Snapshots are usually used to create image-based VM backups. Storage snapshots are an alternative to the usual VM snapshots used, and they have certain advantages in terms of backup performance and impact on production environments.
In this blog post, we explain VMware virtual machine backup from HPE snapshots to achieve high efficiency in environments with heavily loaded storage, including the working principle and configuration basics.
What Are HPE Storage Snapshots?
HPE storage snapshots are point-in-time image-level views of data that capture the state of a storage volume or a set of volumes at a particular point in time. For VMs whose disks are hosted on HPE storage systems, these systems create and manage storage snapshots of these VMs.
One key feature of storage snapshots in general and HPE storage snapshots, in particular, is their minimal impact on system performance. Utilizing techniques like copy-on-write or redirect-on-write, snapshots are created and maintained efficiently, copying data only when changes occur. This approach reduces the amount of storage needed and the time required to create snapshots.
Another significant advantage of HPE storage snapshots is storage space efficiency. A storage snapshot can be created quickly (within seconds) and consumes a small amount of space. HPE storage systems also offer tools to automate the creation, management, and deletion of snapshots. Users can schedule regular snapshots to ensure consistent data protection without manual intervention, integrating snapshots with backup and disaster recovery solutions to enhance data resilience.
Integration with applications and databases is another aspect of HPE storage snapshots. This ensures that snapshots are aware of the application’s state, thus enabling data consistency. This feature is particularly important for transactional systems like databases, where data consistency is critical. Application-consistent snapshots are coordinated with the applications to quiesce the data, ensuring that the snapshot reflects a stable and consistent state.
Remember that snapshots are not backups, but can be leveraged to create backups.
How Storage Snapshots Help to Back Up VMs
Let’s explore how VM backup with traditional VM snapshots works and the difference between using VM snapshots and storage snapshots in the VM backup process.
Backup using VM snapshots
The VM backup process involves three main steps:
- The VM backup software triggers snapshot creation for the source VM:
- VM disks are switched to read-only mode.
- Each VM disk must have a delta file. Changes made to VM disks from now on are written to this delta file instead of VM disks.
- The VM backup software copies data from VM disks to create a backup for the VM.
- After the backup has been created for the source VM, delta files are merged into VM disks.
- VM disks shall switch to normal operation mode, which allows for changes to be written.
- Delta files are deleted.
This approach can be too resource-intensive in environments where VMs process large amounts of data while backups are created because delta files can grow to a very large size. Big delta files can make production storage work harder and take a long time to merge into VM disks. Therefore, this process impacts the production environment.
To illustrate this process in detail, let’s consider an example and analyze how much data should be read and written when creating and deleting a VM snapshot using the regular VM snapshot approach.
- Let’s say that a VM performs new writes at 50 MB per second.
If a VM snapshot has a lifetime of 10 minutes, the delta disk file size will be 30000 MB or 29.3 GB.
- To delete this snapshot, a system must perform 29.3 GB of reads + 29.3 GB of writes.
- If an ESXi server is able to perform these two operations at 90 MB per second (read + write), then:
- The time to delete a snapshot takes 667 seconds or ~11 minutes.
- However, the VM continues to write data at 50 MB per second during snapshot deletion, and these writes are saved in another delta file.
This is a practical example of a configuration whereby it is difficult to provide a reliable and efficient VM snapshot-based backup if the VM snapshot can be deleted only after 11 minutes. In this example, it takes at least 11 minutes to read the changed blocks of virtual disks and write these changes to a backup (incremental backup in this case).
Backup using storage snapshots
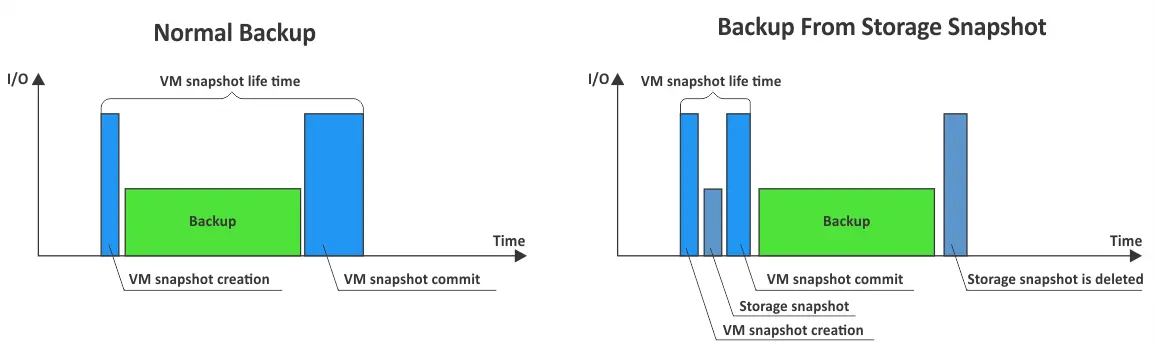
In the backup from storage snapshot process, a VM snapshot is created first, a storage snapshot is created, and the VM snapshot is removed. This way a VM snapshot only exists for a short time because a storage snapshot takes only a small amount of time to be created and contains all required data for performing a VM backup (delta and Changed Block Tracking data).
For example, if users want to back up 50 VMs on the same volume at once, a VM snapshot of the first VM can only be committed together with all other VMs. This makes the VM snapshot lifetime of this VM longer than backing up a single VM and the size of delta files could grow very quickly. The backup from the storage snapshot process can reduce the VM snapshot lifetime by processing only a limited number of VMs at the same time. Therefore, the VM snapshot lifetime of the first VM can be reduced significantly.
Benefits of Using HPE Snapshots to Create Backups
Using HPE storage snapshots for VMware vSphere virtual machine (VM) backup offers several benefits that enhance data protection, efficiency, and management. The key benefits of using HPE storage snapshots for VMware VM backups are:
- The baseline backup is created much faster. There is no need to use time-consuming read-and-write operations of all required data to back up for write-intensive virtual machines on ESXi hosts.
- The lifetime of VM snapshots is extremely short – they are retained for a few seconds until a storage snapshot is created, and then they are deleted. Virtual disk delta files accumulate only a small amount of data during this short period of VM snapshot existence.
- Snapshots are created using techniques such as copy-on-write or redirect-on-write, which only copy data when changes occur. This minimizes the performance impact on the running VMs and ensures that production workloads continue to run smoothly.
- Consolidation of VM snapshots is much faster because the snapshots (virtual disk delta files) contain small amounts of data that can be written into them for a few seconds of their lifetime. As a result, the impact on an ESXi host and storage system performance is low.
- You can exploit all benefits of storage snapshots without performance penalties for backed-up VMs and other VMs running on an ESXi host and the same storage system. It is critical for large write-intensive production environments.
- HPE storage snapshots integrate seamlessly with VMware vSphere, leveraging VMware APIs for Data Protection (VADP). This integration ensures that snapshots are taken in a manner consistent with VMware best practices, improving the reliability of backups. HPE storage snapshots can integrate with VMware vSphere to ensure application-consistent snapshots. This means that VMs and applications are in a stable state when the snapshot is taken, reducing the risk of data corruption.
Storage Snapshots and vVols
When using VMware vSphere Virtual Volumes (vVols) instead of traditional VMDK virtual disks, the approach to backing up VMware vSphere VMs with HPE storage snapshots changes significantly, providing additional advantages.
With traditional VMDK-based backups, snapshots are created and managed at the hypervisor level, which involves the VMware hypervisor handling the snapshot operations. This process can introduce performance overhead and potential VM performance degradation during snapshot creation, consolidation, and deletion, as mentioned above. The backup software interfaces with VMware vSphere APIs to manage these snapshots, which means that the entire VMDK file is involved in snapshot operations, making it more challenging to ensure application consistency and minimize impact on performance.
With vVols, each VM is composed of a set of storage objects directly managed by the HPE storage array through VMware vSphere API for Storage Awareness (VASA). This allows for more granular and efficient integration between VMware and HPE storage arrays. Snapshots are offloaded to the storage array, reducing performance overhead and speeding up snapshot operations. The storage array can manage snapshots at a more granular level, leading to faster, more efficient backups and recovery operations. The storage array handles snapshots natively, using advanced data services like deduplication, compression, and replication more effectively.
Supported HPE Devices
There are multiple HPE storage devices that support integration with VMware vSphere and can create storage snapshots for VM backups: HPE 3PAR, HPE Nimble, HPE Primera, and HPE Alletra.
HPE 3PAR
HPE 3PAR is a high-end, scalable storage solution designed for enterprise environments requiring high performance and advanced features. It offers robust performance, high availability, and extensive data services. Configuration of HPE 3PAR can be complex because this solution provides advanced capabilities and an extensive feature set. This device utilizes HPE SSMC (StoreServ Management Console) for management and configuration.
HPE Nimble
HPE Nimble Storage is a mid-range storage solution focused on simplicity, ease of use, and predictive analytics. It is designed for both primary storage and backup/DR use cases. This storage device is easier to configure compared to HPE 3PAR, with a focus on simplicity and ease of use. HPE Nimble uses NimbleOS and HPE InfoSight for management and monitoring.
HPE Primera
HPE Primera is a high-end, mission-critical storage solution designed for maximum performance and availability. It offers advanced features with a focus on simplicity and reliability. This solution is designed for high performance and low latency, that allows administrators to ensure minimal impact on VM operations during snapshot activities. It provides a simplified configuration compared to HPE 3PAR, with a focus on ease of deployment and management. The device uses HPE Primera Management Console and integrates with HPE InfoSight for predictive analytics and management.
HPE Alletra
HPE Alletra is the latest storage platform from HPE, designed to deliver cloud-native data infrastructure with a focus on simplicity, scalability, and performance. It represents the evolution of storage towards a more cloud-like operating model. Highly simplified configuration process, designed to be intuitive and user-friendly, reducing the complexity typically associated with enterprise storage. HPE Alletra is managed through HPE Data Services Cloud Console, providing a unified cloud-based management interface.
All platforms support VMware vSphere integration, but HPE Alletra offers the most modern approach, aligning with hybrid and cloud-native environments. HPE 3PAR uses SSMC, HPE Nimble uses NimbleOS and InfoSight, HPE Primera uses the Primera Management Console and InfoSight, and HPE Alletra uses the HPE Data Services Cloud Console for unified cloud-based management.
HPE 3PAR is the most complex to configure due to its extensive feature set and enterprise capabilities. HPE Primera offers a balance of advanced features with a simplified configuration. HPE Nimble focuses on ease of use and simplicity, making it easier to configure and manage. HPE Alletra provides the most user-friendly and intuitive configuration experience and is designed for a cloud-native operational model.
VM Backup Using Storage Snapshots with NAKIVO
NAKIVO Backup & Replication is a professional data protection solution that supports VMware vSphere VM backup from HPE storage snapshots to optimize performance and reliability for virtual environments with high input/output (I/O) workloads. The solution supports HPE 3PAR, HPE Nimble, HPE Primera and HPE Alletra to back up VM data directly from storage snapshots. Incremental, image-based agentless backups are supported.
Steps to Back up from HPE Storage Snapshots Using NAKIVO
Let’s look at how to back up VMware virtual machines from HPE storage snapshots with NAKIVO Backup & Replication. The VMware ESXi host or vCenter Server with the VMs you want to back up must be added to the NAKIVO inventory first. You must also add your HPE storage device to the NAKIVO inventory.
Adding HPE devices to the inventory
Perform the following steps to add the needed HPE storage device to the inventory of NAKIVO Backup & Replication:
- In the web interface of NAKIVO Backup & Replication, go to Settings > Inventory and click the + (plus) button to add a new item.
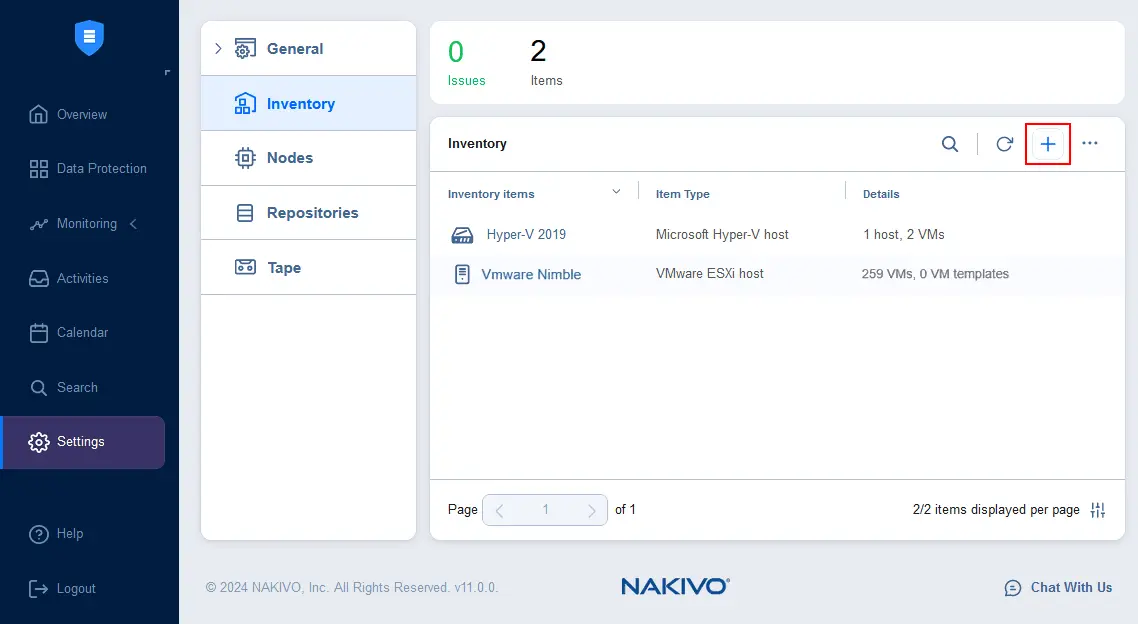
The Add Inventory Item wizard opens.
- At the first step of the wizard, select Storage Devices. Hit Next to continue.
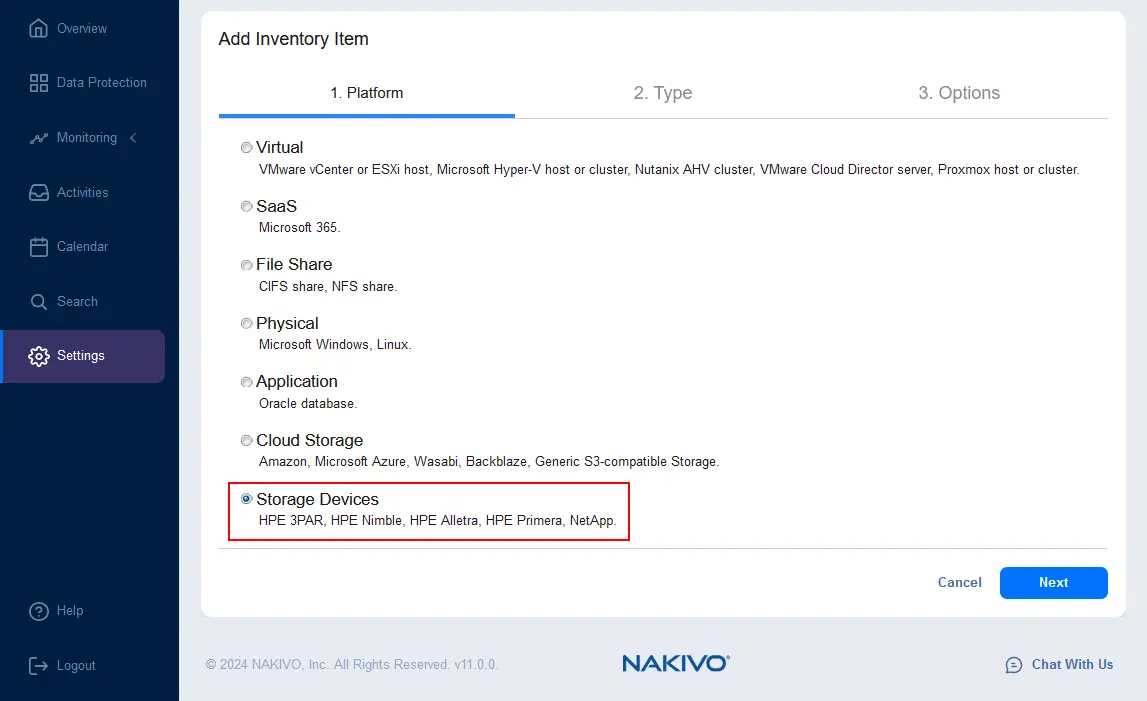
- Select Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) as the type.
Note that NAKIVO also supports backup from NetApp storage snapshots for VMware.
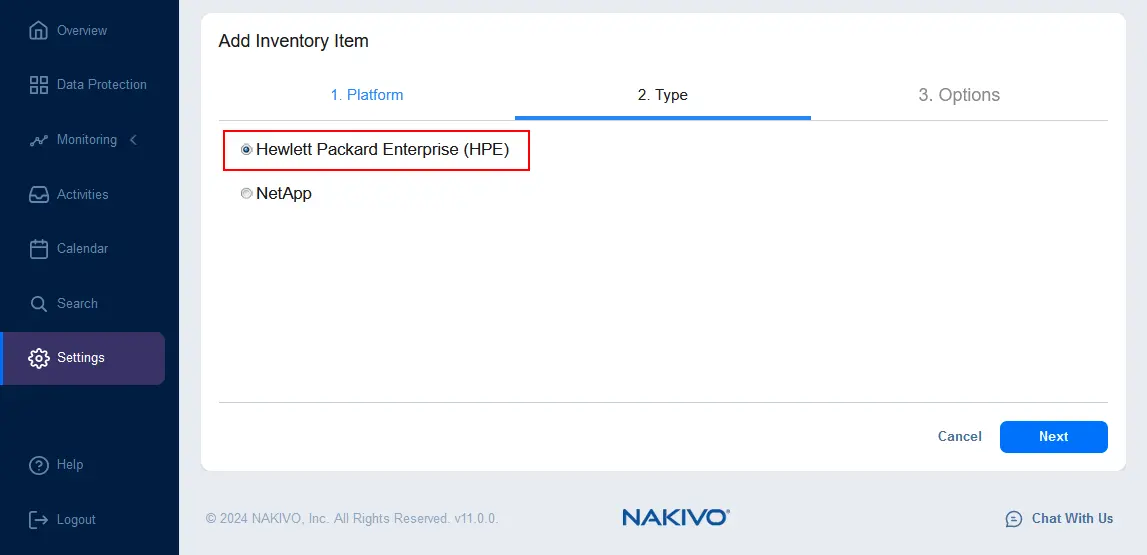
- Set the required parameters at the Options step:
- Display name: Enter a name to be displayed in the NAKIVO inventory
- Type: Select a type of your HPE storage system, for example, we select HPE Nimble.
- Hostname or IP: Enter the IP address of your HPE storage device.
- Username: Enter a username of the account with administrative permissions on the selected HPE storage device.
- Password: Enter the password for the defined user.
- REST API port: Select the correct port, for example, 5392 (by default for HPE Nimble)
Hit Finish to apply settings and add your HPE storage device to the NAKIVO inventory to enable a VM backup from HPE snapshots.
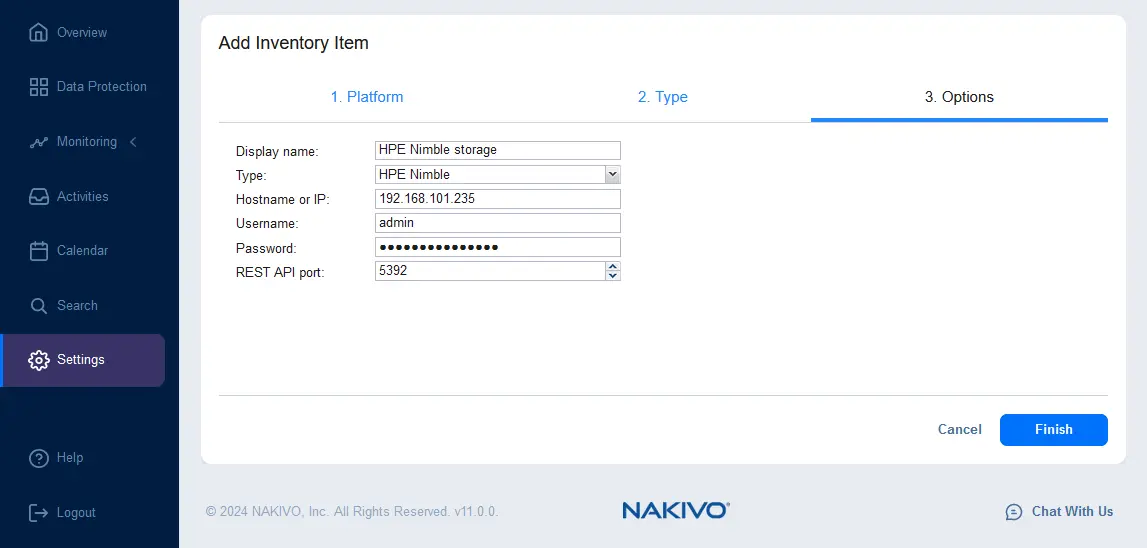
The supported types of HPE storage devices listed in the drop-down list are HPE 3PAR, HPE Nimble, HPE Alletra 5000/6000, HPE Alletra 9000, and HPE Primera.
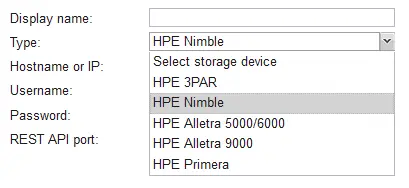
Once an HPE storage device has been added, go to Settings > Inventory to ensure that all required items are added to the inventory. In this example, HPE Nimble storage was added successfully and the NAKIVO solution automatically displays the number of volumes and snapshots on the storage device.
The VMware VMs we want to back up are located on the Nimble storage device – 259 VMs are on the host called VMware Nimble in the screenshot below – otherwise, using the HPE storage snapshots option will be unavailable.
VM Backup from HPE Devices
Now, once all required items have been added to the inventory, you can create a new VMware backup job using HPE snapshot benefits.
- Go to Data Protection, click + and hit Backup for VMware to create a new VMware VM backup job. Follow the backup job wizard until you get to step 4 with job options (select VMs, configure schedule, retention, etc.).
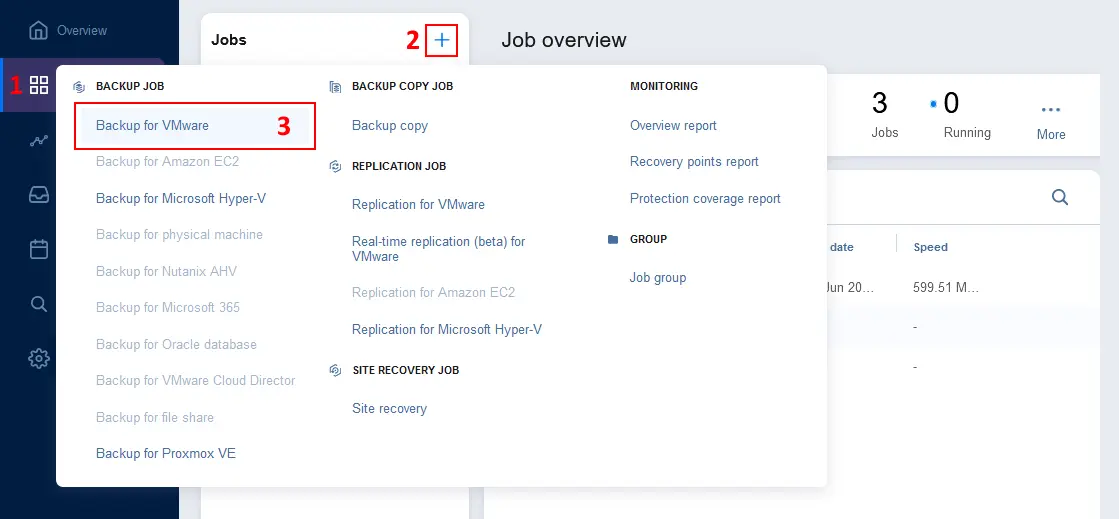
- At the job Options step, find the Backup from storage snapshot option at the end of the page. Click the drop-down list and select the needed options, such as Enabled (proceed on error). Click Finish or Finish & Run to save job settings and run the job.
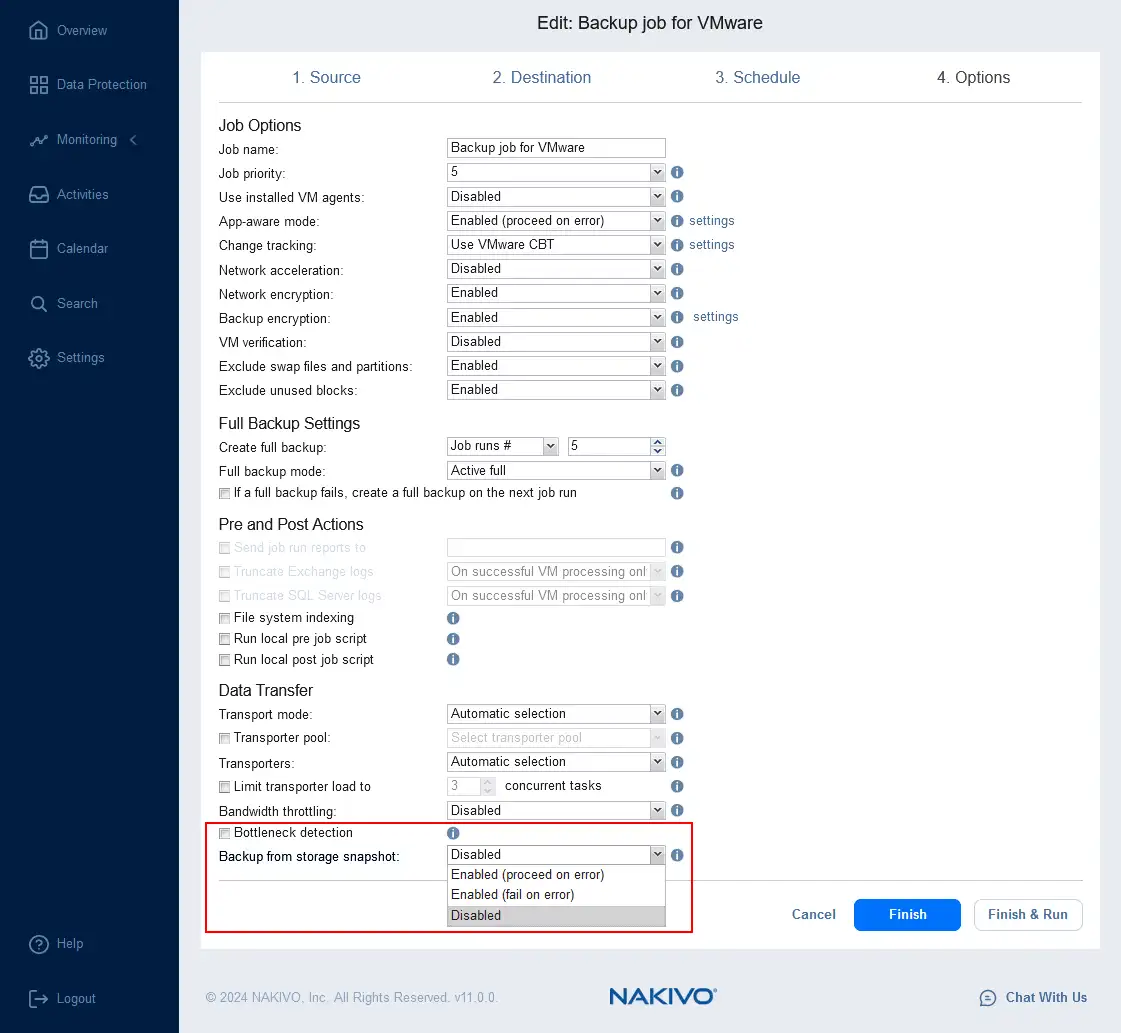
- Wait until the backup job is completed.
Conclusion
HPE storage snapshots can be used to create efficient VMware VM backups with minimal impact on your environment. NAKIVO Backup & Replication can integrate with HPE storage solutions like 3PAR, Primera, Nimble and Alletra to streamline the backup process and ensure reliable data protection with optimal performance.
Source:
https://www.nakivo.com/blog/backup-from-storage-snapshots/













