Il comando date è un programma esterno basato su bash che consente di impostare o visualizzare la data e l’ora del sistema. Fornisce anche diverse opzioni di formattazione. Il comando date è installato in tutte le distribuzioni Linux di default.
$ which date $ type -a date
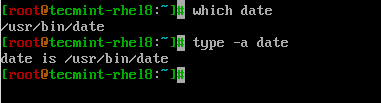
Digitare comando date in terminale, che mostrerà la data e l’ora corrente.
$ date
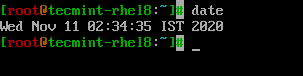
Cambiare data e ora del sistema Linux
Usando comando date, è possibile modificare la data, l’ora e il fuso orario del sistema e il cambiamento deve essere sincronizzato con l’orologio hardware.
$ date --set="Thu Nov 12 13:06:59 IST 2020" $ hwclock --systohc
Opzioni di formattazione
A good place to get the list of formatting options will be the man page.
$ man date
Ora vediamo alcune delle opzioni di formattazione più comuni che userò.
- Per applicare il formattaggio usare ” +” seguito da ” formattatore “.
- Per ottenere una lista delle opzioni di formattazione per GNU\LINUX consultare la pagina manuale collegata.
- Per ottenere una lista delle opzioni di formattazione per BSD consultare la pagina manuale collegata.
Le due parti importanti del comando date sono l’uso del formato +% e l’opzione -date.
Ora applichiamo un po’ di formattazione sul comando data. Per applicare la formattazione, aggiungi il segno più (+) seguito da %formatter come mostrato negli esempi.
Gestione della Data in Linux
Diamo un’occhiata a come utilizzare i formattatori correlati alla data in uno script shell semplice chiamato ‘date.sh‘.
# PRINT YEAR,MONTH,DAY AND DATE... echo "We are in the year = $(date +%Y)" echo "We are in the year = $(date +%y)" # Difference between %Y and %y is %Y will print 4 digits while %y will print the last 2 digits of the year. echo "We are in the month = $(date +%m)" echo "We are in the month = $(date +%b)" echo "We are in the month = $(date +%B)" # Difference between %B and %b is, %B will print full month name while %b will print abbreviated month name. echo "Current Day of the month = $(date +%d)" echo "Current Day of the week = $(date +%A)" echo "Current Day of the week = $(date +%a)" # Difference between %A and %a is, %A will print full Weekday name while %a will print abbreviated weekday name. # Instead of formatting to get the date, we can use %D which will print the date as %m/%d/%y or %F which prints in %Y-%M-%d format. echo "Date using %D = $(date +%D)" echo "Date using %F = $(date +%F)"
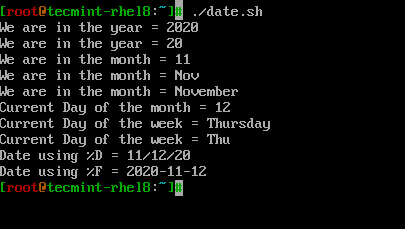
Gestione dell’Ora in Linux
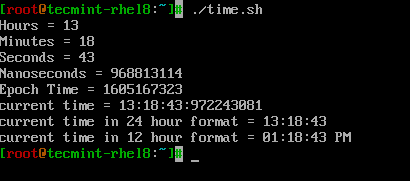
Diamo un’occhiata a come utilizzare i formattatori correlati all’ora in uno script shell semplice chiamato ‘time.sh‘.
# PRINT HOURS, MINS, SECONDS, NANO SECONDS echo Hours = $(date +%H) echo Minutes = $(date +%M) echo Seconds = $(date +%S) echo Nanoseconds = $(date +%N) echo Epoch Time = $(date +%s) echo "current time = $(date +%H:%M:%S:%N)" # can also use %T which displays Time in HH:MM:SS format. echo "current time in 24 hour format = $(date +%T)" # can also use %r to display time in 12 hour format. echo "current time in 12 hour format = $(date +%r)"
Con l’Opzione –date o -d
Con l’opzione --date o -d l’input può essere passato come stringa e il comando data sa come gestirlo intelligentemente.
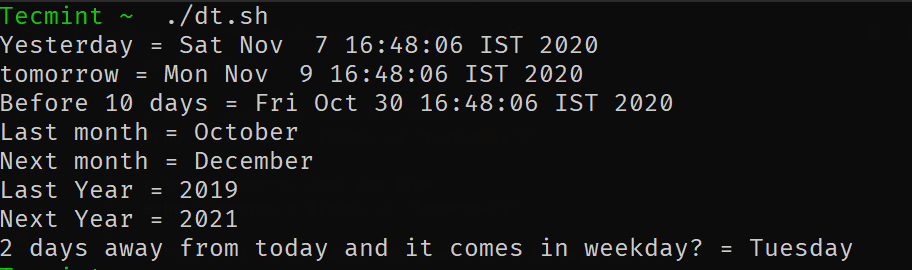
Vediamo alcuni esempi per capire come funziona.
# Print yesterday's date and time. echo "Yesterday = $(date -d "Yesterday")" # Print Tomorrow date and time. echo "tomorrow = $(date -d "tomorrow")" # Find what is the date and time before 10 days from now. echo "Before 10 days = $(date -d "tomorrow -10 days")" # Find last month and next month echo "Last month = $(date -d "last month" "%B")" echo "Next month = $(date -d "next month" "%B")" # Find last year and next year echo "Last Year = $(date -d "last year" "+%Y")" echo "Next Year = $(date -d "next year" "+%Y")" # Forecast the weekday echo "2 days away from today and it comes on weekdays? = $(date -d "Today +2 days" "+%A")
Operazioni Comuni
calcolare il numero di giorni tra 2 date date.
$ echo $(( ( $(date -d "2020-11-10" "+%s") - $(date -d "2020-11-01" "+%s") ) / 86400))
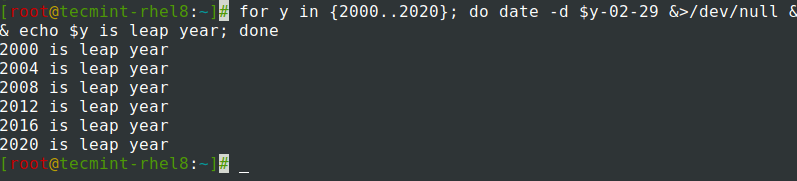
Trovare se l’anno dato è bisestile o meno.
$ for y in {2000..2020}; do date -d $y-02-29 &>/dev/null && echo $y is leap year; done
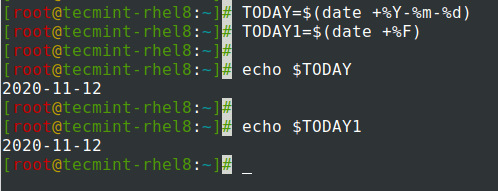
Assegnare l’output del comando date a una variabile.
$ TODAY=$(date +%Y-%m-%d) OR $ TODAY1=$(date +%F) $ echo $TODAY $ echo $TODAY1
Creare file di log con la data aggiunta al nome del file.
Aggiungere data e ora durante la creazione di file di log, backup o file di testo è un’operazione comune che incontreremo più spesso. Prendiamo un esempio, per fare un backup, abbiamo creato uno script shell.
Questo script effettuerà un backup dalle 00:00 alle 23:59 e verrà pianificato per essere eseguito quotidianamente alle 00:00 del giorno successivo. Vogliamo creare file di log con il formato della data di ieri.
CUSTOM_FORMAT=$(date --date "Yesterday" "+%d-%y-%H:%M")
LOG_FILE=/var/log/custom_application/application_${CUSTOM_FORMAT}.log
echo "Script started" >> ${LOG_FILE}
...
CODE BLOCKS
...
echo "Script completed" >> ${LOG_FILE}
Ecco tutto per questo articolo. In questo articolo abbiamo visto come utilizzare la data e l’ora di bash in Linux. Fateci sapere i vostri commenti.
Source:
https://www.tecmint.com/change-linux-system-date-and-time/













