.lookup("java:/comp/env/jdbc/MyLocalDB");
```
For a complete example, read [Tomcat DataSource JNDI Example](/community/tutorials/tomcat-datasource-jndi-example-java).
If you use `DataSource` to get the Database connection, usually the code to get the connection is tightly coupled with the Driver specific DataSource implementation. Also most of the code is boiler-plate code except the choice of the DataSource implementation class. Apache DBCP helps us in getting rid of these issues by providing DataSource implementation that works as an abstraction layer between our program and different JDBC drivers. Apache DBCP library depends on Commons Pool library, so make sure they both are in the build path. For a complete example, read [Apache DBCP Example](/community/tutorials/java-datasource-jdbc-datasource-example).
When we use JDBC Transactions for data integrity, DBMS uses locks to block access by others to the data being accessed by the transaction. DBMS uses locks to prevent Dirty Read, Non-Repeatable Reads and Phantom-Read issue. JDBC transaction isolation level is used by DBMS to use the locking mechanism, we can get the isolation level information through Connection getTransactionIsolation() method and set it with the setTransactionIsolation() method.
| Isolation Level | Transaction | Dirty Read | Non-Repeatable Read | Phantom Read |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| TRANSACTION\_NONE | Not Supported | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | Not Applicable |
| TRANSACTION\_READ\_COMMITTED | Supported | Prevented | Allowed | Allowed |
| TRANSACTION\_READ\_UNCOMMITTED | Supported | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| TRANSACTION\_REPEATABLE\_READ | Supported | Prevented | Prevented | Allowed |
| TRANSACTION\_SERIALIZABLE | Supported | Prevented | Prevented | Prevented |
JDBC `RowSet` holds tabular data in more flexible ways that ResultSet. All RowSet objects are derived from ResultSet, so they have all the capabilities of ResultSet with some additional features. RowSet interface is defined in `javax.sql` package. Some additional features provided by RowSet are:
- Functions as Java Beans with properties and their getter-setter methods. RowSet uses JavaBeans event model and they can send notifications to any registered component for events such as cursor movement, update/insert/delete of a row and change to RowSet contents.
- RowSet objects are scrollable and updatable by default, so if DBMS doesn't support scrollable or updatable ResultSet, we can use RowSet to get these features.
RowSet are broadly divided into two types:
1. **Connected RowSet Objects** - These objects are connected to database and are most similar to ResultSet object. JDBC API provides only one connected RowSet object `javax.sql.rowset.JdbcRowSet` and it's standard implementation class is `com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl`
2. **Disconnected RowSet Objects** - These RowSet objects are not required to connected to a database, so they are more lightweight and serializable. They are suitable for sending data over a network. There are four types of disconnected RowSet implementations.
- CachedRowSet - They can get the connection and execute a query and read the ResultSet data to populate the RowSet data. We can manipulate and update data while it is disconnected and reconnect to database and write the changes.
- WebRowSet derived from CachedRowSet - They can read and write XML document.
- JoinRowSet derived from WebRowSet - They can form SQL JOIN without having to connect to a data source.
- FilteredRowSet derived from WebRowSet - We can apply filtering criteria so that only selected data is visible.
RowSet objects are derived from ResultSet, so they have all the features of ResultSet with some additional features. One of the huge benefit of RowSet is that they can be disconnected and that makes it lightweight and easy to transfer over a network. Whether to use ResultSet or RowSet depends on your requirements but if you are planning to use ResultSet for longer duration, then a disconnected RowSet is better choice to free database resources.
Some of the common JDBC Exceptions are:
1. java.sql.SQLException - This is the base exception class for JDBC exceptions.
2. java.sql.BatchUpdateException - This exception is thrown when Batch operation fails, but it depends on the JDBC driver whether they throw this exception or the base SQLException.
3. java.sql.SQLWarning - For warning messages in SQL operations.
4. java.sql.DataTruncation - when a data values is unexpectedly truncated for reasons other than its having exceeded MaxFieldSize.
Character Large OBjects (CLOBs) are character string made up of single-byte characters with an associated code page. This data type is appropriate for storing text-oriented information where the amount of information can grow beyond the limits of a regular VARCHAR data type (upper limit of 32K bytes). Binary Large Objects (BLOBs) are a binary string made up of bytes with no associated code page. This data type can store binary data larger than VARBINARY (32K limit). This data type is good for storing image, voice, graphical, and other types of business or application-specific data.
When we work with transactions, there is a chance that a row is updated and at the same time, another query can read the updated value. This results in a dirty read because the updated value is not permanent yet, the transaction that has updated the row can rollback to a previous value resulting in invalid data. Dirty Read is prevented by isolation levels TRANSACTION\_READ\_COMMITTED, TRANSACTION\_REPEATABLE\_READ, and TRANSACTION\_SERIALIZABLE.
When we work in distributed systems where multiple databases are involved, we are required to use 2 phase commit protocol. 2 phase commit protocol is an atomic commitment protocol for distributed systems. In the first phase, the transaction manager sends commit-request to all the transaction resources. If all the transaction resources are OK, the transaction manager commits the transaction changes for all the resources. If any of the transaction resources responds as Abort, then the transaction manager can rollback all the transaction changes.
On a broad level, there are two types of locking mechanism to prevent data corruption because of more than one user working with the same data.
1. Optimistic Locking - This locking is achieved with code. An extra column is introduced in the table to keep a count of updates. When you select the row, you read this column too, say 'version'. Now when you are trying to update/delete the row, you pass this 'version' in the where clause. So if there are updates from other threads performed in between, the update will fail. It's a good way to avoid data corruption but it can be error prone if someone missed updating the 'version' in their update statement. The update query looks something like below in this way of locking.
```
mysql> update emp SET name = 'David', version = 5 WHERE id = 10 and version = 4;
```
2. Pessimistic Locking - Locking the record from the select to read, update and commit phase. This is usually done by database vendor software and triggered by the use of `SELECT FOR UPDATE` query. This way of locking the row can lead to slow performance and deadlock if threads are handling the lock for longer time.Apart from that some DBMS systems provide locking mechanism to lock single row, table or database.
Data Definition Language (DDL) statements are used to define the database schema. Create, Alter, Drop, Truncate, Rename statements comes under DDL statements and usually they don't return any result. Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements are used to manipulate data in the database schema. Select, Insert, Update, Delete, Call etc are example of DML statements.
java.util.Date contains information about the date and time whereas java.sql.Date contains information only about the date, it doesn't have time information. So if you have to keep time information in the database, it is advisable to use Timestamp or DateTime fields.
We can use BLOB to insert image or raw binary data into database.
A phantom read is the situation where a transaction executes a query multiple times and get different data. Suppose a transaction is executing a query to get data based on a condition and then another transaction inserts a row that matches the condition. Now when same transaction will execute the query again, a new row will be part of the result set. This new row is referred as Phantom Row and this situation is termed as Phantom Read. Phantom read can be prevented only with TRANSACTION\_SERIALIZABLE isolation level.
SQLWarning is the subclass of SQLException and we can retrieve it by calling getWarnings() method on Connection, Statement, and ResultSet objects. SQL Warnings doesn't stop the execution of the script but alerts the user about the warning.
If Oracle Stored Procedure has IN/OUT parameters as DB Objects then we need to create an Object array of the same size in the program and then use it to create Oracle STRUCT object. Then we can set this STRUCT object for the database object by calling setSTRUCT() method and work with it.
You get No suitable driver found exception when the SQL URL String is not properly formatted. You can get this exception in both simple java application using DriverManager or with JNDI resource using DataSource. The exception stack trace looks like below.
```
org.apache.tomcat.dbcp.dbcp.SQLNestedException: Cannot create JDBC driver of class 'com.mysql.jdbc.Driver' for connect URL ''jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/UserDB'
at org.apache.tomcat.dbcp.dbcp.BasicDataSource.createConnectionFactory(BasicDataSource.java:1452)
at org.apache.tomcat.dbcp.dbcp.BasicDataSource.createDataSource(BasicDataSource.java:1371)
at org.apache.tomcat.dbcp.dbcp.BasicDataSource.getConnection(BasicDataSource.java:1044)
java.sql.SQLException: No suitable driver found for 'jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/UserDB
at java.sql.DriverManager.getConnection(DriverManager.java:604)
at java.sql.DriverManager.getConnection(DriverManager.java:221)
at com.journaldev.jdbc.DBConnection.getConnection(DBConnection.java:24)
at com.journaldev.jdbc.DBConnectionTest.main(DBConnectionTest.java:15)
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
at com.journaldev.jdbc.DBConnectionTest.main(DBConnectionTest.java:16)
```
While debugging this exception, just check the URL getting printed in the logs, as in above logs the URL String is 'jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/UserDB whereas it should be jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/UserDB.
Some of the JDBC Best Practices are:
- Database resources are heavy, so make sure you close it as soon as you are done with it. Connection, Statement, ResultSet and all other JDBC objects have close() method defined to close them.
- Always close the result set, statement and connection explicitly in the code, because if you are working in connection pooling environment, the connection might be returned to the pool leaving open result sets and statement objects resulting in resource leak.
- Close the resources in the finally block to make sure they are closed even in case of exception scenarios.
- Use batch processing for bulk operations of similar kind.
- Always use PreparedStatement over Statement to avoid SQL Injection and get pre-compilation and caching benefits of PreparedStatement.
- If you are retrieving bulk data into result set, setting an optimal value for fetchSize helps in getting good performance.
- The database server might not support all isolation levels, so check it before assuming.
- More strict isolation levels result in slow performance, so make sure you have optimal isolation level set for your database connections.
- If you are creating database connections in a web application, try to use JDBC DataSource resources using JNDI context for re-using the connections.
- Try to use disconnected RowSet when you need to work with ResultSet for a long time.
Questo è tutto per le domande e risposte dell’intervista su JDBC, spero che ti sia utile nelle interviste su JDBC. Fammi sapere se ho saltato qualche domanda importante e la aggiungerò alla lista.
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/jdbc-interview-questions-and-answers













