Spring Boot @SpringBootApplication Annotation
Die Spring Boot @SpringBootApplication-Annotation wird verwendet, um eine Konfigurationsklasse zu markieren, die eine oder mehrere @Bean-Methoden deklariert und auch die Auto-Konfiguration und die Komponentensuche auslöst. Es ist dasselbe wie das Deklarieren einer Klasse mit den Annotationen @Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration und @ComponentScan.
Spring Boot SpringApplication-Klasse
Die Klasse SpringApplication wird verwendet, um eine Spring-Anwendung von einer Java-Main-Methode aus zu initialisieren und zu starten. Diese Klasse erstellt automatisch den ApplicationContext aus dem Klassenpfad, scannt die Konfigurationsklassen und startet die Anwendung. Diese Klasse ist sehr hilfreich beim Starten einer Spring MVC– oder Spring REST-Anwendung mit Spring Boot.
Beispiel für SpringBootApplication und SpringApplication
In dem letzten Tutorial zum Spring RestController haben wir einen Spring-RESTful-Webdienst erstellt und auf Tomcat bereitgestellt. Wir mussten eine web.xml-Datei und eine Spring-Kontextdatei erstellen. Außerdem mussten wir manuell Spring MVC-Abhängigkeiten hinzufügen und ihre Versionen verwalten. Hier werden wir das Projekt so ändern, dass es als Spring Boot-Anwendung ausgeführt wird und die Konfigurationsdateien loswerden. Dies erleichtert das schnelle Testen unserer Anwendungslogik, da wir das Projekt nicht manuell erstellen und auf den externen Tomcat-Server bereitstellen müssen.
Sie sollten das bestehende Projekt aus unserem GitHub-Repository überprüfen, in den folgenden Abschnitten werden wir die erforderlichen Änderungen an den Projektdateien vornehmen.
Das folgende Bild zeigt unsere abschließende Projektstruktur. 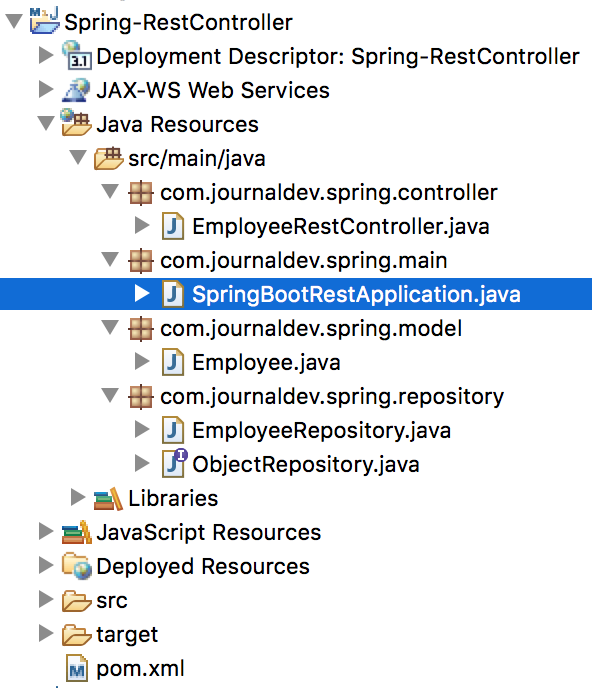
Hinzufügen von Spring Boot Maven-Abhängigkeiten
Der erste Schritt besteht darin, die Datei pom.xml aufzuräumen und für Spring Boot zu konfigurieren. Da es sich um einen REST-Webdienst handelt, benötigen wir nur die Abhängigkeit spring-boot-starter-web. Wir müssen jedoch die JAXB-Abhängigkeiten beibehalten, da wir Java 10 verwenden und auch XML-Anfragen und -Antworten unterstützen möchten. Außerdem müssen wir das Plugin spring-boot-maven-plugin hinzufügen. Mit diesem Plugin können wir unsere einfache Java-Anwendung als Spring Boot-Anwendung ausführen. Hier ist unsere aktualisierte pom.xml-Datei.
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>Spring-RestController</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring-RestController</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>10</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- JAXB for XML Response needed to explicitly define from Java 9 onwards -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.xml.bind</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.glassfish.jaxb</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb-runtime</artifactId>
<version>2.3.0</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.activation</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.activation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.2.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<!-- added to remove Version from WAR file -->
<finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Wir können das Verzeichnis WebContent löschen oder wie es ist belassen, es wird von unserer Spring Boot-Anwendung nicht verwendet.
Spring Boot-Anwendungsklasse
Jetzt müssen wir eine Java-Klasse mit einer main-Methode erstellen, sie mit der Annotation @SpringBootApplication markieren und die Methode SpringApplication.run() aufrufen.
package com.journaldev.spring;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootRestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootRestApplication.class, args);
}
}
Führen Sie die Klasse als Java-Anwendung aus und sie wird die folgende Ausgabe erzeugen. Ich habe einige Logger entfernt, die uns hier nicht interessieren. Die Anwendung wird nicht beendet und wartet auf Client-Anfragen.
2018-06-18 14:33:51.276 INFO 3830 --- [ main] c.j.spring.SpringBootRestApplication : Starting SpringBootRestApplication on pankaj with PID 3830 (/Users/pankaj/Documents/eclipse-jee-workspace/Spring-RestController/target/classes started by pankaj in /Users/pankaj/Documents/eclipse-jee-workspace/Spring-RestController)
2018-06-18 14:33:51.280 INFO 3830 --- [ main] c.j.spring.SpringBootRestApplication : No active profile set, falling back to default profiles: default
2018-06-18 14:33:51.332 INFO 3830 --- [ main] ConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext : Refreshing org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext@38467116: startup date [Mon Jun 18 14:33:51 IST 2018]; root of context hierarchy
2018-06-18 14:33:52.311 INFO 3830 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat initialized with port(s): 8080 (http)
2018-06-18 14:33:52.344 INFO 3830 --- [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service [Tomcat]
2018-06-18 14:33:52.344 INFO 3830 --- [ main] org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet Engine: Apache Tomcat/8.5.31
2018-06-18 14:33:52.453 INFO 3830 --- [ost-startStop-1] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext
2018-06-18 14:33:52.453 INFO 3830 --- [ost-startStop-1] o.s.web.context.ContextLoader : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 1127 ms
2018-06-18 14:33:52.564 INFO 3830 --- [ost-startStop-1] o.s.b.w.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean : Servlet dispatcherServlet mapped to [/]
2018-06-18 14:33:52.927 INFO 3830 --- [ main] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/rest/employee/get/{id}],methods=[GET]}" onto public com.journaldev.spring.model.Employee com.journaldev.spring.controller.EmployeeRestController.getEmployeeByID(int)
2018-06-18 14:33:52.928 INFO 3830 --- [ main] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/rest/employee/getAll],methods=[GET]}" onto public java.util.List<com.journaldev.spring.model.Employee> com.journaldev.spring.controller.EmployeeRestController.getAllEmployees()
2018-06-18 14:33:52.929 INFO 3830 --- [ main] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/rest/employee/create],methods=[POST]}" onto public com.journaldev.spring.model.Employee com.journaldev.spring.controller.EmployeeRestController.createEmployee(com.journaldev.spring.model.Employee)
2018-06-18 14:33:52.929 INFO 3830 --- [ main] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/rest/employee/search/{name}],methods=[GET]}" onto public com.journaldev.spring.model.Employee com.journaldev.spring.controller.EmployeeRestController.getEmployeeByName(java.lang.String)
2018-06-18 14:33:52.929 INFO 3830 --- [ main] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/rest/employee/delete/{id}],methods=[DELETE]}" onto public com.journaldev.spring.model.Employee com.journaldev.spring.controller.EmployeeRestController.deleteEmployeeByID(int)
2018-06-18 14:33:53.079 INFO 3830 --- [ main] o.s.j.e.a.AnnotationMBeanExporter : Registering beans for JMX exposure on startup
2018-06-18 14:33:53.118 INFO 3830 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''
2018-06-18 14:33:53.124 INFO 3830 --- [ main] c.j.spring.SpringBootRestApplication : Started SpringBootRestApplication in 2.204 seconds (JVM running for 2.633)
Einige wichtige Punkte, die wir aus den Protokollen ableiten können:
- Die Prozess-ID der Spring Boot-Anwendung lautet 3830.
- Die Spring Boot-Anwendung startet Tomcat auf Port 8080.
- Unser Anwendungskontextpfad ist „“. Das bedeutet, dass wir beim Aufruf unserer APIs keinen Servlet-Kontext angeben müssen.
- Der Logger gibt alle konfigurierten APIs aus, siehe Meldungen wie „
Mapped "{[/rest/employee/get/{id}],methods=[GET]}"„.
Das folgende Bild zeigt ein Beispiel für den Aufruf der von unserer Spring Boot-Anwendung bereitgestellten APIs. 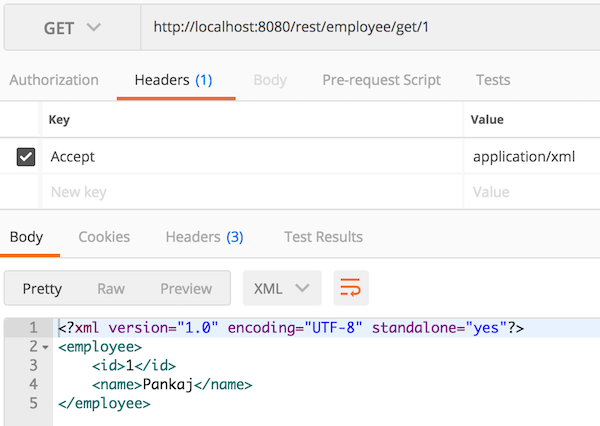
SpringBootApplication scanBasePackages
Standardmäßig durchsucht SpringApplication das Paket der Konfigurationsklasse und alle Unterpakete. Wenn sich unsere SpringBootRestApplication-Klasse im Paket com.journaldev.spring.main befindet, durchsucht es nicht das Paket com.journaldev.spring.controller. Wir können diese Situation mit der Eigenschaft scanBasePackages von SpringBootApplication beheben.
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages="com.journaldev.spring")
public class SpringBootRestApplication {
}
Spring Boot Auto-konfigurierte Beans
Da Spring Boot eine Auto-Konfiguration bereitstellt, werden viele Beans von ihm konfiguriert. Wir können eine Liste dieser Beans mit dem folgenden Code-Snippet abrufen.
ApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(SpringBootRestApplication.class, args);
String[] beans = ctx.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for(String s : beans) System.out.println(s);
Unten ist die Liste der von unserer Spring Boot-Anwendung konfigurierten Beans.
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalRequiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
springBootRestApplication
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory
employeeRestController
employeeRepository
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationPackages
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.BeanTypeRegistry
propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration$TomcatWebSocketConfiguration
websocketContainerCustomizer
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration$EmbeddedTomcat
tomcatServletWebServerFactory
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
servletWebServerFactoryCustomizer
tomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer
server-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerProperties
org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor
org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationBeanFactoryMetadata
webServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor
errorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration$DispatcherServletConfiguration
dispatcherServlet
mainDispatcherServletPathProvider
spring.mvc-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcProperties
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration$DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration
dispatcherServletRegistration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration
defaultValidator
methodValidationPostProcessor
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration$WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration
error
beanNameViewResolver
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration$DefaultErrorViewResolverConfiguration
conventionErrorViewResolver
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration
errorAttributes
basicErrorController
errorPageCustomizer
preserveErrorControllerTargetClassPostProcessor
spring.resources-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ResourceProperties
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration$WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter$FaviconConfiguration
faviconHandlerMapping
faviconRequestHandler
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration$EnableWebMvcConfiguration
requestMappingHandlerAdapter
requestMappingHandlerMapping
mvcConversionService
mvcValidator
mvcContentNegotiationManager
mvcPathMatcher
mvcUrlPathHelper
viewControllerHandlerMapping
beanNameHandlerMapping
resourceHandlerMapping
mvcResourceUrlProvider
defaultServletHandlerMapping
mvcUriComponentsContributor
httpRequestHandlerAdapter
simpleControllerHandlerAdapter
handlerExceptionResolver
mvcViewResolver
mvcHandlerMappingIntrospector
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration$WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter
defaultViewResolver
viewResolver
welcomePageHandlerMapping
requestContextFilter
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration
hiddenHttpMethodFilter
httpPutFormContentFilter
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration
mbeanExporter
objectNamingStrategy
mbeanServer
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration$Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilderCustomizerConfiguration
standardJacksonObjectMapperBuilderCustomizer
spring.jackson-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonProperties
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration$JacksonObjectMapperBuilderConfiguration
jacksonObjectMapperBuilder
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration$ParameterNamesModuleConfiguration
parameterNamesModule
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration$JacksonObjectMapperConfiguration
jacksonObjectMapper
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration
jsonComponentModule
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration$StringHttpMessageConverterConfiguration
stringHttpMessageConverter
spring.http.encoding-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpEncodingProperties
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.JacksonHttpMessageConvertersConfiguration$MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverterConfiguration
mappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.JacksonHttpMessageConvertersConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration
messageConverters
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration$JacksonCodecConfiguration
jacksonCodecCustomizer
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration
spring.info-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoProperties
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration
spring.security-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityProperties
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration
restTemplateBuilder
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration$TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizerConfiguration
tomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration
characterEncodingFilter
localeCharsetMappingsCustomizer
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration
multipartConfigElement
multipartResolver
spring.servlet.multipart-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartProperties
Das ist eine riesige Liste, es gibt viele auto-konfigurierte Beans, die wir nicht verwenden. Wir können unsere Spring Boot-Anwendung optimieren, indem wir diese mit @SpringBootApplication exclude oder excludeName deaktivieren. Das folgende Code-Snippet deaktiviert die JMX- und Multipart-Auto-Konfiguration.
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = "com.journaldev.spring", exclude = {
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration.class, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration.class })
public class SpringBootRestApplication {
}
Beachten Sie, dass wir beim Ausschließen von nicht-auto-konfigurierten Klassen einen Fehler erhalten und unsere Anwendung nicht startet.
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = "com.journaldev.spring", exclude = {com.journaldev.spring.controller.EmployeeRestController.class })
public class SpringBootRestApplication {
}
Das obige Code-Snippet wirft den folgenden Fehler:
2018-06-18 15:10:43.602 ERROR 3899 --- [main] o.s.boot.SpringApplication: Application run failed
java.lang.IllegalStateException: The following classes could not be excluded because they are not auto-configuration classes:
- com.journaldev.spring.controller.EmployeeRestController
Das war alles zur SpringBootApplication-Annotation und zum SpringApplication-Beispiel.
Sie können das endgültige Projekt von unserem GitHub-Repository herunterladen.
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/springbootapplication-springapplication













