Decorator design pattern is used to modify the functionality of an object at runtime. At the same time other instances of the same class will not be affected by this, so individual object gets the modified behavior. Decorator design pattern is one of the structural design pattern (such as Adapter Pattern, Bridge Pattern, Composite Pattern) and uses abstract classes or interface with composition to implement.
Decorator Design Pattern
We use inheritance or composition to extend the behavior of an object but this is done at compile time and its applicable to all the instances of the class. We can’t add any new functionality of remove any existing behavior at runtime – this is when Decorator pattern comes into picture. Suppose we want to implement different kinds of cars – we can create interface Car to define the assemble method and then we can have a Basic car, further more we can extend it to Sports car and Luxury Car. The implementation hierarchy will look like below image. 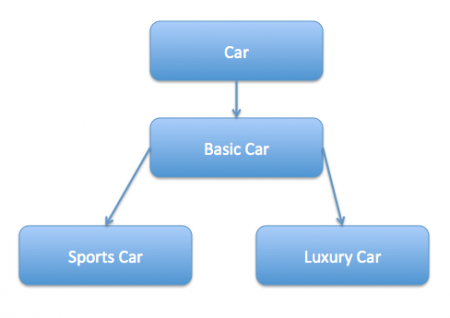 But if we want to get a car at runtime that has both the features of sports car and luxury car, then the implementation gets complex and if further more we want to specify which features should be added first, it gets even more complex. Now imagine if we have ten different kind of cars, the implementation logic using inheritance and composition will be impossible to manage. To solve this kind of programming situation, we apply decorator pattern in java. We need to have following types to implement decorator design pattern.
But if we want to get a car at runtime that has both the features of sports car and luxury car, then the implementation gets complex and if further more we want to specify which features should be added first, it gets even more complex. Now imagine if we have ten different kind of cars, the implementation logic using inheritance and composition will be impossible to manage. To solve this kind of programming situation, we apply decorator pattern in java. We need to have following types to implement decorator design pattern.
-
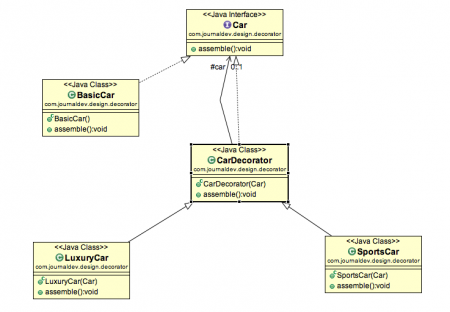
Component Interface – The interface or abstract class defining the methods that will be implemented. In our case
Carwill be the component interface.package com.journaldev.design.decorator; public interface Car { public void assemble(); } -
Component Implementation – The basic implementation of the component interface. We can have
BasicCarclass as our component implementation.package com.journaldev.design.decorator; public class BasicCar implements Car { @Override public void assemble() { System.out.print("Basic Car."); } } -
Decorator – Decorator class implements the component interface and it has a HAS-A relationship with the component interface. The component variable should be accessible to the child decorator classes, so we will make this variable protected.
package com.journaldev.design.decorator; public class CarDecorator implements Car { protected Car car; public CarDecorator(Car c){ this.car=c; } @Override public void assemble() { this.car.assemble(); } } -
Concrete Decorators – Extending the base decorator functionality and modifying the component behavior accordingly. We can have concrete decorator classes as
LuxuryCarandSportsCar.package com.journaldev.design.decorator; public class SportsCar extends CarDecorator { public SportsCar(Car c) { super(c); } @Override public void assemble(){ super.assemble(); System.out.print(" Adding features of Sports Car."); } }package com.journaldev.design.decorator; public class LuxuryCar extends CarDecorator { public LuxuryCar(Car c) { super(c); } @Override public void assemble(){ super.assemble(); System.out.print(" Adding features of Luxury Car."); } }
Decorator Design Pattern – Class Diagram
Decorator Design Pattern Test Program
package com.journaldev.design.test;
import com.journaldev.design.decorator.BasicCar;
import com.journaldev.design.decorator.Car;
import com.journaldev.design.decorator.LuxuryCar;
import com.journaldev.design.decorator.SportsCar;
public class DecoratorPatternTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car sportsCar = new SportsCar(new BasicCar());
sportsCar.assemble();
System.out.println("\n*****");
Car sportsLuxuryCar = new SportsCar(new LuxuryCar(new BasicCar()));
sportsLuxuryCar.assemble();
}
}
Notice that client program can create different kinds of Object at runtime and they can specify the order of execution too. Output of above test program is:
Basic Car. Adding features of Sports Car.
*****
Basic Car. Adding features of Luxury Car. Adding features of Sports Car.
Decorator Design Pattern – Important Points
- Decorator design pattern is helpful in providing runtime modification abilities and hence more flexible. Its easy to maintain and extend when the number of choices are more.
- The disadvantage of decorator design pattern is that it uses a lot of similar kind of objects (decorators).
- Decorator pattern is used a lot in Java IO classes, such as FileReader, BufferedReader etc.
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/decorator-design-pattern-in-java-example